Inflammasome activation is known to be involved in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Vinpocetine is a derivative of vincamine and is reported to suppress the activation of inflammasome.
MethodsThis study explored the therapeutical potential of Vinpocetine on NASH. Mice were fed with a choline-deficient (MCD) or chow diet in the presence or absence of Vinpocetine for 8 weeks. H&E staining and biochemical assays were determined to evaluate the hepatic steatosis and fibrosis symptoms. In addition, primary hepatocytes and Kupffer cells were isolated and induced by MCD or lipopolysaccharides/cholesterol crystals with or without Vinpocetine. ELISAs, qPCR, and Western blotting were applied to determine the levels of NASH-related biomarkers in both in vivo mouse model and in vitro cell models.
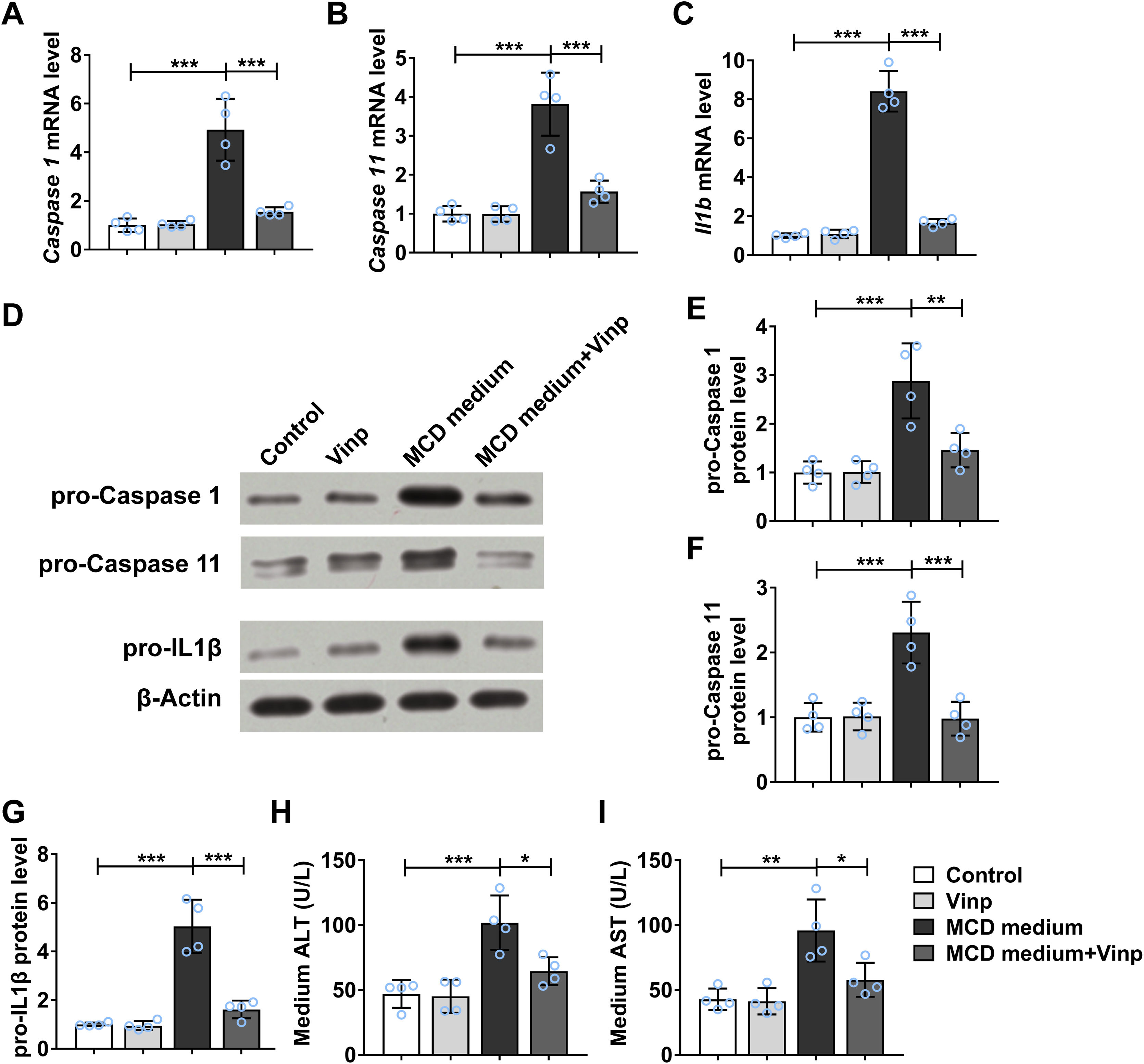
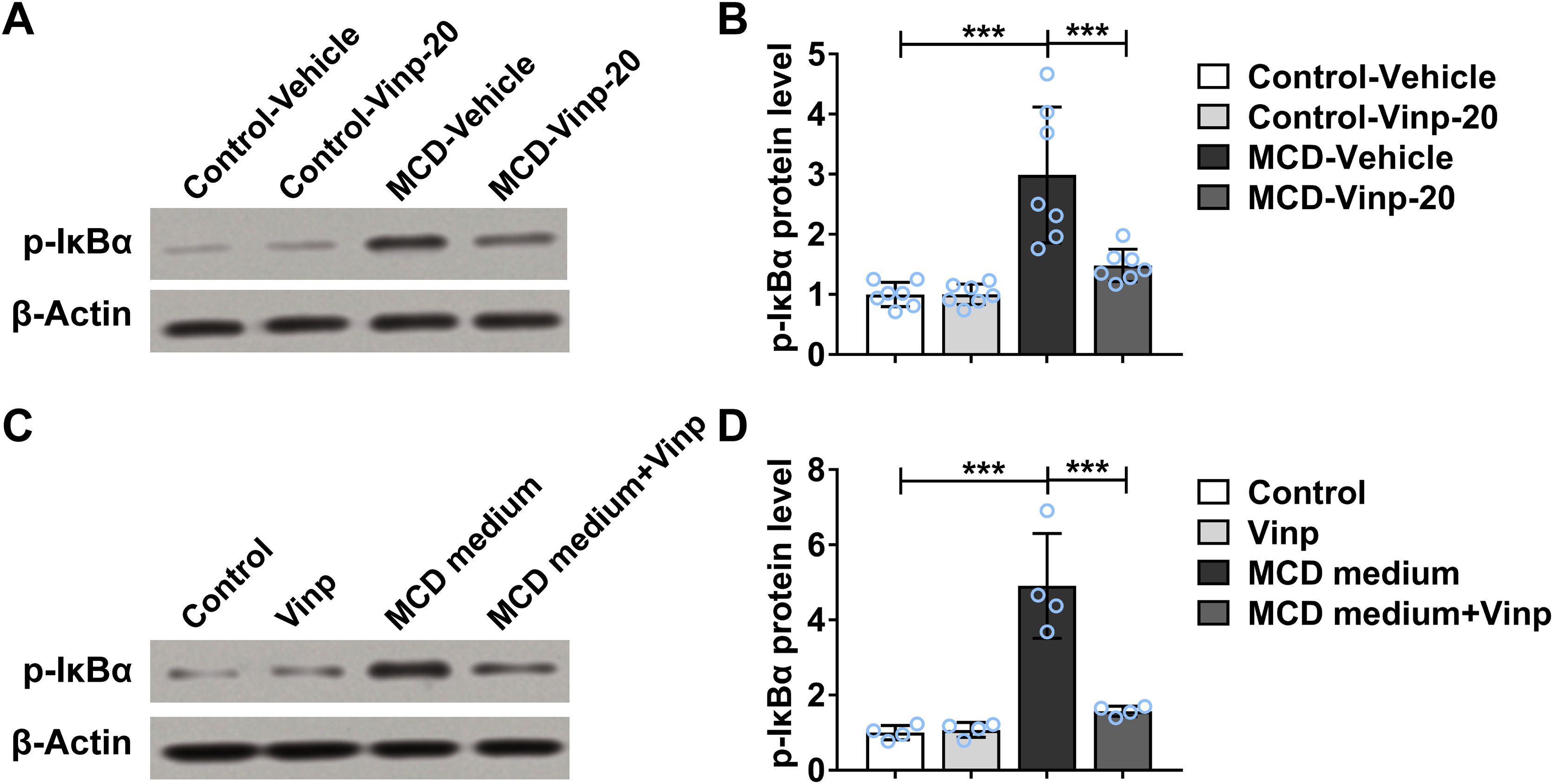
ResultsTreatment of Vinpocetine did not cause observable side effects against and MCD-induced cells and mouse NASH model. However, treatment of Vinpocetine ameliorated hepatic steatosis and fibrosis and suppressed the levels of alanine transaminase and aspartate transferase in the mouse NASH model. In addition, treatment of Vinpocetine suppressed the mRNA and protein levels of inflammasome components both in vitro and in vivo.
ConclusionVinpocetine suppressed NASH in mice by mediating inflammasome components via nuclear factor κB signaling.
