Los cambios climáticos son reflejados en las variaciones de diferentes parámetros. Las secuencias sedimentarias de lagos son buena fuente de esta información debido a que proveen grabaciones continuas y detalladas de cambios paleoclimáticos.
Para determinar los cambios en el clima al SE de la llanura Pampeana, se presentan estudios de magnetismo de rocas realizados en un testigo colectado del fondo de la Laguna La Brava (Argentina). También se midieron contenidos totales de sulfuro, carbón orgánico e inorgánico (TS, TOC y TIC), elementos alcalinos, metales pesados y livianos, y cambios en las comunidades de vegetación. Se realizaron cinco determinaciones de edades radiocarbónicas y se calcularon las edades calibradas. La tasa promedio de acumulación de sedimento es 1.3mm/año y la secuencia representa los últimos 4800 años en edades calibradas (cal. BP).
El objetivo principal fue reconstruir el balance hidrológico de la laguna, cambios erosionales y de contribución de sedimento dentro del área de aporte, y explorar la medida en que pueden estar relacionados con cambios climáticos y/o actividades humanas. Los resultados de este trabajo y estudios previos sugieren cambios periódicos de condiciones frías a cálidas y húmedas. La relación entre plantas sumergidas y emergentes es consistente con el comportamiento de susceptibilidad magnética κ. Los cambios en TOC sugieren un ambiente húmedo durante períodos de mejoramiento magnético. Se identificaron eventos de desbordes y bajos niveles de la laguna. Para los últimos 50cal. BP, cambios en la contribución de sedimento y procesos deposicionales fueron causados por impacto humano, en particular por el uso de recursos naturales.
Climatic changes are reflected in variations of different parameters. Sequences of lake sediments are good sources of this information because they provide continuous and detailed records of palaeoclimatic changes. In order to determine the changes in climate in SE Pampas plain, in this paper we present a series of rock magnetic studies performed on a bottom core collected from Lake La Brava (Argentina).
In order to establish lake level variations, we also measure total sulphur, organic and inorganic carbon (TS, TOC and TIC) content, alkaline elements, light and heavy metals and changes in vegetation communities. Five radiocarbon age determinations were made from samples of organic-rich clay and calibrated ages were calculated. The averaged sediment accumulation rate is 1.3mm/yr and the sequence represents a temporal extent of about 4800 calibrated years before the present (cal. BP).
The main aim was to reconstruct the hydrological balance of the lake, the changes in erosional strength and sediment supply within the catchment area since the Middle Holocene, and to explore the extent to which these may be linked to changes in climate and/or human activities. The results of this work and previous studies suggest periodic changes from cooler to warmer and humid conditions. Relationships between submerged and emergent plants are consistent with the behaviour of magnetic susceptibility. TOC changes suggest wet environment during magnetic enhancement. Floods and lower lake level events were identified in detail. Changes in sediment contribution and depositional processes for the last 50cal. BP are caused by human impact, particularly by the use of natural resources.
Lakes are very useful deposits of material that came from different sources, sometimes arriving from great distances via the atmosphere. More immediate and important sources are the catchment area and materials produced within the lake itself. Lake sediments are very sensitive archives of changes in rainfall, wind, trophic state, anthropogenic use of the catchment area, etc. Numerous studies have been published using magnetic parameters to investigate lake sediments (e.g. Sandgren and Risberg, 1990; Forester et al., 1994; Dearing et al., 2001; Abbott et al., 2003; Chaparro et al., 2008; Irurzun et al., 2009, Gogorza et al., 2004; 2006; 2012). Magnetic properties of sediments may act as sensitive recorders of palaeoclimatic changes, but they need to be interpreted in terms of climate by establishing models and correlations based on multi-proxy analyses that include both magnetic and non-magnetic techniques (Maher and Thompson, 1999; Geiss et al., 2003).
The reconstruction of Holocene environmental variability across the subtropical Pampean plains of South America has been limited by the paucity of complete and well-dated palaeoclimatic archives (Piovano et al., 2009). Results suggest that climate archives show a complex pattern of timing and climate interactions throughout the Holocene. The precise chronology and magnitude of some of these climatic shifts is still a matter of debate. According to Tonni et al. (1999) the climate was mostly arid until 1500cal. BP and wet until the present. On the other hand, according to Piovano et al. (2009) and Zárate et al. (2000) the climate was dry; especially at around 4200cal. BP. Mancini et al. (2005) suggest that from ~ 5000cal. BP the climate became drier with episodic flooding events as a consequence of humid Atlantic air masses that spread into the continent (Schäbitz and Liebricht, 1998). Prieto et al. (2004) suggest a subhumid-dry climate from mid to late Holocene in the NE Pampas and that the aeolian input increased (Prieto, 1996). The data are also consistent with trends of precipitation decrease quantitatively estimated for the late Holocene southwestern Pampa region (Tonello and Prieto, 2010) and drying suggested by episodes of aeolian reactivation across the Pampa region during the mid- and late Holocene (Zárate and Tripaldi, 2012). In the last two millennia climate has been rather unstable, with wetter phases interrupted by dry phases, such as the Little Ice Age (Cioccale, 1999; Piovano et al., 2002; Laprida et al., 2009a; Stutz et al., 2012).
The Pampas Plain is one of the most important zones for agricultural production in Argentina and one of the most likely to be affected by climate changes (Laprida et al., 2009a). To know the natural trends and the anthropogenic effect on the system is extremely necessary. The study of magnetic parameters in shallow lake sediments in the Pampean plain is extremely scarce. Most of the works have been carried out on soils and paleosols (Nabel et al., 1999; Orgeira et al., 2003; 2004; 2009; Bidegain et al., 2009; Zárate et al., 2009) or short shallow lake sediment cores for the last 500 years (Lirio et al., 2007; Laprida et al., 2009a-b;2011; Stutz et al., 2002; 2012).
