To analyse the characteristics and use of digital health tools (DHT) in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
MethodsWe performed a qualitative study based on a narrative literature review, a questionnaire and on the opinion of 3 expert gastroenterologists. Several searches were carried out until September 2022 through Medline to identify articles on the use of DHT in IBD by healthcare professionals. A structured questionnaire was designed to be answered by health professionals involved in the care of patients with IBD. The experts generated a set of recommendations.
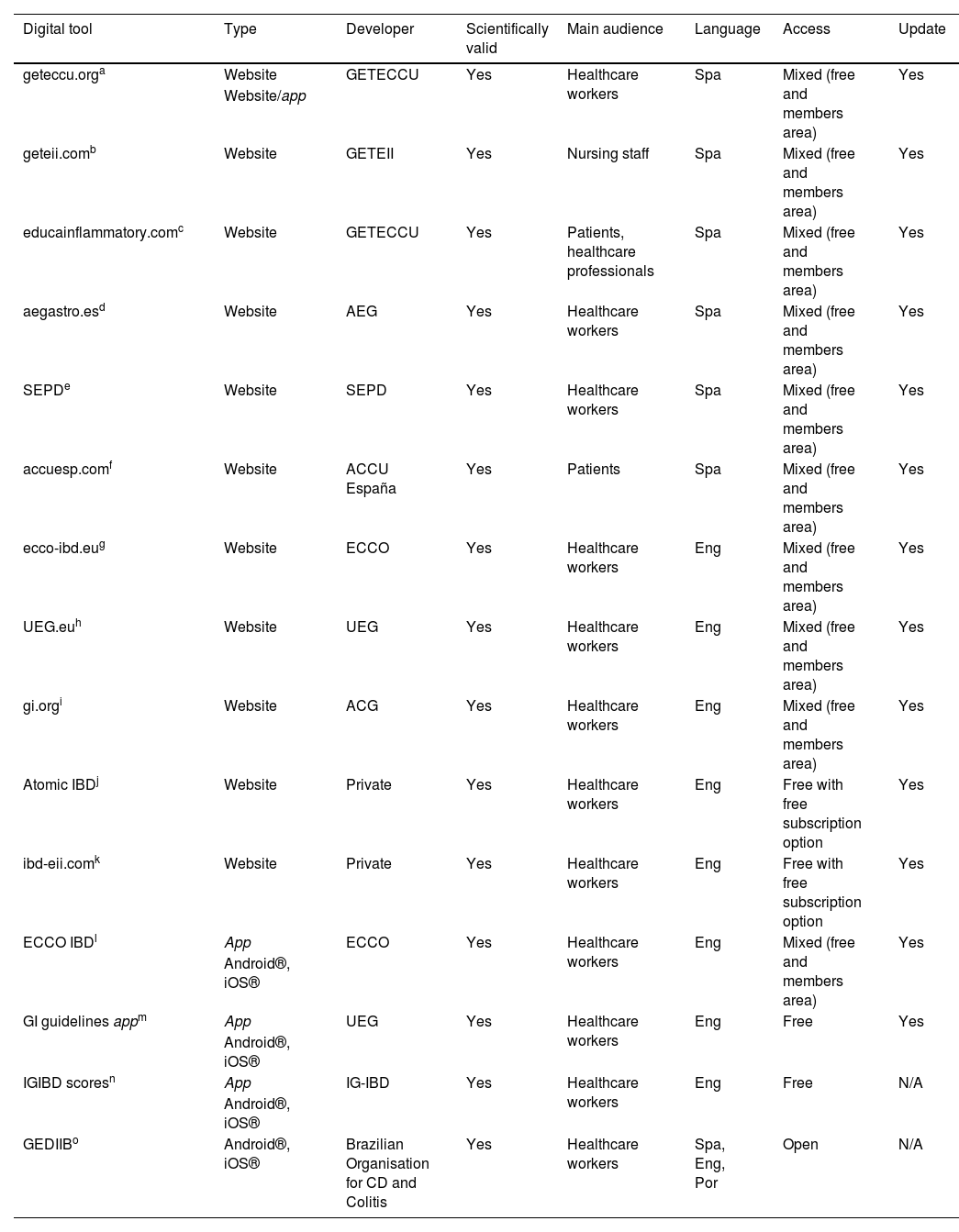
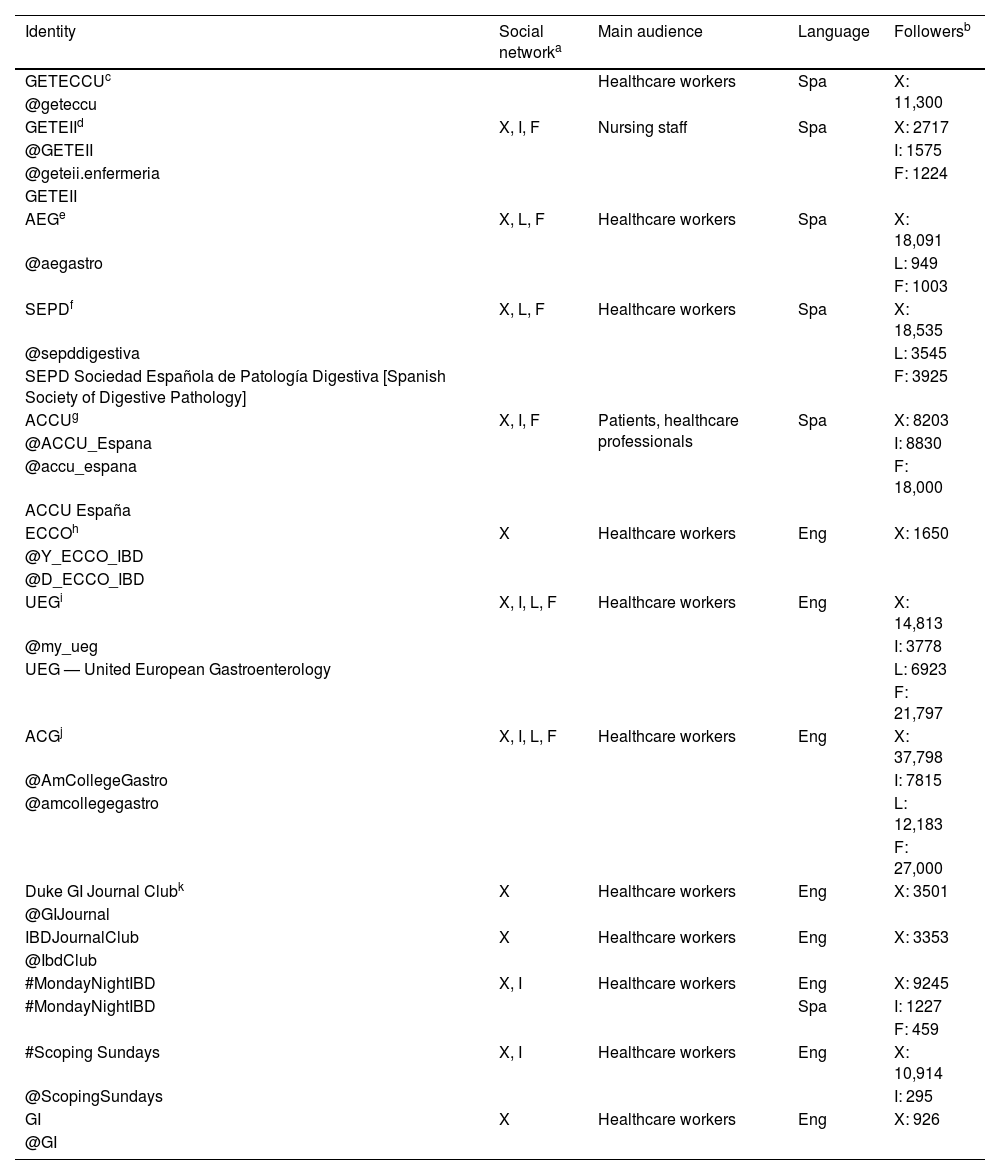
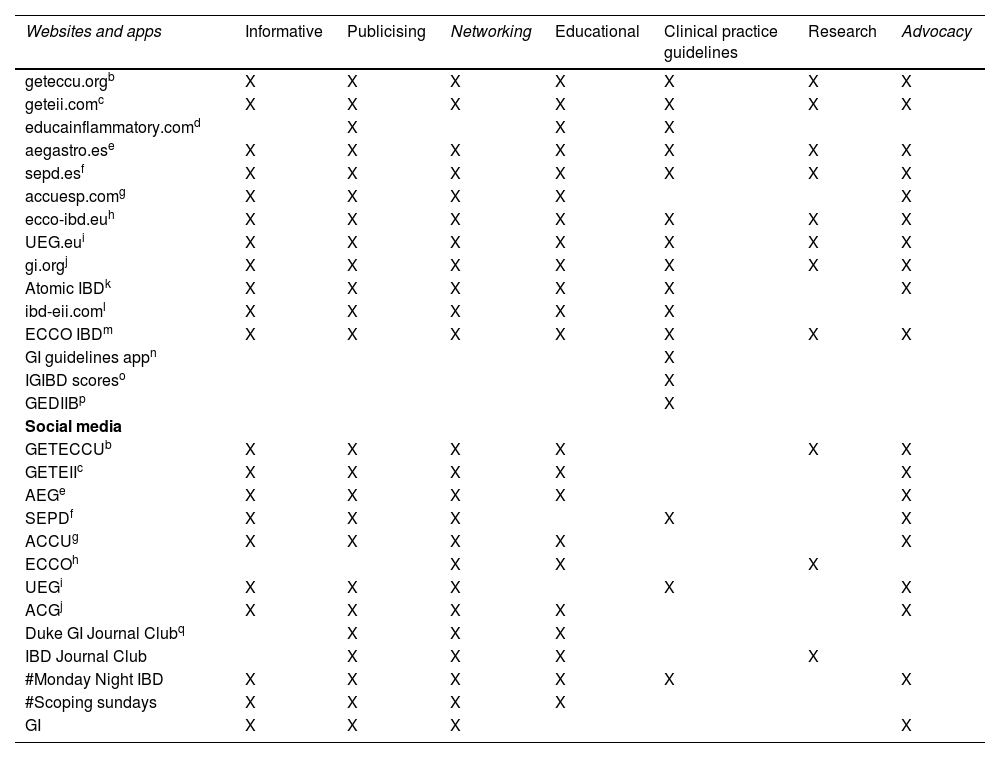
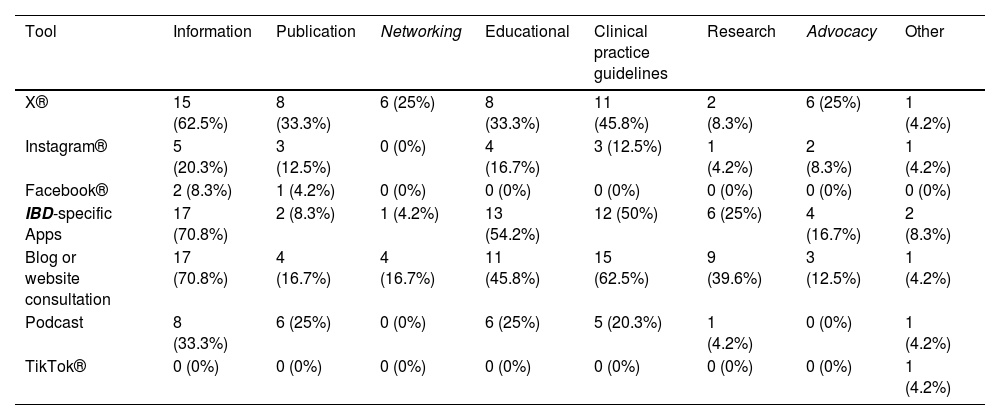
ResultsThere are multiple DHT for IBD with different characteristics and contents. We received 29 questionnaires. Almost 50% of the participants were 41–50 years old, the majority were women (83%) and 90% were gastroenterologists. A total of 96% reported the use of several DHT, but 20% used them occasionally or infrequently. Web pages were