This study aims to assess whether the association between chronic pathologies and depressive and/or anxious disorders is high, resulting in a reduction in the patient's quality of life.
Patients and methodsThis is a prospective cross-sectional study with a descriptive and analytical design. Sociodemographic data and lifestyle habits were collected. Subsequently, the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) were applied.
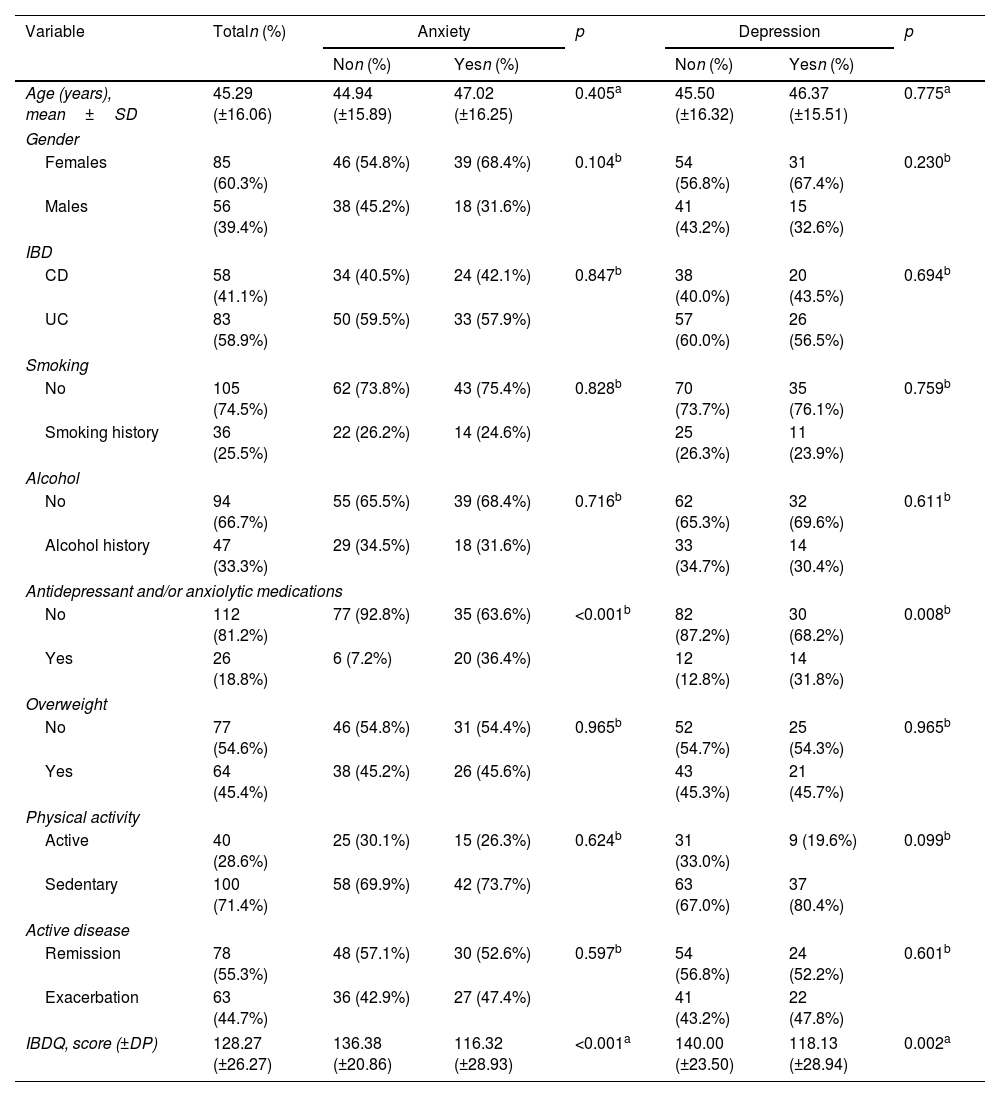
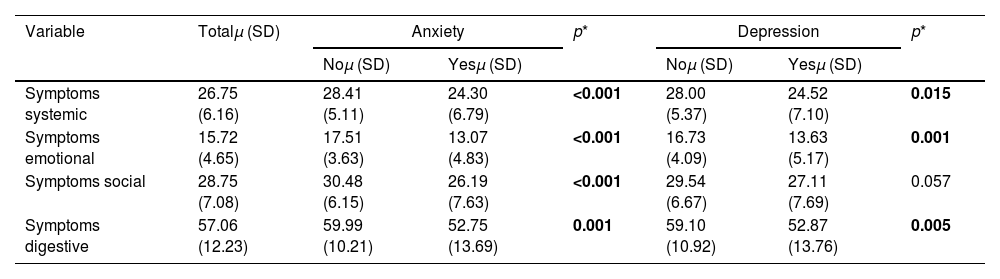
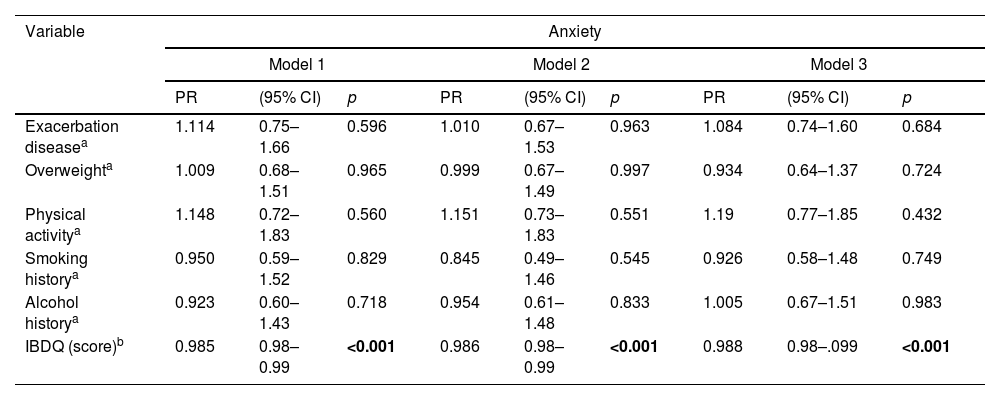
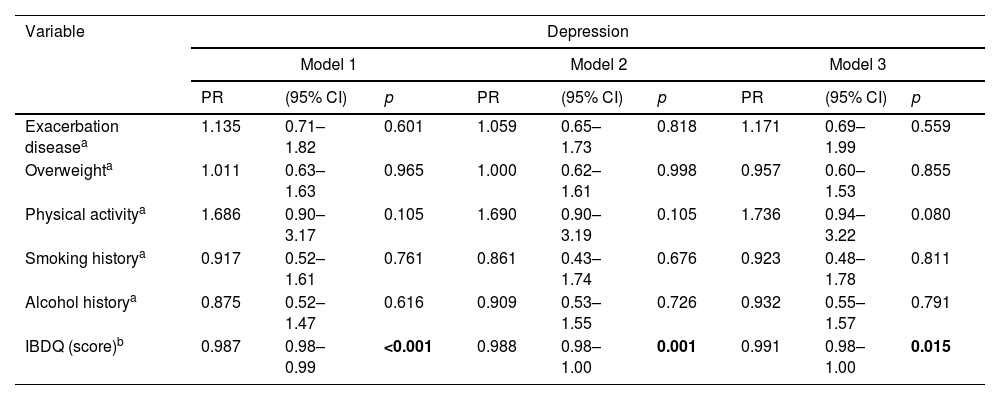
ResultsA total of 141 patients participated in the study, with a mean age of 45.78 (SD 16.01) years, of which 60.3% were female (n=85) and 39.7% were male (n=56). 58.9% had ulcerative colitis (UC) (n=83), and 41.1% had Crohn's disease (CD) (n=58). 16.5% of patients had a previous diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and/or major depression (MD) (n=23). Regarding IBDQ scores, participants with anxiety had significantly lower mean scores in all IBDQ items (p<0.001), while the depression diagnosis obtained significantly lower mean values for systemic (p=0.015), emotional (p=0.001), and intestinal symptoms (p=0.005).
ConclusionThe results indicate that anxiety and depression negatively impact the quality of life of patients with IBD independently of the disease activity.