It is evident the need to obtain longer sequences to better understand long-term variations in environmental changes. In this work we are going to focus on palaeoenvironmental changes to achieve lake level variations for the last 4800 yrs using rock magnetic studies. Additionally, grain size, palynological, geochemical and preliminary micropalaeontological analyses were conducted.
Study site descriptionLake La Brava (37°52′S 57°59′W) is one of the few permanent freshwater shallow lakes. The lake is located in the northern area of the Tandilia range, a low-altitude mountain system of the Pampas plains (Figure 1). Lake La Brava is an elongated shallow lake (surface area: 4.5km2, ca. 4.8m maximum depth; 69m a.s.l.).The modern regional vegetation is grasslands with a shrubby edaphic-dominant community in the low-altitude ranges. The present-day local climate is humid-temperate, with a mean annual precipitation of 800mm; the area has a mean annual temperature of 13.3°C (INTA, 2008). S and SE winds predominate with an average speed of 20km/h, reaching gusts of 40−50km/h (Balcarce Municipality; www.balcarce.gob.ar).
The origin of the lake, like most lakes of the region, is a wind deflation basin (Dangvas, 2005) formed during the times when the creek El Peligro was dry or had a temporary regime. The basin was formed as consequence of deposition of deflationed sediment at the northern edges which formed the paleodunes closing the original depression. The basin of the lake has the higher slope to the west, near La Brava Hill, and an elongated depocentre (Figure 1) with two sub-basins with maximum depths of 4.8 and 3.5m (Lirio et al., 2007). The mean depth is 3.4 m and Secchi disk transparency of 1.4m (Quirós, 1988), these conditions are insufficient for a stable thermal profile, sufficiently deep to avoid light penetration to the bottom sediments and adequate to support photosynthesis of higher aquatic plants (Quirós, 2004).
Lake La Brava is in an advanced state of eutrophication with nitrogen/phosphorus ratios of 0.42 (Quirós et al., 2002) and is classified as bicarbonate-sodium oligohaline (INIDEP, 2001). This shallow lake has shown changes in the average water level during the last three decades, mainly through groundwater which is controlled by the variability of the precipitation (Kruse, 1987). For instance, between 2006 and 2008 the mean annual precipitation (MAP) oscillated between 685 and 785mm/yr; during 2009 the MAP dropped to 606mm/yr and in 2010 the MAP rose again up to 833mm/ yr (http://www.siia.gov.ar/). The lake level, from a mark made in the dock (Sup. Data 1) dropped 50 cm from 2006 to 2009 and rose 40 cm from 2009 to 2010 (Sanzano, P. personal communication).
Sporadically it overflows into the Tajamar stream (Kruse, 1987), and has a tributary creek, El Peligro, which develops a delta where abundant vegetation grows (Lirio et al., 2007). The lake plant community is characterised by aquatic plants (emergent, submerged and floating). In the deepest zones with medium to high lighting Myriophyllum elatinoides, Ludwigiarepens and Ceratophyllum demersum develop. At the lake margins and in sheltered habitats Azolla fliculoides, Potamogeton pectinatus, Ricciocarpus natans and Lemnasp. are present (Cordini, 1942; Romanelli, 2006). The dominant shore species is Schoenoplectus californicus (bulrush), accompanied by Typha latifolia (cattail) to the southward margin. The bulrush occupies an almost continuous belt along 63% of the lake shore. The belt width is variable between years and in different sectors, varying between 9 and 30m in 2006 (Romanelli, 2006) and between 20 and 130m in1942 (Cordini, 1942). This fringe is more extended at the end of the summer and occupies ca. 20% of the surface.
Materials and methodsField work and samplingA long core (Br4, Figure 1 and Table I) was collected with a push corer installed on a raft with a central hole in water depths of about 3.4m. The core sections were 2m long with a diameter of 6 cm, and were collected in PVC tubes. Once the core was brought to the surface, they were cut into 1m segments and split into halves by means of a nylon thread. The core was described, and subsampled with cubic plastic boxes of 8cm3 at intervals of 2.5 to 3cm, and weighed in an electronic balance, Acculab GS-200 (precision of 0.1g). A total of 204 subsamples were collected.
General information from core sampling and information derived from dating processes and age model from core Br4. The calibration ages were obtained with Oxcal 4.1 (Bronk Ramsey, 2008).
| Length [cm] | N° of samples obtained | Laboratory number | Depth from the top | Age 14C±s [yrs] | d13C | Calibrated years BP. ± s [yrs] |
| 551 | 204 | Br4/10 | 27.5cm | -- | -- | 50±20* |
| LTL595A - BRAVA20 | 54cm | 684±40 | -24.2±0.2 | 597±30 | ||
| AA81420 - LB 4-67 | 184cm | 1899±37 | -24.2 | 1753±49 | ||
| LTL594A - BRAVA114 | 305.5cm | 2579±50 | -28.8±0.2 | 2690±53 | ||
| AA81422 -LB 4-154 | 407.5cm | 3589±40 | -24.4 | 3757±54 | ||
| LTL596A - BRAVS200 | 539cm | 4124±65 | -30.4±0.4 | 4693±103 |
The following studies were carried out:
- *
for all the samples: volumetric magnetic susceptibility κ using a Bartington MS2 Susceptibility meter. Isothermal remanent magnetisation (IRM) in 24 increasing steps: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 800mT, 1 and 1.2 T, reaching saturation (SIRM); back-field, in growing steps until cancelling the magnetic remanence were measured. Associated parameters were calculated: S-ratio (IRM−300mT/SIRM) and coercivity of the remanence (BCR). Anhysteretic remanent magnetisation (ARM), with a direct field of 0.05mT and a peak alternating field of 100mT were determined. The inter-parametric ratios: ARM/ SIRM and SIRM/k were calculated. Remanent magnetisations were measured using a Minispin spinner fluxgate magnetometer Molspin Ltd.; a pulse magnetiser IM-10-30 AC Scientific was used for IRM experiments and an alternating field demagnetiser Molspin Ltd. with an ARM device was used for ARM acquisition., TS, TOCand TIC were measured by using a Leco elemental analyser. Analysis of the clay, silt and sand fractions were performed using Beckman Coulter LS 13 320 laser diffraction particle size analyzer. Prior to the analysis the organic matter was eliminated with H2O2 (10%) heated to 80°C and samples were disaggregated with sodium hexametaphosphate (40%), stirred for 2 hours and dispersed with ultrasound for a few minutes.
