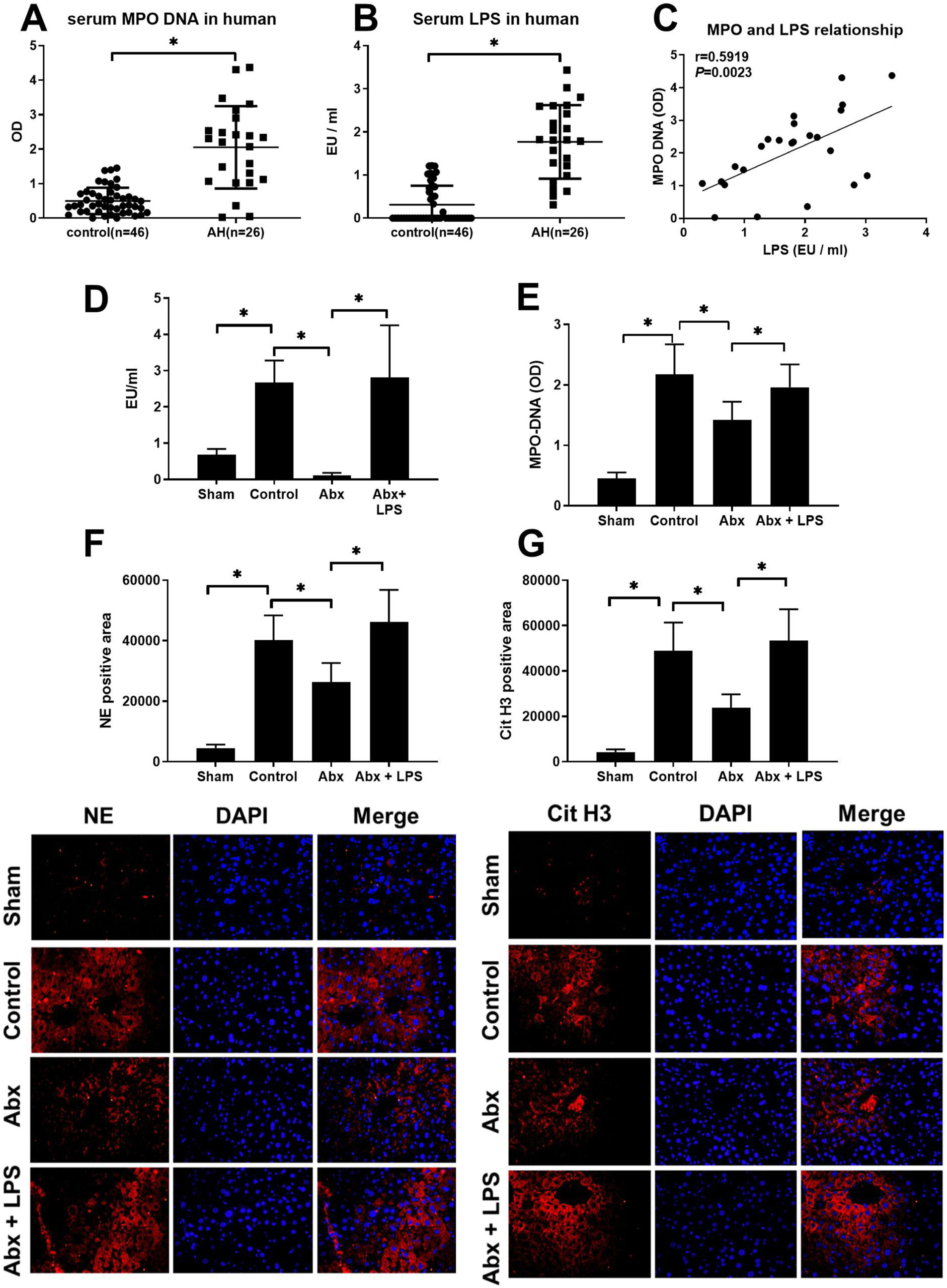
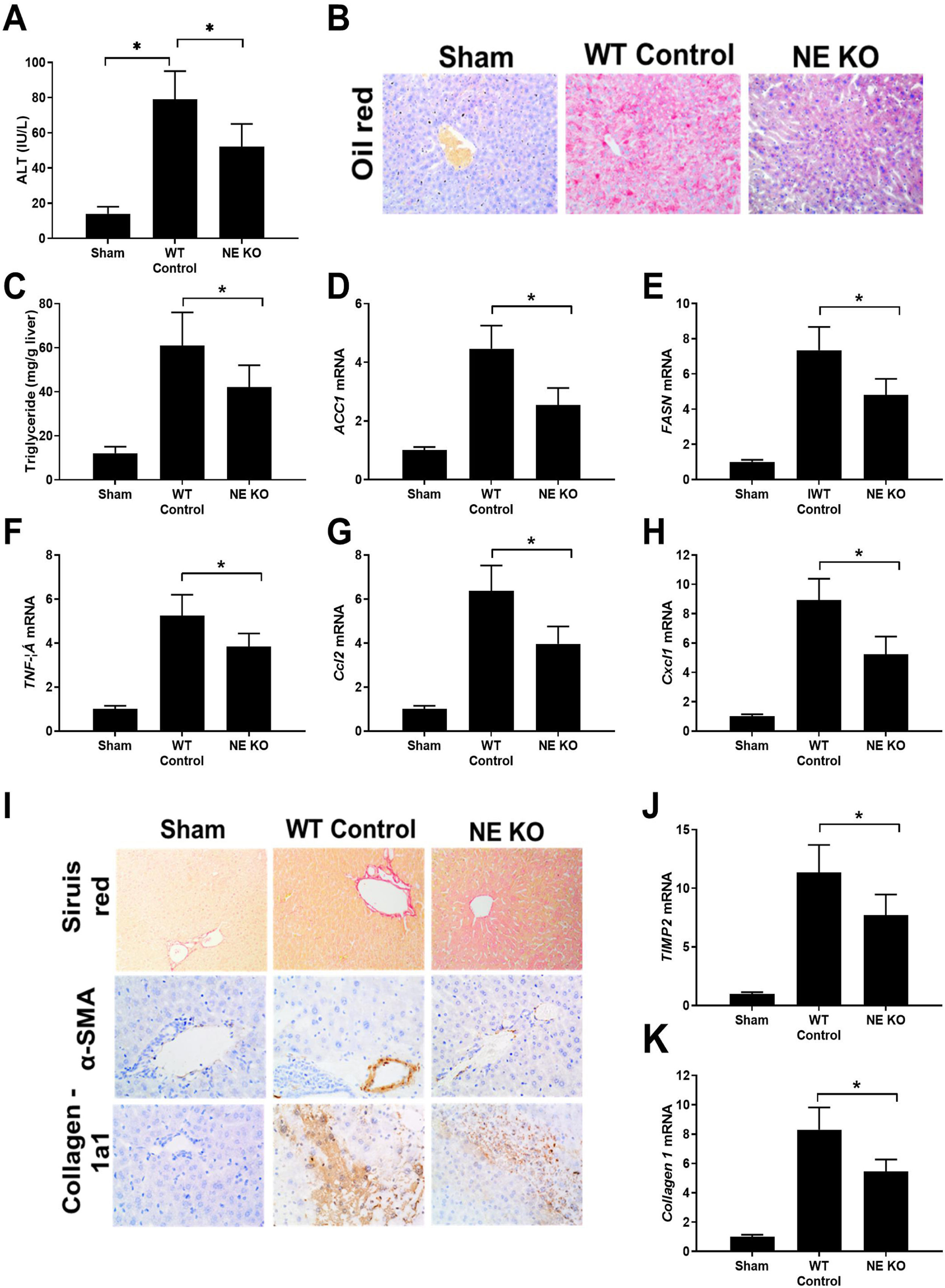
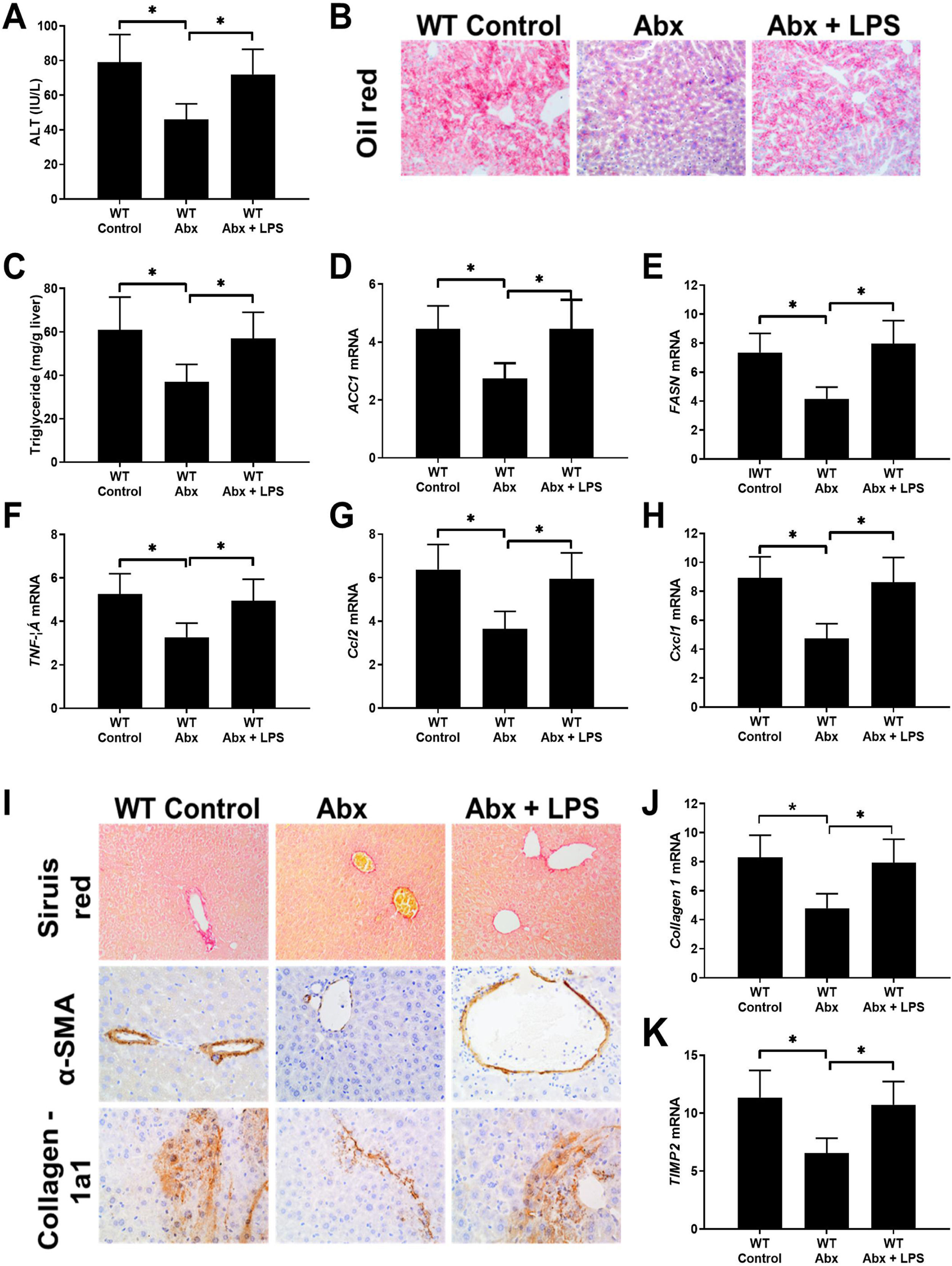