found the most used (62%). DHT are mostly used to get information (80%), followed by clinical practice issues (70%) and educational purposes (62%). G-Educainflamatoria website is the best known and most used HDS (96% and 64%, respectively). The main barriers to the use of DHT in IBD were the lack of time (55%), doubts about the benefit of DHT (50%) and the excess of information (40%).
ConclusionsHealthcare professionals involved in the care of patients with to IBD frequently use DHT, although actions are needed to optimize their use and to guarantee their efficient and safe use.
Analizar las características y el uso de herramientas digitales en salud (HDS) en la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII).
MétodosEstudio cualitativo basado en una revisión narrativa de la literatura, un cuestionario y en la opinión de 3 gastroenterólogos expertos en la EII. Se realizó una búsqueda en Medline hasta septiembre de 2022 para identificar artículos sobre HDS relacionadas con la EII usadas por profesionales de la salud. Se diseñó un cuestionario estructurado para ser contestado por profesionales de la salud relacionados con el cuidado de pacientes con EII. En base a esto, se han generado recomendaciones sobre este tema.
ResultadosExisten múltiples HDS para la EII con distintas características y contenidos. Se recibieron 29 cuestionarios. Aproximadamente el 50% de los participantes tenían entre 41-50 años, la mayoría eran mujeres (83%) y el 90% gastroenterólogos. El 96% refería utilizar alguna HDS, el 20% hacía un uso puntual o poco frecuente, y las HDS más utilizadas eran las páginas web (62%). El motivo principal de uso es la obtención de información (80%), seguido de la práctica clínica (70%) y la educación (62%). La web G-Educainflamatoria es la HDS más conocida y usada (96 y 64%, respectivamente). Las principales barreras al uso de HDS en la EII eran la falta de tiempo (55%), las dudas de su beneficio (50%) y el exceso de información (40%).
ConclusionesLos profesionales sanitarios dedicados a la EII utilizan con frecuencia HDS si bien se precisan acciones para optimizar el uso de HDS en la EII y garantizar un uso eficiente y seguro de las mismas.