- *
For a group of selected samples: A set of 62 samples was selected to perform thermal demagnetisation of SIRM to obtain Curie temperatures (TC) of the different magnetic minerals present in the sediments. The selected samples correspond to highs or lows in the curves of concentration, mineralogy or magnetic grain size parameters. The samples were dried out in pyrex holders and consolidated with sodium silicate before the heating process in a Thermal SpecimenDemagnetiser, model TD-48 ASC Scientific. A good description of all magnetic measurements is shown in Chaparro, 2006 and Turner, 1997. The analysis of the total elemental composition was carried out after total acid digestion with HF (48%) in a microwave oven. A set of 42 samples was analysed for 17 elements: Li, K, Na (alkaline), Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba (light metals) and Cr, Cu, Mn, Fe, Al, Zn, Ni, Co, Cd and Pb (heavy metals). Analyses were performed by optic emission spectrometry using inductively coupled plasma (solid state detector). Concentrations were obtained after three measurements per element. Macroscopic sedimentological description was performed with a binocular magnifying glass. For pollen analyses, 66 subsamples were prepared with standard techniques (Faegri and Iversen, 1989). Pollen samples were mounted in jelly and counted using a Nikon H550S microscope at 1000x and 400x magnification. Pollen assemblages from lakeshore plants, aquatic macrophytes and introduced European taxa were selected from the total pollen. The two first were clustered on the assumption that distinctive zones of aquatic vegetation are associated with particular waterdepths. They were arranged from shore to inner of the lake as emergent (Cyperaceae, Typha, Eryngium and Ranunculus), submerged (Myriophyllum and Ceratophyllum leaf spines) and floating (Azollafiliculoides, Lemnaceae, Iridaceae and Elodea-type). Introduced pollen included exotic trees (Eucalyptus and Pinus) and ruderal weeds (Brassicaceae, Erodium, Carduus-type and Rumex). Pollen percentages were calculated on the sum of all pollen.
The grain size results of core Br4 are shown in figure 2. The presence of a few tephra levels situated between 83 and 86 cm indicate volcanic ash falls from the Andean volcanoes situated 700km westward to the Lake La Brava. Plant remains such as leaves and blades and charcoal lenses were also found (Lirio et al., 2007).
Logs of lithology, dated samples (cal. BP±σ, see Table I for details) and calibration curve according to Oxcal 4.1 (Bronk Ramsey C.; 2008) vs. depth. Gaps in the upper figure only indicate core breaks.
The grain-size composition is clearly dominated by silt, but subtle changes in clay and silt proportions allow the recognition of four intervals. The basal interval (548−370.5cm) is composed by clayed silt, with sporadic minor proportion of sand (<10%). From 370.5 and 186cm, clayed silt, and sporadic sandy silt levels has been observed. The third interval (171−43cm) is composed mainly by sandy silt with sporadic clayed silt, indicating an increase in the mean of grain size. The topmost 43cm of the core is composed by clayed silt and subordinated silty clay. Geochemical parameters do not show drastic changes or discontinuities between intervals. Subtle changes in lithology cannot be interpreted only as changes in the source area or in the input, because the lake basin is rather small and its morphology is relatively simple, covered by Late Pleistocene loess deposits reworked during the Late Holocene by eolian activity (Muhs and Zarate, 2001). Additionally, lake level is nowadays highly dependent on in situ rainfall and hydrological balance, and thus subtle changes in lithology can be mainly interpreted as changes in the lake level. High lake level is indicated by low mean grain size, whereas higher content of sand indicates fluvial facies migration to the lake center during predominantly relative dry phases.
ChronologyFive bulk sediment samples were dated by the14C-AMS dating technique (see Table I for details) and calibrated with SHCal04 (MacCormac et al., 2004). An age-depth model (Figure 2) was calculated with the Oxcal 4.1 calibration software (Bronk Ramsey, 2001; 2008). From pollen analysis the introduced taxa (Figure 3k) appear on the top ten samples. It is historically documented (BalcarceMunicipality, http://www.balcarce.gov.ar) that the onset of this impact began at the end of the nineteenth century with the arrival of the first colonists. For this reason the age assigned to sample 10 is 50cal. BP.
The basal age of this core is ca. 4800cal. BP. An average sedimentation rate of 1.3mm/ yr for core Br4 was obtained, with variations between 0.4 to 3.6mm/yr.
Rock magnetic analysisThe magnetic concentration parameters, κ(Figure 3a), ARM (Figure 3b) and SIRM (Figure 3c) show similar features, suggesting they are mainly controlled by the concentration of the magnetic minerals (Irurzun et al., 2009). Logs of κ, SIRM and ARM show an oscillatory behaviour around their mean values and have three maxima at 4100, 1000cal. BP and in the first 50cal. BP. There is another local maximum between 2600 and 2100cal. BP in the κ curve, less suggested in ARM and SIRM.