Se sabe que la activación del inflamasoma está implicada en la esteatohepatitis no alcohólica (EHNA). La vinpocetina es un derivado de la vincamina que, según los informes, suprime la activación del inflamasoma.
MétodosEste estudio exploró el potencial terapéutico de la vinpocetina en la EHNA. Durante 8 semanas se alimentó a ratones con una dieta deficiente en colina (MCD) o con una dieta chow en presencia o ausencia de vinpocetina. Se realizaron tinciones de H&E y ensayos bioquímicos para evaluar los síntomas de esteatosis hepática y fibrosis. Además, se aislaron hepatocitos primarios y células de Kupffer y se indujeron mediante MCD o cristales de lipopolisacáridos/colesterol con o sin vinpocetina. Se aplicaron ELISA, qPCR y Western blotting para determinar los niveles de biomarcadores relacionados con la EHNA tanto en el modelo de ratón in vivo como en los modelos celulares in vitro.
ResultadosEl tratamiento con vinpocetina no causó efectos secundarios observables contra las células y el modelo de ratón de EHNA inducidos por MCD. Sin embargo, el tratamiento con vinpocetina mejoró la esteatosis hepática y la fibrosis y suprimió los niveles de alanina transaminasa y de aspartato transferasa en el modelo de EHNA de ratón. Además, el tratamiento con vinpocetina suprimió los niveles de ARNm y proteínas de los componentes del inflamasoma tanto in vitro como in vivo.
ConclusionesLa vinpocetina suprimió la EHNA en ratones por mediación de los componentes del inflamasoma a través de la señalización del factor nuclear κB.