TPE drastically reduces serum triglyceride (sTG), but its role in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis (HTG-AP) or at risk of developing it, is not well established. The objectives were to assess the effectiveness and safety of TPE in the treatment of severe HTG (sHTG), as well as to evaluate the severity of HTG-AP treated with TPE.
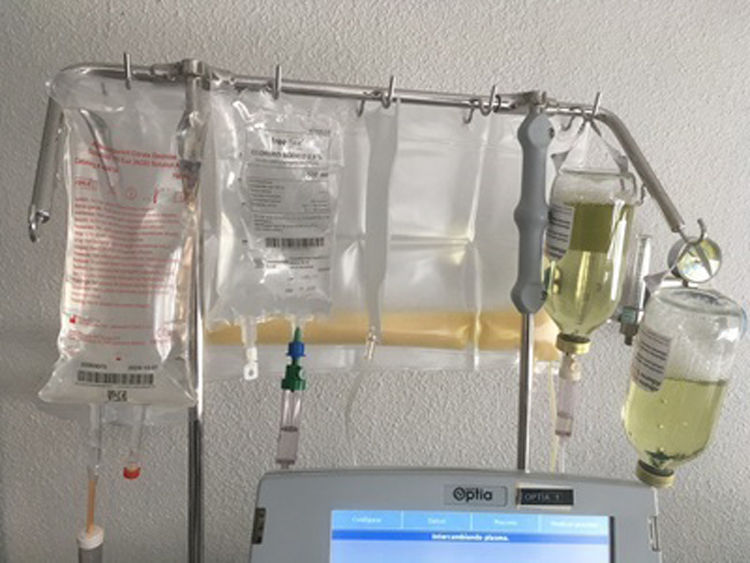
Materials and methodsObservational-retrospective-single-center study, in which a descriptive analysis of sHTG treated with TPE was conducted, with the aim of treating HTG-AP or preventing its recurrence. TPE was performed if sTG≥ 1000mg/dl after 24hours of admission.
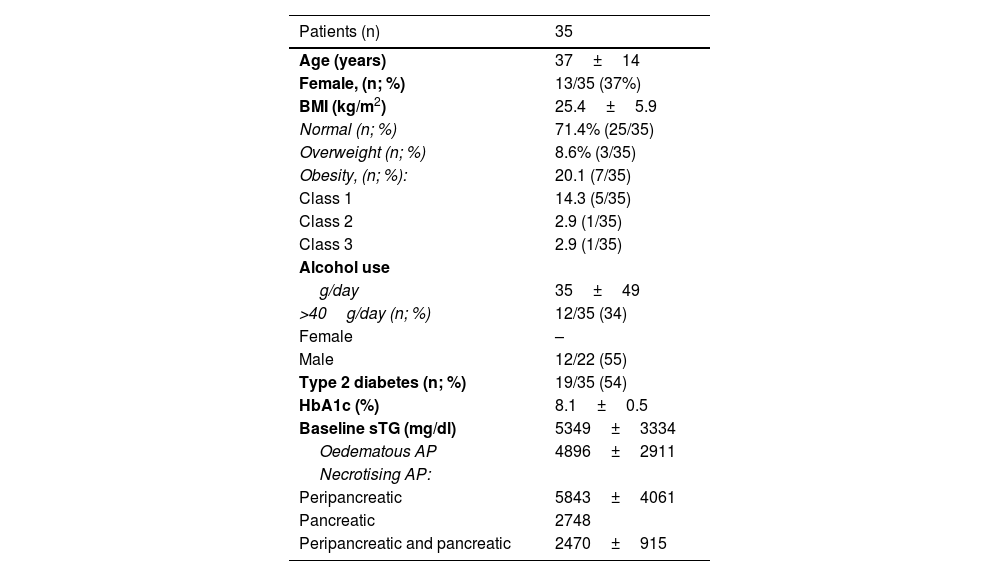
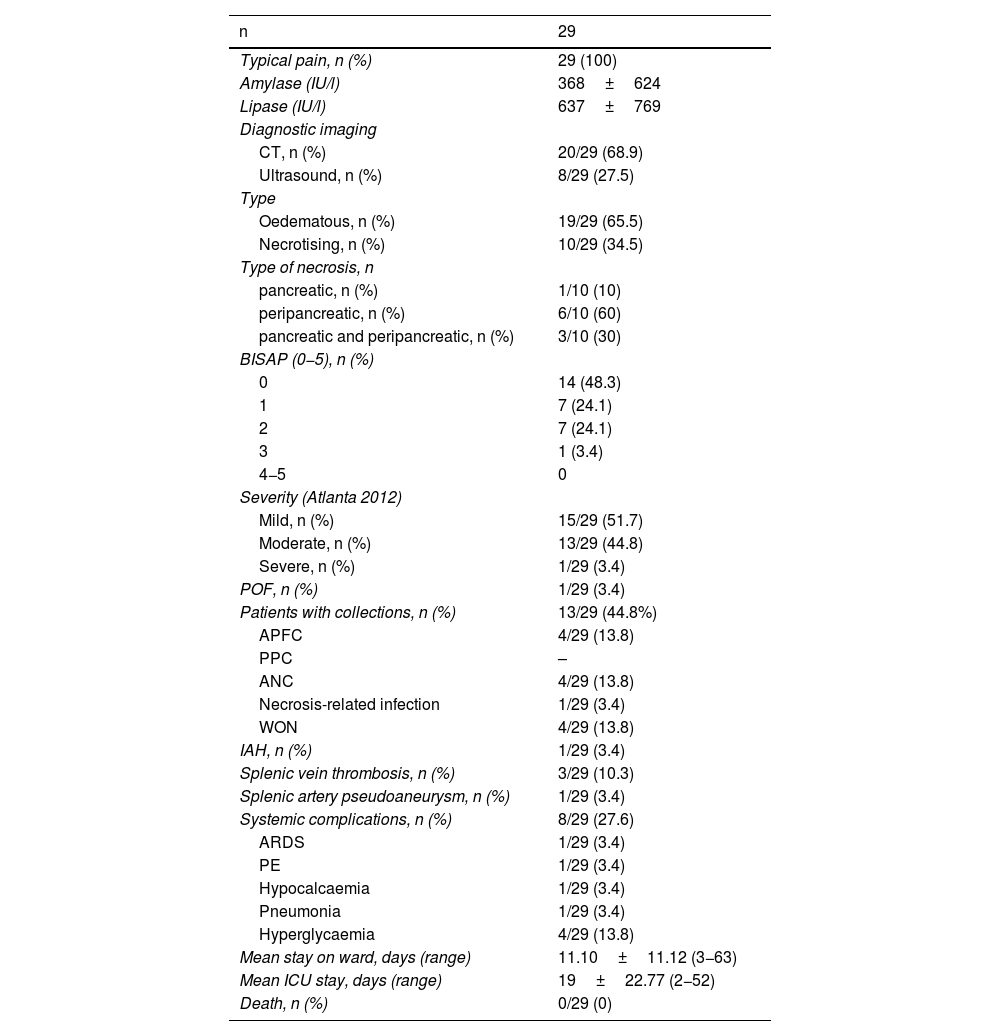
Results42 TPE were performed to treat 35 sHTG in 23 patients: 29 HTG-AP, and 6 sHTG with previous HTG-AP. Among the patients, 37% (13/55) were women, with 37±14 years-old, 74.3% had normal BMI (25/35), 34% (12/35) were drinking >40g/alcohol/day and 54% (19/35) were diabetics. TPE significantly reduced the baseline sTG (4425±2782mg/dl vs. 709±353mg/dL, p<0.001) in a single session, achieving a mean percentage reduction of 79±13%; 20% (7/35) of sHTG cases required two TPE sessions to reduce sTG to <1000mg/dL. Adverse effects were reported in 4/42 TPE sessions (9,5%). sHTG-AP was observed in 3% of cases (1/29), and there were no deaths. sTG at 24h of admission showed no relation with the severity of APs.
ConclusionThe treatment of sHTG with TPE, with the aim of treating HTG-AP or preventing its recurrence, reduces sTG quickly and safety.