To investigate the magnetic mineralogy, parameters derived from IRM curves were analysed to identify soft/hard magnetic minerals. Stepwise acquisition of the isothermal remanence (Figure 4a) shows that 90% of the SIRM is acquired with applied fields of about 250mT. After progressive removal of SIRM by back-field demagnetisation, BCR mean values of 66±12mT were obtained. Values higher than 80mT (Figure 3g) suggest the presence of oxidised (titano) magnetite (Kruiver et al., 2001; Roberts and Turner, 1993; Reynolds et al., 1994) and/or antiferromagnetic minerals in low concentrations. A group of samples acquired 84% of the SIRM at 300mT (Figure 4a), also indicating the presence of a small proportion of antiferromagnetic minerals.
a) IRM acquisition curves of selected samples from the studied core. The grey dot is indicating the mean value obtained for BCR. b) SIRM/k vs. BCR. The regions on ellipses are the main sectors found by Peters & Dekkers (2003), most of the samples are located in the region for magnetite as main carrier. c) k vs. SIRM for all samples in order to estimate concentration and magnetic grain size according to Thompson & Oldfield (1986).
S-ratio (Figure 3f) exhibits an oscillatory behaviour around 0.82 from the bottom of the core to 100cal. BP, then abruptly changes to 0.9 and remains almost constant until the present. Soft minerals like magnetite have low BCR and high S-ratio. Minima/maxima of BCR correspond to maxima/minima of S-ratio, indicating that both parameters recorded the same trend in magnetic mineralogy. But the variations are more noticeable in BCR, suggesting that differences in mineralogy are better captured by coercivity. BCR shows its maxima at 4000, 2700 and 750cal. BP. SIRM/k vs. BCR (Peters and Dekkers, 2003) is plotted to discriminate magnetic mineralogy. Most samples have values in a region with characteristic magnetite and (titano) magnetite as dominant magnetic carrier.
Around 15% of the samples are out from that region which could be explained by the presence of a low content of hematite and/or greigite.
Assuming a magnetic mineralogy with predominance of soft minerals like magnetite is possible to use the figure (Figure 4c) of Thompson and Oldfield (1986) to estimate percentages per unit volume of magnetite in the samples and to distinguish between grain sizes. The percentage of magnetite varies between0.003 and 0.02% and the magnetic grain size observed is between 2 and 8µm. The results obtained suggest that magnetic grain sizes are in the range of pseudo single-domain (PSD) magnetite (Thompson and Oldfield, 1986) which is probably due to a mixture of different magnetic grain sizes. Only two samples are finer than 2µm and correspond to the BCR extreme values (Figure 3g) and one of them is in the region of greigite (Figure 4b).
Inter-parametric ratios (SIRM/k andARM/ SIRM, Figure 3d and 3e) generally increase with decreasing grain size and a higher proportion of single domain (SD) grains are present (Hunt et al., 1995; Turner, 1997). ARM is sensitive to fine ferromagnetic grains (0.02−0.1mm) and the ratioARM/SIRM is independent of paramagnetic and diamagnetic grains because only remanences are involved (Turner, 1997). On the other hand, k also involves paramagnetic and diamagnetic grains and the ratio SIRM/k is also used to point out the presence of greigite (Roberts et al., 2011). The ratios show oscillating values around their mean values, 2×10−2 for ARM/SIRM and 15 for SIRM/k. The general behaviour belongs to a mixture of different sizes in the period 5000−4300cal. BP and finer grain sizes between 3200−2400cal. BP and 300−50cal. BP. According to SIRM/k, the finest magnetic grain size is observed at 4700, 4060, 3200 and 2660cal. BP. But at 4700 and 4060cal. BP ARM/SIRM show low relative values suggesting an apparent increase in magnetic grain size. High BCR and S-ratio values between 0.77 and 0.87 suggest the presence of hard coercivity magnetic minerals for those samples. These results are in agreement with the results of Figure 4b for greigite. At 3200 and 2600cal. BP ARM/SIRM shows also high values indicating fine magnetic grain sizes.
Figure 5 shows the result of thermal demagnetisation curves of SIRM and the obtained TC. Sample 20 (Figure 5a) shows the behaviour of 85% of the samples. With two magnetic phases: a first magnetic phase with a characteristic temperature between 369 and 453°C. These temperatures correspond to the presence of (titano) magnetite with a low proportion of Ti (Dankers, 1978; Gogorza et al., 2004) or magnetite partially oxidised during the heating process (Dankers, 1978). The second phase is the principal magnetic phase, where more than 85% of remanence is lost at a mean value of TC3=572°C (Figure 5d), indicating that magnetite is the principal magnetic carrier (Dankers, 1978; Hunt et al., 1995; Dunlop and Özdemir, 1997; Irurzun et al., 2009). Another two phases are found. According to a review made by Roberts et al. (2011), the Curie temperature of greigite is not exactly found but greater than 350°C, but the shape of the heating curves shows an abrupt decrease between 290 and 320°C. TC1 between 266 and 342°C (Figure 5c) could correspond to greigite samples (Krs et al., 1992; Dekkers et al., 2000; Sagnotti et al., 2005). TC4 is found between 596 and 664°C which correspond tosamples with the presence of antiferromagnetic minerals (Dankers, 1978). 10% of the samples have the same behaviour as the sample 186 (Figure 5b), were TC2 and TC4 are present. The samples from core Br4 hold a percentage of their magnetization after 580°C indicating the presence of a mix of magnetite with haematite materials (TC=675°C). This percentage oscillates between 0.2% for samples like 20 (Figure 5a) and 6.8% for samples like 186 (Figure 5b). Figure 5d shows the Curie temperatures as a function of the ages. Several peaks were found in the intervals 4690−4060cal. BP and 2840−2070cal. BP. Greigite is suggested at 4700 and 4060cal. BP, consistent with high SIRM/k, high TOC and high TS (Figure 3). The high values of percentages of hematite were found at 4380, 2820 and 1290cal. BP.
a) Thermal demagnetisation curves of SIRM:a) Sample 20 (54cm, 597cal. BP). b) Sample 186 (491cm, 4412cal. BP). c) Sample 201 (542cm, 4704cal. BP). d) Curie temperatures vs. age. TC1 correspond to typical greigite temperatures, TC2 to typical titano-magnetite temperatures, TC3 to magnetite temperatures and TC4 to hematite temperatures. The zone between magnetite and hematite was denominated as mix of magnetite and hematite region.