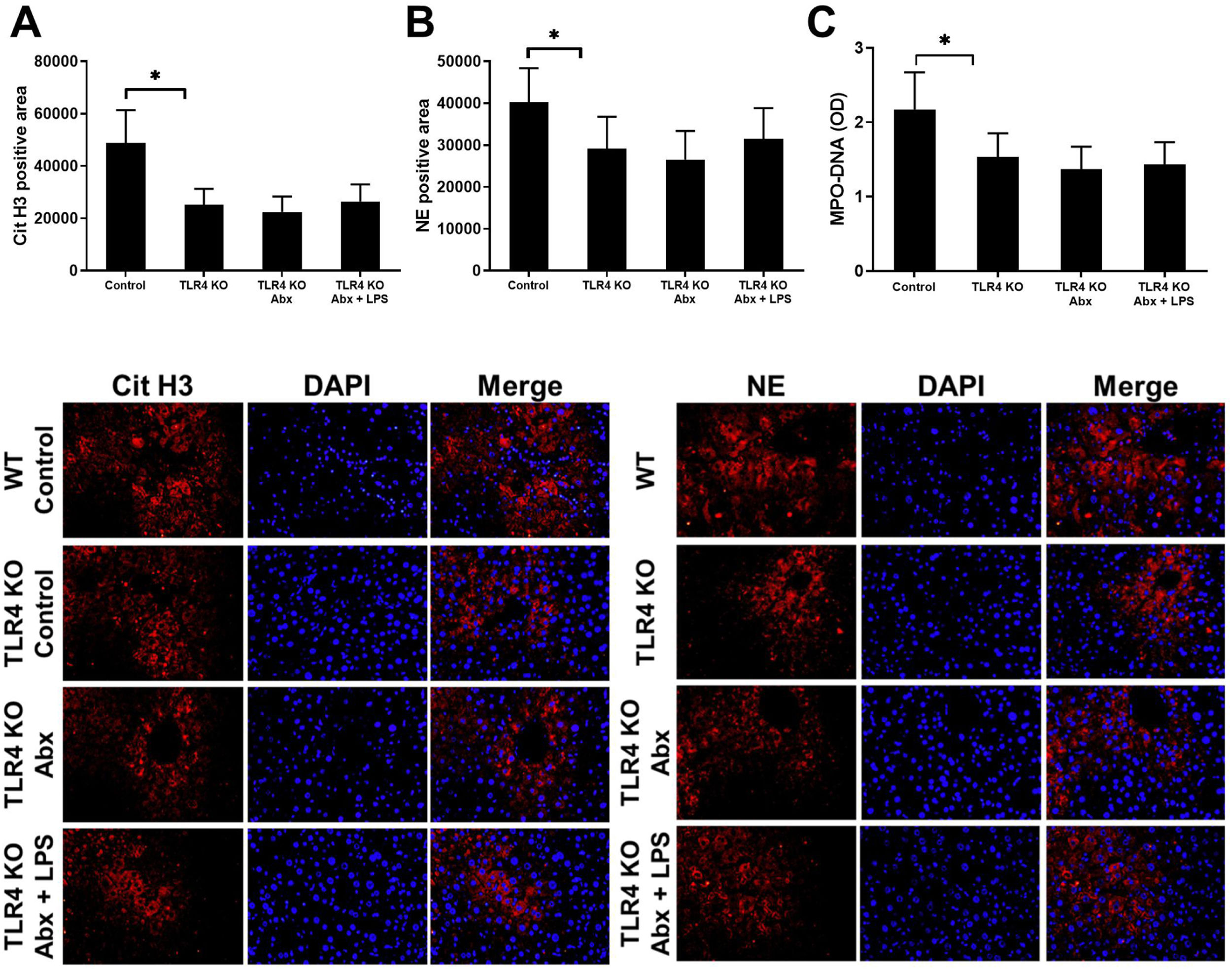
Intrahepatic infiltration of neutrophils is a character of alcoholic hepatitis (AH) and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are an important strategy for neutrophils to fix and kill invading microorganisms. The gut-liver axis has been thought to play a critical role in many liver diseases also including AH. However, whether NETs appear in AH and play role in AH is still unsure.
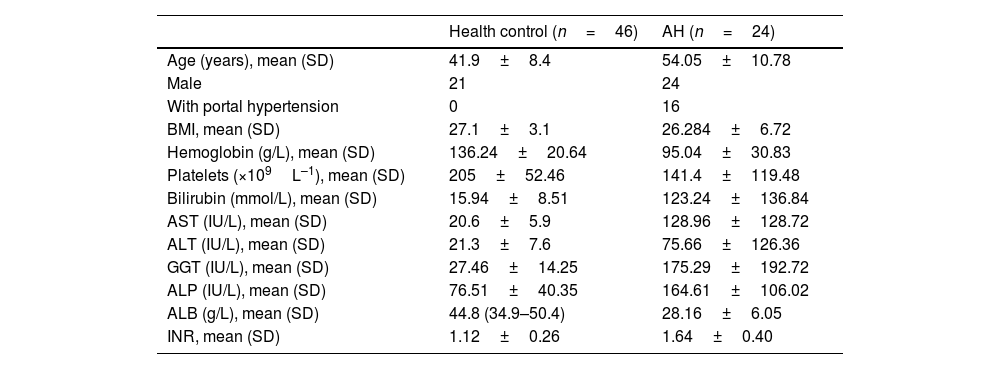
MethodsSerum samples from AH patients were collected and LPS and MPO-DNA were detected. WT, NE KO, and TLR4 KO mice were used to build the AH model, and the intestinal bacteria were eliminated at the same time and LPS was given. Then the formation of NETs and AH-related markers were detected.
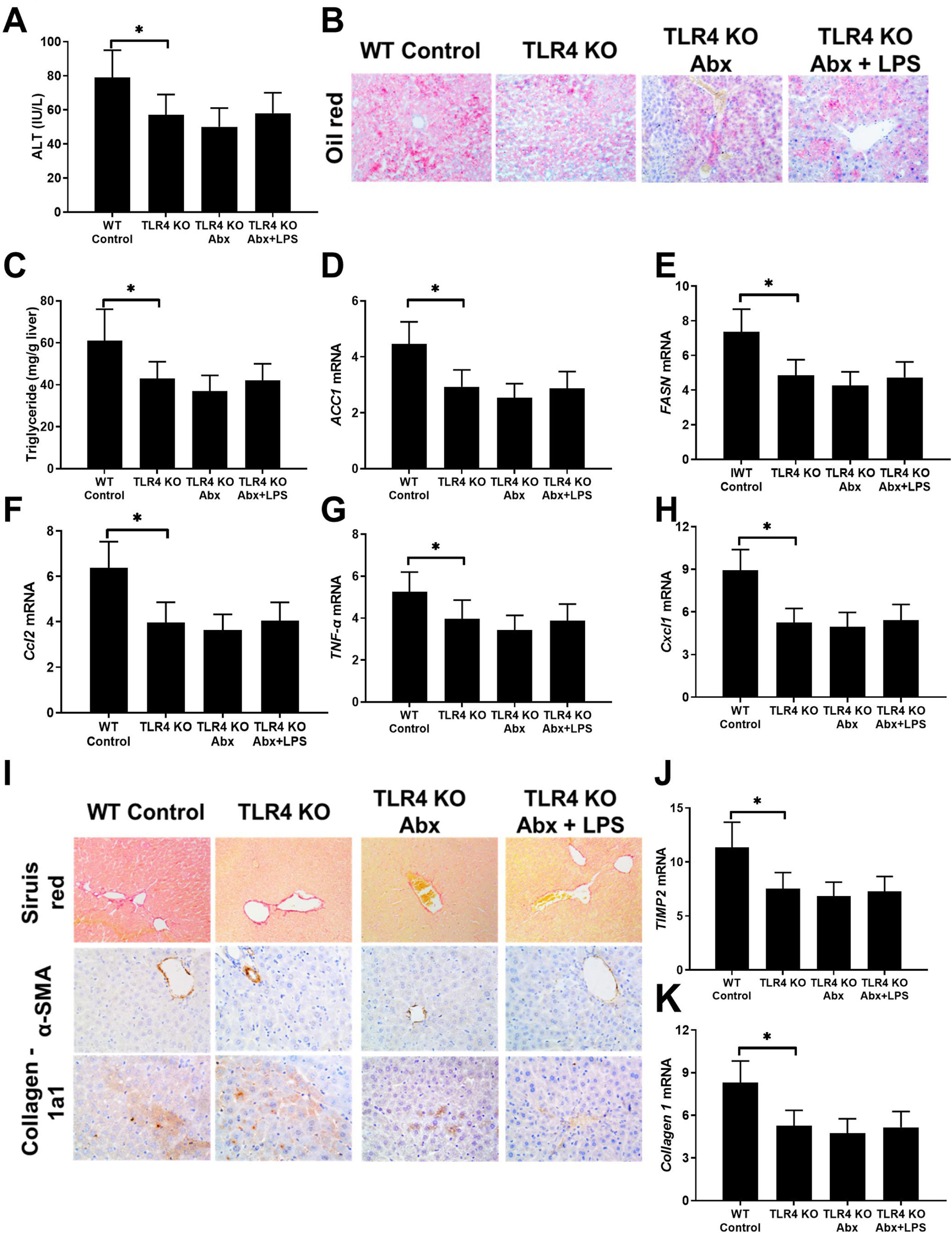
ResultsThe serum MPO-DNA and LPS concentration was increased in AH patients and a correlation was revealed between these two indexes. More intrahepatic NETs formed in AH mice. NETs formation decreased with antibiotic intervention and restored with antibiotic intervention plus LPS supplement. While NETs formation failed to change with gut microbiome or combine LPS supplement in TLR4 KO mice. As we tested AH-related characters, liver injury, intrahepatic fat deposition, inflammation, and fibrosis alleviated with depletion of NE. These related marks were also attenuated with gut sterilization by antibiotics and recovered with a combined treatment with antibiotics plus LPS. But the AH-related markers did show a difference in TLR4 KO mice when they received the same treatment.
ConclusionIntestinal-derived LPS promotes NETs formation in AH through the TLR4 pathway and further accelerates the AH process by NETs.
La infiltración intrahepática de neutrófilos es una característica de la hepatitis alcohólica (AH, por sus siglas en inglés) y las trampas extracelulares de neutrófilos (NET, por sus siglas en inglés) son una estrategia importante para que los neutrófilos fijen y maten microorganismos invasores. Se ha pensado que el eje intestino/hígado desempeña un papel crítico en muchas enfermedades hepáticas, incluida la AH. Sin embargo, aún no está claro si las NET aparecen en la AH y desempeñan un papel en la misma.
MétodosSe recogieron muestras de suero de pacientes con AH, y se detectaron LPS y MPO-ADN. Se utilizaron ratones WT, NE KO y TLR4 KO para construir el modelo de la AH, y las bacterias intestinales se eliminaron al mismo tiempo y se administró LPS. Luego se detectó la formación de NET y los marcadores relacionados con la AH.
ResultadosLa concentración sérica de MPO-ADN y LPS aumentó en los pacientes con HA, y se reveló una correlación entre estos 2 índices. Se formaron más NET intrahepáticos en ratones con AH. La formación de las NET disminuyó con la intervención antibiótica, y se restauró con la intervención antibiótica más suplemento de LPS. Mientras que la formación de NET no pudo cambiar con el microbioma intestinal o combinar el suplemento de LPS en ratones TLR4 KO. A medida que probamos los caracteres relacionados con la AH, la lesión hepática, la deposición de grasa intrahepática, la inflamación y la fibrosis se aliviaron con el agotamiento de las NET. Estas marcas relacionadas también se atenuaron con la esterilización intestinal con antibióticos, y se recuperaron con un tratamiento combinado con antibióticos más LPS. Pero los marcadores relacionados con la AH mostraron una diferencia en los ratones TLR4 KO cuando recibieron el mismo tratamiento.
ConclusiónEl LPS de origen intestinal promueve la formación de NET en la AH a través de la vía TLR4, y acelera aún más el proceso de AH por NET.