El presente estudio tiene como objetivo evaluar si la asociación entre patologías crónicas y trastornos depresivos y/o ansiosos es alta, resultando en una reducción de la calidad de vida del paciente.
Pacientes y métodosSe trata de un estudio prospectivo transversal con un diseño descriptivo y analítico. Se recogieron datos sociodemográficos y hábitos de vida. Posteriormente se aplicaron el Cuestionario de Enfermedad Inflamatoria Intestinal (IBDQ) y la Escala Hospitalaria de Ansiedad y Depresión (HADS).
ResultadosParticiparon en el estudio 141 pacientes, con una edad media de 45,78 (DE 16,01) años, de los cuales el 60,3% eran mujeres (n=85) y el 39,7% varones (n=56). La mayoría padecían colitis ulcerosa (CU) (n=83 [58,9%]), y el 41,1% enfermedad de Crohn (EC) (n=58). El 16,5% de los pacientes tenían un diagnóstico previo de trastorno de ansiedad generalizada (TAG) y/o depresión mayor (DM) (n=23). En cuanto a las puntuaciones del IBDQ, los participantes con ansiedad presentaron puntuaciones medias significativamente inferiores en todos los ítems del IBDQ (p<0,001), mientras que el diagnóstico de depresión obtuvo valores medios significativamente inferiores para los síntomas sistémicos (p=0,015), emocionales (p=0,001) e intestinales (p=0,005).
ConclusiónLos resultados indican que la ansiedad y la depresión afectan negativamente a la calidad de vida de los pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal, independientemente de la actividad de la enfermedad.