The TOC record (Figure 3h) exhibits several fluctuations ranging between 1.2% and 23% and high values were determined between 4750 and 4450cal. BP. TOC and TS (Figure 3j) show a significant positive correlation (R=0.84) and minima values between 4000 and 3500cal. BP, 2600 and 2200cal. BP and from 200cal. BP, suggesting an organic origin for sulphur. TIC values (Figure 3i) range from 0 to 2.1%. Values lower than 1% are found between 4800 and 4200cal. BP, 2500 and 2100cal. BP and from 1500cal. BP, whereas maxima values were found at 4100,3800cal. BP, 3500cal. BP, 3250cal. BP and around 2700cal. BP.
Soft magnetic minerals are significant when TS has the lowest values. Around 4680 and 4510cal. BP the maxima values of TS are found, but not so significant changes are found in κ. At 4020cal. BP, κ has minima values consistent with TOC and TIC maxima values whereas TS is almost constant, indicating a low presence of any magnetic mineral. TOC logs display a general inverse behaviour to κ and S-ratio. TIC has an inverse relationship with κ in the period 400-4200cal. BP, but both parameters have an increasing trend from 4800 to 4200cal. BP and for the last 450cal. BP.
The more significant results from elemental analyses are shown in Figure 3n and 3o. These elements show an oscillatory behaviour around their mean values, except Zn and Ca. Fe, Al and κ show similar behaviour between each other. There are increases in heavy metals and K at 4200, 3600, 2200 and around 200cal. BP, which suggest a greater proportion of clay minerals at these ages (Abdul Aziz and Langereis, 2004), confirmed by grain size results. Ca, Mg and Sr show several coincident minima synchronized with high values of κ. There is a coincidence among the peaks of light metals, but Sr has less evident variations. The maxima in Ca coincide with maxima in TIC, suggesting that most of the inorganic carbon is in the form of calcium carbonate minerals. Low values of light metals coincide with high values of alkaline metals, pointing to the presence of eroded minerals from less-weathered depths in the catchment (Higgitt et al., 1991).
Pollen analysisLocal vegetation pollen record (Figure 3k, 3l and 3m) is dominated by emergent plants mostly characterized by Cyperaceae (Schoenoplectus), showing a general decreasing trend with a superimposed oscillating behaviour, with maxima at 347cal. BP, and a decrease to the present. Between 4780 and 4160cal. BP, emergent plants show fluctuating values from 20 to 60%. Floating plants (mainly Azollafiliculoides) are present along the record with values less than 3.7%, reaching two maxima, at 4780cal. BP (36%) and 990cal. BP (24%). Submerged plants (mainly Myriophyllum) have an increasing tendency between 4780 and 4370cal. BP, reaching the highest value (30%) at 4400cal. BP. Then, they decrease abruptly and present slight variations along the record. The last 50cal. BP shows the impact of humans on the vegetation of the Lake La Brava region; an increase of introduced European weeds (Rumex, Erodium and Carduus-type) represent the agriculture and grazing activities developed in the last decades of the 20th-century which have modified the landscape surroundings of the shallow lake. Eucalyptus and Pinus pollen are related to the establishment of exotic arboreal vegetation near the farmer settlements.
DiscussionLakes are “containers” of material coming from the atmosphere and the catchment area. A complete and continuous sediment sequence is indicated by not disturbed levels and it is reinforce by both the age-depth model as well as the smoothed total pollen concentration curve (Prieto, A.R. unpublished data) which indicate not significant change in the rate of sediment accumulation. Only a relatively higher rate of sedimentation occurs during anthropogenic settlement, probably due to larger external input of inorganic material into the lake owing to agricultural erosion.
The most frequently used parameter for lithostratigraphic correlation and preliminary palaeoclimatic assessment as rainfall indicator is κ (Maher and Thompson, 1999). When κ is high, higher concentration of magnetic minerals is expected. In this sense, lower TOC can be found because of a greater percentage of clastic influx during discharge into the lake owing to extreme flood events. Silt is almost constant in the sediments, so the opposite variation of clay and sand can be used as indicators of changes in the lake level as well. When the lake level is high, small particle size is expected in the centre of the lake (Nichols, 2009). If the lake level is low, then the shore is nearer of our coring site and coarser particles can be found. Inter-parametric ratios are used to determine periods of entrance of coarser or finer magnetic particles. As in the case of clay and sand, if high inter-parametric ratios (fine magnetic grain size) are found, then the shore is far from the coring site, indicating a high lake level or a wet period (Vazquez, 2012) and vice versa.
Another possible interpretation can be considered. Finer particles are easily transported by wind, whereas coarser particles need a more energetic transport way, like water, to reach the lake (Bagnold et al., 1979). If a high energetic environment could transport coarse particles, then low inter-parametric ratios should be found during rainfall periods. This is also argued by Lascu et al. (2012). For TOC interpretations, lower values of TOC can be found during periods of higher amount of minerogenic materials as a consequence of a dryer environment and a lower lake level than today.
The trends in pollen percentages of emergent macrophytes could reflect temporal movements of vegetation belts toward the shore and could be interpreted as a gradual relative rising of the level lake since 4800cal. BP. The spread of macrophytes towards the centre of the lake may result from a lake-level lowering, or the natural progressive infilling of the lake (Hannon and Gaillard, 1997).
The environmental interpretation of TIC is not so straightforward. TIC and Ca, Mg and Sr show positive correlation, and suggest that the TIC concentration reflects basically calcite occurrence. Assuming that TIC mainly represents calcite and given the relative low amount of calcareous fossils, most of the carbonates originate either from allochthonous sources or, more likely, are formed authigenically by precipitation (Shapley et al., 2005). As allochthonous source, El Peligro Creek is located at the highest sector of the basin, where quartzitic strata and quartzitic debris mixed with fine clastic sediments occur (Romanelli et al., 2010b). Since there is no carbonate outcrops in the basin, allochthonous sources of carbonates via surface influent El Peligro Creek can be dismissed. In fact, based on isotopic and geochemical data, El Peligro Creek can be considered as a “channeled” component of the groundwater (Romanelli et al., 2010b). The high contribution of spring water(Romanelli et al., 2011) indicates a direct and indirect wetland recharge via surface and subsurface runoff from the ranges, preferentially through the quartzite fracture system, and therefore they cannot be considered as a significant allochthonous source for carbonate or calcite ions to the lake water. Hence, in our model of authigenically carbonate origin, TIC minima imply a restriction of calcite precipitation, and TIC maxima imply favourable conditions of carbonate precipitation in the lake. In either case, the fluctuations in TIC indicate that Lake La Brava experienced significant environmental changes. Controls of authigenic carbonate burial include the rate of groundwater recharge, vegetation type, phytoproductivity and evaporation rate, which are in turn all linked to climate (Shapley et al., 2009). Except for the last 50cal. BP, no evident changes in regional vegetation have been detected; authigenic carbonate production may be supported by groundwater exchange (Shapley et al., 2005) or by evaporation acting on water body.
In La Brava Lake, the relation between the lake and the aquifer is well known. In this way, the effluent- influent behaviour of la Brava Lake has been defined (Kruse, 1987; Romanelli et al., 2010b). Mixing water estimation to identify the proportions in which recharge sources contribute to the lake water shows that 50.77% of it corresponds to groundwater (Romanelli et al., 2011). In turn, groundwater recharge function of the lake is of significant importance since it provides water to the aquifer system and contributes to the maintenance of phreatic levels (Romanelli et al., 2011). Isotopic and hydrochemical data indicate that the recharge to the aquifer is influenced by the natural rainfall input, wetland discharge and the concentration of surface run-off from the range fringes to inter-range depressions (Romanelli et al., 2011). Recharge areas coincide with the hills, with a magnesium- or calcium-bicarbonate water type and relative low pH and electrical conductivity values, in coincidence with the area of groundwater calcite undersaturation (Quiroz Londoño et al., 2008). Afterwards, as a consequence of evaporation and promoted by higher pH, water lake evolves to a sodium bicarbonate water type as a consequence of calcite precipitation which preferentially removes Ca+2 and Mg+2 in a softening process (magnesium and calcium exchange for sodium) (Romanelli et al., 2010a). Due to the shallowness of Lake La Brava its hydrology is highly dependent on in situ rainfall (Quirós et al., 2002). As aquifer system recharge depends solely on rainwater infiltration, when precipitation decreases, groundwater recharge diminishes, lake level drops and higher pH and evaporative concentration promoted calcite precipitation in the lake. In conclusion, assuming that major proportion of carbonates has authigenic origin, increase amount of flux of TIC (percentage of TIC divided by sedimentation rate) in the central lake basin sediments could reflect periods of low lake level and vice versa.
Relatively insoluble metals like Ca, Sr, Mg, Ba, among others; tend to accumulate in the sediment. In periods with dilute conditions (wetter and high lake level) these same metals remain in solution and do not precipitate (Davison, 1992). Dry periods may occur during high evaporation rates. Increasing concentration of TS in the water and consequent precipitation of the solid phase mean the water level must be low, corresponding with low rainfall (Hillesheim et al., 2005).
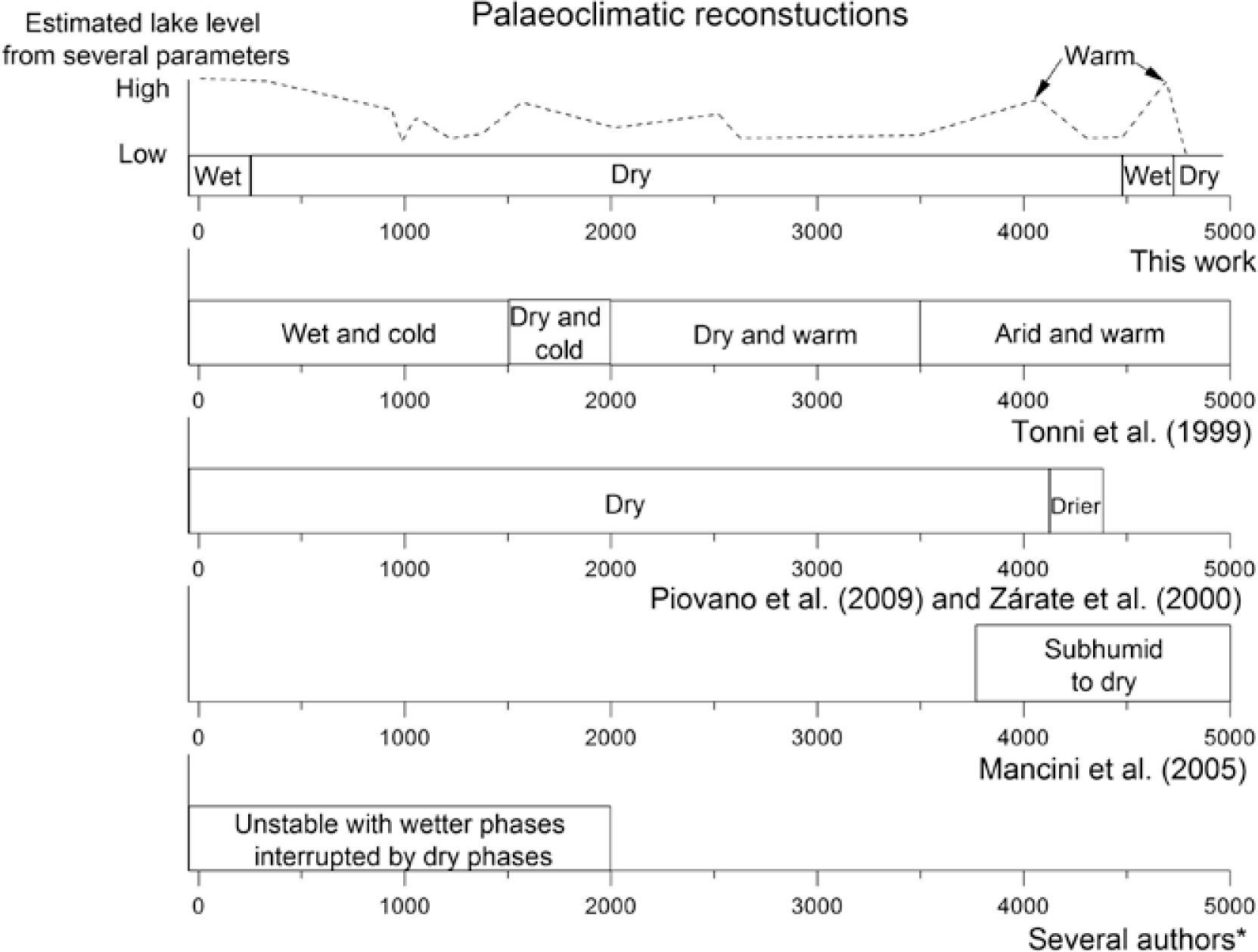
Lake level variations and palaeoclimatic implicationsThree intervals which integrate general behaviours can be considered. The first is estimated between 4800 and 4500cal. BP (and an event at 4060cal. BP), the second between 4500 and 260cal. BP and the third between 260cal. BP and the present.
Finer magnetic grain size particles according to inter-parametric ratios are found from 4800 to 4500cal. BP and at around 4060. Advances of marginal vegetation between ca. 4780 and 4160cal. BP are indicated by high percentages of emergent plants. Values up to 90% of Cyperaceae characterized the modern pollen data set from communities that represent flooded depressions and shallow lakes shores of the Pampa grasslands (Tonello and Prieto, 2008). Between 4700 and 4200cal. BP some low lake levels are indicated by the floating fern which floats at the water surface in sheltered habitats because it is vulnerable to the destructive effects of wave action. At 4780cal. BP, low values of TOC, moderate high κ and an extremely high percentage of floating fern were found indicating a very low lake levels or a dry event (Figure 6) in accordance with previous studies of Mancini et al. (2005)
Summary of palaeoclimatic reconstructions for the last 5000cal. BP in the Pampas Plain (other authors) and Lake La Brava (this work). All the ages are in calibrated years before present (cal. BP). * Cioccale (1999); Piovano et al. (2002); Stutz et al. (2002); Laprida et al. (2009a).
High percentages of clay and in consequence high lake levels are found at around 4650cal. BP. SIRM, κ and ARM have shown similar features, indicating that the signal of the magnetic parameters is dominated by changes in the concentration of magnetic minerals. The concentration parameters show opposite to TOC variations of less amplitude. Considering the aforementioned results, TOC variations at 4650cal. BP are variations related to a period of more rainfall and mild temperatures (Figure 6). Warm temperatures were found by Tonni et al. (1999).
In general terms, the similarities between κ, Fe, K and Al indicate very little or no diagenetic overprinting (Riedinger et al., 2005). At 4060cal. BP a change in mineralogy is suggested by differences between κ and Fe and Al (Figure 3a and 3o) indicating autochthonous elements are responsible for the magnetic signal. As a consequence, the formation of authigenic phases like greigite could be considered. Temperature experiments suggest greigite (Figure 5c and 5d) in samples with high SIRM/k values (Figure 3d and e). From 4800 to 4500cal. BP another two samples with greigite were found around 4700cal. BP. A high organic matter and a low oxygenated environment of the bottom lake sediments due to eutrophication during quiet sediment conditions could be the reason for an intense reductive dissolution of the original magnetic particles (Maher and Thompson, 1999, Geiss et al., 2003). Greigite can grow when dissolved iron and sulphide are available during diagenesis (Roberts et al., 2011) consistent with high TOC (Figure 3h) and high TS (Figure 3j). ARM/SIRM shows a relative decrease, suggesting coarser magnetic grain size in the greigite samples. So dissolution of the original magnetite to form greigite is possible (Geiss et al., 2004). According to Ariztegui and Dobson (1996) greigite is a well-defined palaeoenvironmental proxy as it is formed during a wet period in eutrophic lakes consistent with low flux of TIC. Pampean shallow lakes are not thermally stratified (Sosnovsky et al., 2010). Because of their shallowness, these lakes are strongly influenced by wind and are therefore polymictic (Rennella and Quirós, 2002, Miretzky et al., 2004). As a consequence, they lack chemical or thermal stratification (Quirós and Drago, 1999) and greigite cannot be formed unless there is a change in environmental conditions. In consequence, the greigite found may suggest particularly warm and wet times.
Greigite can preserve in sediments during a rapid sedimentation rate (Blanchet et al., 2009). A relative high sedimentation rate is found at the beginning of the record, from 1.3mm/yr in average to 3mm/yr at 4700cal. BP, which might allow greigite preservation. In summary, the presence of greigite in the base indicates higher than present lake levels consistent with low TIC and submerged plants (Figure 3i and 3m) during probably warm temperatures (high TOC). This short episode of a probably relative high lake level was not found by other authors.
From 4500 to 300cal. BP, ARM/SIRM varies in less than an order of magnitude indicating a broadly stable environment. Coarser magnetic grain size particles were found around 4350 and between 1040 and 960cal. BP. Low ARM/SIRM could suggest either low lake level because the shore is near, or high lake level because of increased rainfall. At around 4330 and 1000cal. BP, emergent pollen taxa are high indicating the climate conditions were humid and the lake level high. A contribution dominated by high energy sources, like fluvial sediment sources which reach the lake carrying coarse terrigenous elements from La Brava Hill and El Peligro Creek or strong winds can be considered. All these periods are consistent with relative high κ and low TIC, so it is more likely that the sediments were transported by fluvial sources. An unstable environment from 2000cal. BP to the present was found by Laprida et al (2009a).
The taxa of submerged plants are more abundant at the centre of the lake when the body of water is reduced, suggesting a shallower lake level at maxima values. The variations suggested through submerged and emergent plants are consistent with the behaviour of κ, indicating that this magnetic parameter is a good recorder of lake level changes. Between 4430 and 4250cal. BP, low TOC values suggest a dry environment in the catchment area of Lake La Brava. A low lake level suggested by submerged plants is found in this interval (4410–4370cal. BP), coeval with the presence of haematite. Haematite is a significant proxy of arid climate, because it forms during dry episodes and lower rainfall in the catchment area (Torrent et al., 2006). The presence of haematite in the samples was calculated as the remanent percentage of magnetization at 580°C in the thermal curves. The higher presence of different amount of haematite always precedes the wet periods (TC4 from Figure 5d are between 5 to 6.8 %) and can reach the lake during times dominated by aeolian transport. The presence of haematite suggests an overall dry climate from 4420 to 260cal. BP with episodic wet/rainy environment. Occasionally rain storm were also found by Stutz et al (2012) between 4840 and 1200cal. BP in a lake located 90km in the NE direction from Lake La Brava.
Meanwhile, from 3250 to 450cal. BP, TOC values indicate broadly minor variations on rainfall and climate. During this period, TOC variations decrease when k increases, indicating high clastic input from the catchment. Ca, Sr and Mg indicate wetter periods at around 4000, 2500 – 2000, 1500 and the last 260cal. BP, suggesting more humid conditions than in previous periods. High percentages of clay and in consequence high lake levels are found at around 4330 and between 4000 – 3530 and 2660 – 2170cal. BP. A mostly dry period was found between 3100 and 2600cal. BP, consistent with TS maxima, low κ and relative high ARM/SIRM. At 990cal. BP another dry event is suggested for the magnetic grain size, concentration dependent parameters and a peak in floating fern. A summary of all lake level and climatic changes and a comparison with previous results is shown in Figure 6.
Finer magnetic grain size particles according to inter-parametric ratios are found from 260cal. BP to the present, more noticeable in ARM/SIRM. κ is in an increasing trend region suggesting more erosion of unconsolidated material rich in magnetic minerals (Forester et al., 1994; Dearing and Flower, 1982; Thorndycraft et al., 1998) from the catchment area. Clay reaches the maximum indicating a low energy environment at the centre of the lake. The flux of TIC is very low suggesting a high lake level. In summary, the most likely environment is a quiet climate where the coast was far from the coring site indicating a high lake level. The highest lake level was found for the last 260cal. BP, consistent with the insoluble metals mentioned before. In summary, a high lake level, possibly flood episodes, and increased erosion are suggested in this period.
The last 50cal. BP show a decrease in organic matter content consistent with a decrease in emergent plants. The highest values of κ from 25cal. BP to the present are in agreement with the increasing trend of annual rainfall during the last eight decades (Irigoyen et al., 2008). The logs of S-ratio and κ show an increase as well, but this magnetic enhancement is noticeable from 100cal. BP to the present. This trend is similar to that reported for other lakes (Oldfield et al., 1978; Turner and Thompson, 1981; Zolitschka, 1998; Stockhausen and Zolitschka, 1999; Dearing et al., 2001; Rolph et al., 2004), suggesting changes in sediment delivery and depositional processes caused by human impact (agricultural activities implying different soil erosion). This trend is observed also in vegetation analysis with the appearance of different species (Morellón et al., 2009). The proxy's record for the last decades suggests a mix of natural climate shift and anthropogenic activities. Considering that the values of κ are never that high, is more likely that the human disturbance is primarily responsible for these changes.
ConclusionsThis study allowed us to obtain high-quality palaeoclimatic record for southeast Buenos Aires Province during the last 4800cal. BP. The results from pollen analysis and sedimentology indicate that the lake never dried during this period. BCR, SIRM/k and the combination of both are in the range of (titano) magnetite for most of the samples. The values of TC and SIRM acquisition curves are consistent with sediments dominated by (titano) magnetite with different amount of Ti as the dominant magnetic carrier of remanence but not the only one present in the samples. S-ratio has its mean value at 0.86, suggesting the presence of magnetite with different percentages of antiferromagnetic minerals. The main magnetic carrier is magnetite with grain size into the PSD range(Thompson and Oldfield, 1986). This grain size is probably a combination of MD with small size ferrimagnetic particles (Stockhausen and Zolitschka, 1999). The concentration of magnetite varies from 0.003 and 0.02%.
In combination with geochemical and palynological studies, κ and ARM/SIRM are the better magnetic proxies to infer precipitation; low values of both parameters are found during high lake level or more rainfall. The general trend for all parameters indicates an overall dry environment since 4800cal. BP. Based on magnetic and geochemical studies, a model for palaeoclimatic implications show some flood or high lake level events at 4700, 4060 and 1500cal. BP and a period of high lake level from 2500 to 2100cal. BP were found. Two moments of extremely dry environment were found at 4780 and 990cal. BP.
All the results suggest that climate was the major forcing process of regional fluvial system behaviour (erosion and lake level changes) across the catchment area of Lake La Brava from 4800cal. BP until the beginning of stable human settlement. It was established that anthropogenic influence is the main factor of the changes observed during the twentieth century over imposed to a more humid environment.
The authors wish to thank UNCPBA, IAA and CONICET. They are also grateful for funds provided by the CICYT project MEDEROCAR (CGL2008-0831), PIP-CONICET 1265/08 and the project PICT-O n0 13-11502. The authors wish to thanks Dr.C. Geiss for the comments and suggestions and to the anonymous reviewers for their comments which improve the paper.