El RPT reduce drásticamente los TGs (triglicéridos séricos), pero su papel en el tratamiento de la pancreatitis aguda por hipertrigliceridemia (PA-HTG) o en riesgo de padecerla, no está bien establecido. Los objetivos fueron valorar la efectividad y seguridad del RPT en el tratamiento de la HTG grave (HTGg), y evaluar la gravedad de la PA-HTG tratada con RPT.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional-retrospectivo-unicéntrico, en el que se realizó un análisis descriptivo de las HTGg tratadas mediante RPT, con intención de tratar una PA-HTG o prevenir su recurrencia. El RPT se realizaba si los TGs ≥ 1000mg/dl tras 24h de ingreso.
ResultadosSe hicieron 42 RPT para tratar 35 HTGg en 23 pacientes: 29 PA-HTG, y 6 HTGg con PA-HTG previa. Los pacientes eran: mujeres (13/35;37%), con 37±14 años, IMC normal (25/35; 74,3%), consumo de >40g/alcohol/día (12/35; 34%), y diabéticos (19/35;54%). El RPT redujo significativamente los TGs basales (4425±2782mg/dl vs. 709±353mg/dL, p<0.001) en una sesión, logrando una reducción porcentual media del 79±13%. Un 20% (7/35) de las HTGg requirieron dos sesiones de RPT para reducir los TGs<1000mg/dL. Se reportaron efectos adversos en 4/42 RPT (9,5%). La PA-HTG fue grave en el 3% de los casos (1/29) y no hubo muertes. La cifra de TGs a las 24h del ingreso no mostró relación con la gravedad de la PA.
ConclusiónEl tratamiento de la HTGg con RPT, con intención de tratar la PA-HTG o prevenir su recurrencia, reduce los TGs de una forma rápida, efectiva y segura.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora