There is an obvious need to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma using novel non-invasive and sensitive biomarkers. Circular RNAs have recently attracted great interest as promising biomarkers and treatment targets. However, their function in hepatocellular carcinoma whose etiology related to hepatitis C has been rarely studied.
Aim of workThe current study was conducted to analyze differential expression of circ-ITCH in plasma of Egyptian HCC patients with concomitant HCV infection, compared to normal control subjects, to investigate its correlation with liver function parameters, and to determine the possible diagnostic ability of circ-ITCH in plasma as a non-invasive marker, compared to its linear counterpart.
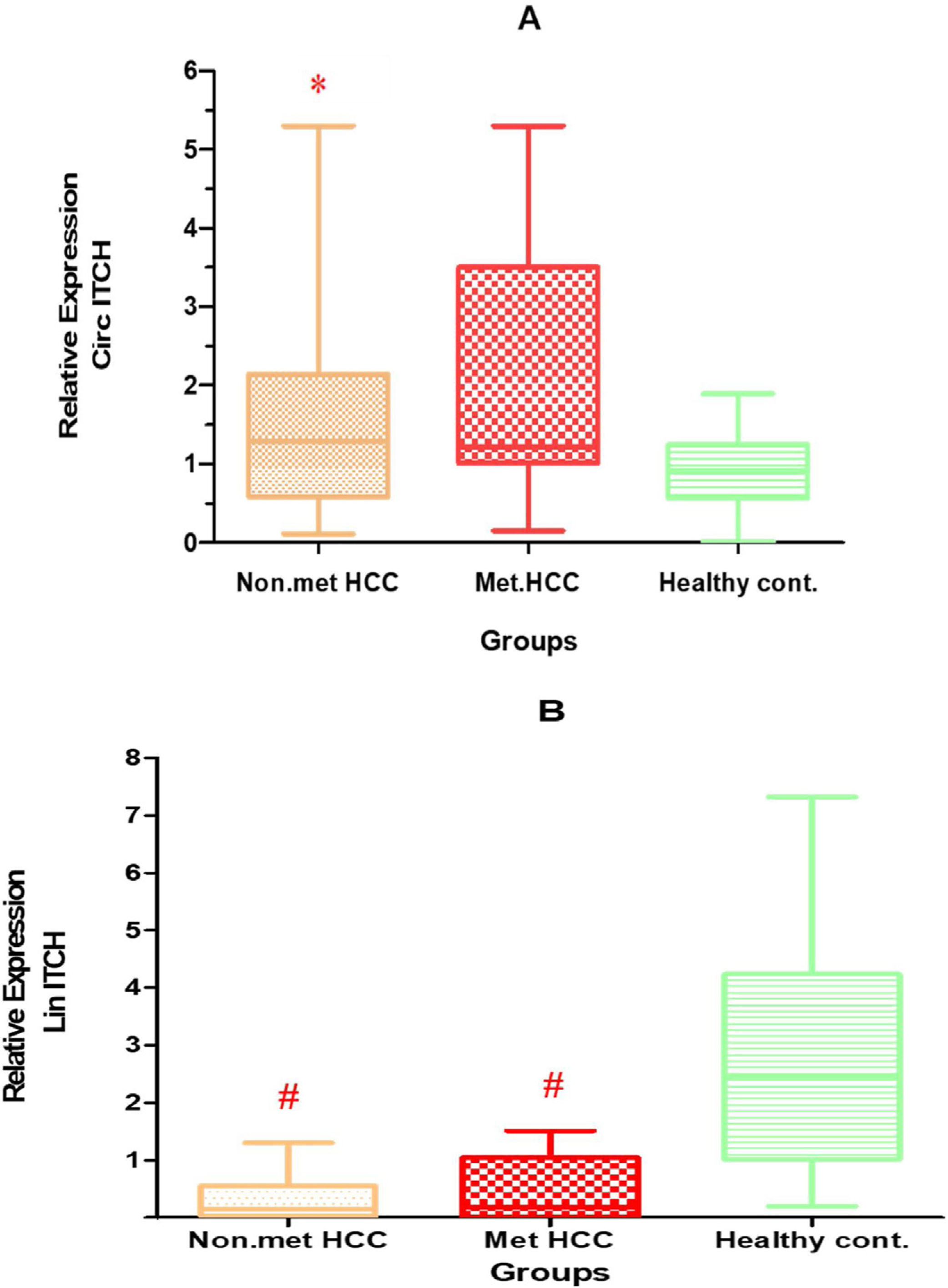
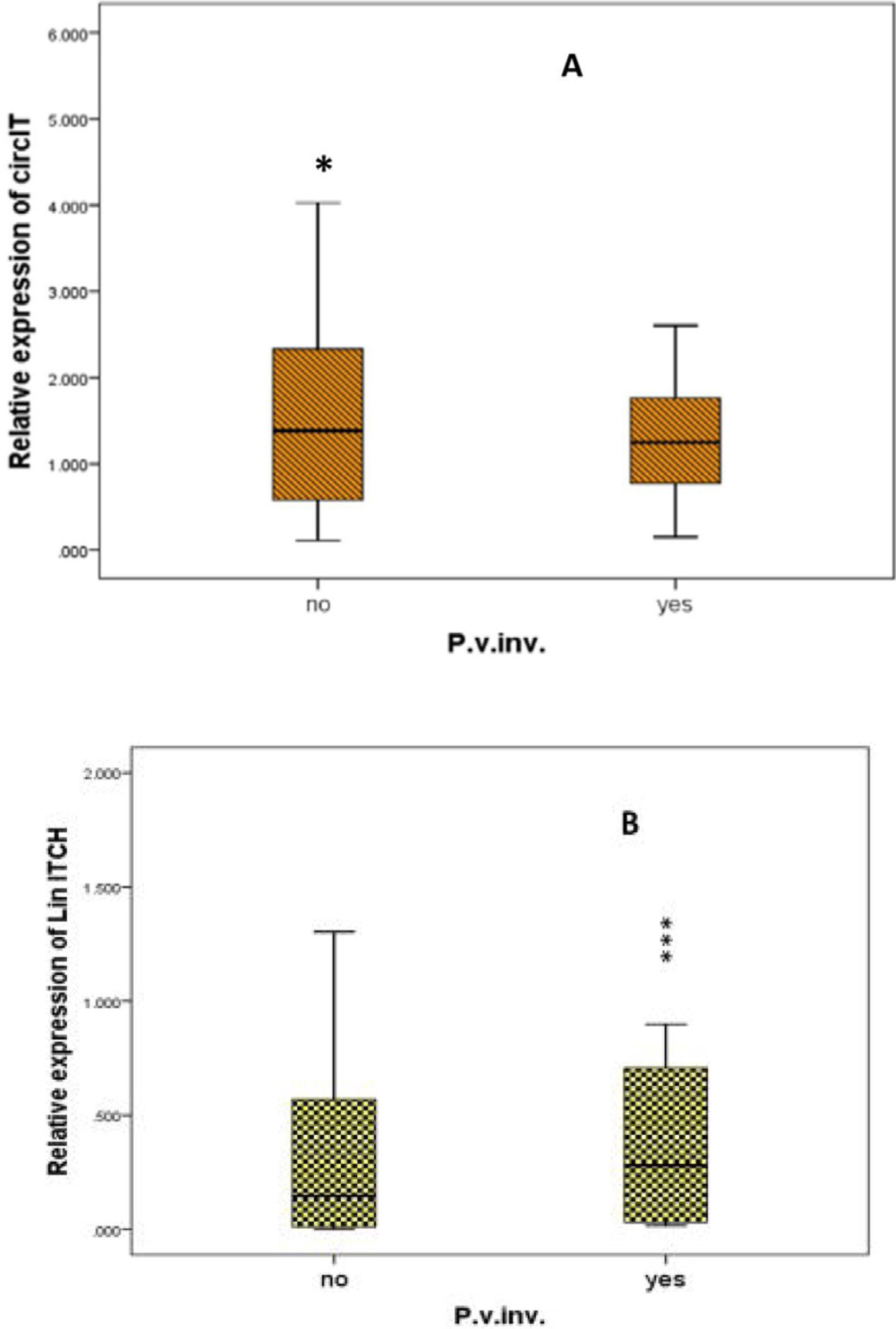
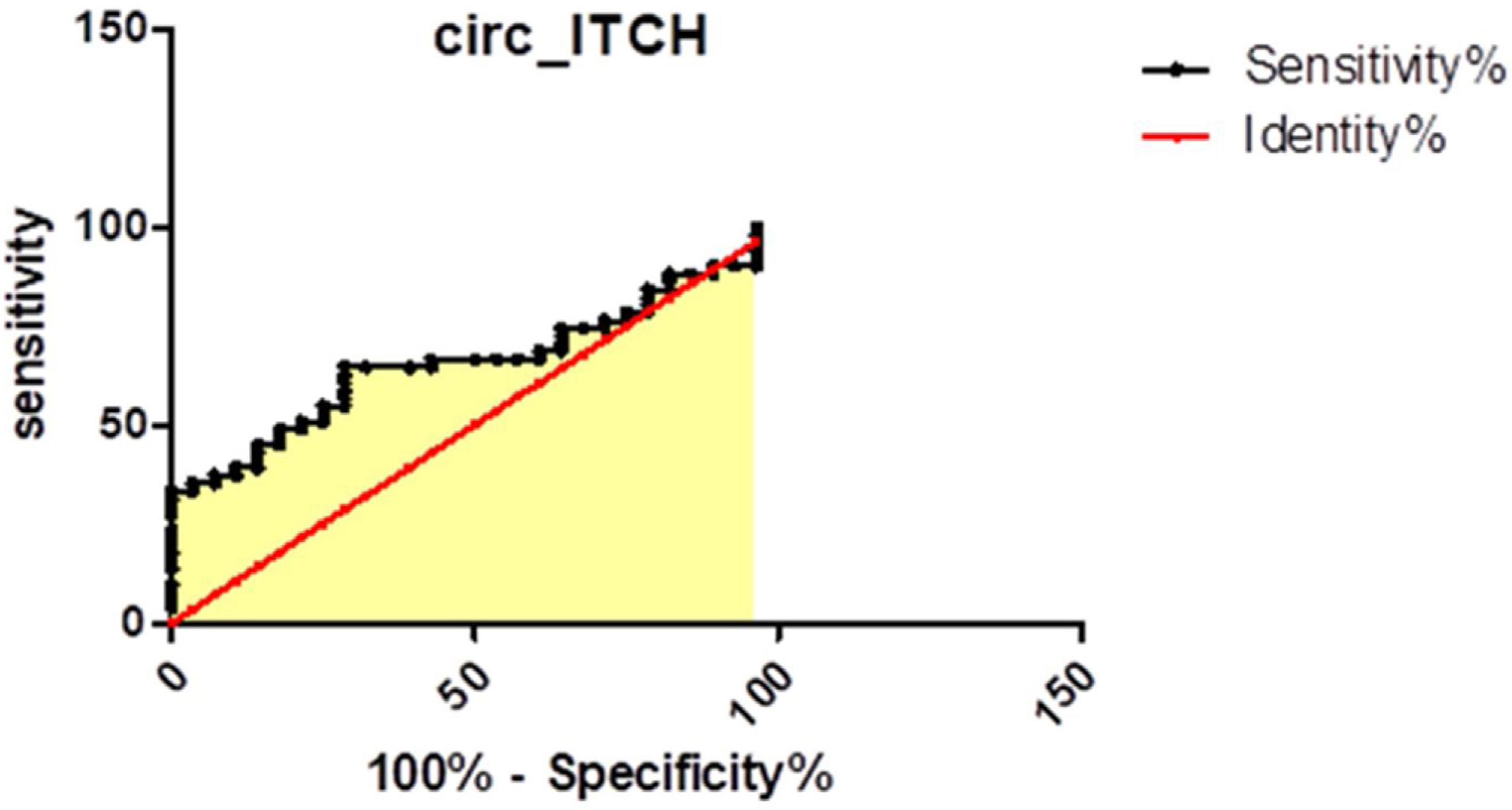
ResultsThe results showed that the relative expression of circ-ITCH was significantly higher in the plasma of HCC patients (P<0.05). Moreover, when comparing its expression in the metastatic and non-metastatic subgroups, it was significantly higher in the non-metastatic HCC group compared to control group (P<0.05). Circ-ITCH was positively correlated with liver enzymes AST, ALT (P<0.001), also was significantly higher in HCC child C patients. To evaluate the potential diagnostic value of circ-ITCH in plasma, a ROC curve was generated, the AUC was 0.661, (95% CI: 0.5433–0.778) with a sensitivity and specificity 65% and 70% respectively.
ConclusionThe results revealed that circ-ITCH is-with no doubt-involved in the pathogenesis of HCC and its high level may be related to HCV infection, further researches in this area will certainly make great contributions in understanding. In conclusion our results suggested that circ-ITCH may be used as a noninvasive diagnostic marker and a promising therapeutic target for HCC.
Existe una necesidad obvia de diagnosticar el carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC) utilizando nuevos biomarcadores no invasivos y sensibles. Los ARN circulares han atraído recientemente un gran interés como biomarcadores prometedores y dianas de tratamiento. Sin embargo, su función en el carcinoma hepatocelular, cuya etiología está relacionada con la hepatitis C, apenas ha sido estudiada.
ObjetivoEste estudio se realizó para analizar la expresión diferencial de circ-ITCH en el plasma de pacientes egipcios con CHC con infección concomitante por VHC, en comparación con sujetos de control normales, para investigar su correlación con los parámetros de la función hepática y para determinar la posible capacidad diagnóstica de circ-ITCH en plasma como marcador no invasivo, en comparación con su contraparte lineal.
ResultadosLos resultados mostraron que la expresión relativa de circ-ITCH fue significativamente mayor en el plasma de pacientes con CHC (p<0,05). Además, al comparar su expresión en los subgrupos metastásico y no metastásico, fue significativamente mayor en el grupo de CHC no metastásico en comparación con el grupo control (p<0,05). Circ-ITCH se correlacionó positivamente con las enzimas hepáticas AST y ALT (p<0,001), y también fue significativamente mayor en pacientes con CHC infantil con VHC. Para evaluar el valor diagnóstico potencial de circ-ITCH en plasma se generó una curva ROC, el AUC fue de 0,661 (IC95%: 0,5433-0,778), con una sensibilidad y una especificidad del 65% y del 70%, respectivamente.
ConclusiónLos resultados revelaron que circ-ITCH está, sin duda, involucrado en la patogénesis del CHC, y su alto nivel puede estar relacionado con la infección por VHC, por lo que investigaciones adicionales en esta área ciertamente harán grandes contribuciones para su comprensión. En conclusión, nuestros resultados sugirieron que circ-ITCH puede usarse como un marcador de diagnóstico no invasivo y una diana terapéutica prometedora para el CHC.