Students’ dietary habits are moving from Mediterranean diet guidelines towards unhealthy eating patterns. The aim of this study was to determine adherence to the Mediterranean diet in a sample of Spanish university students and its association with lifestyle factors.
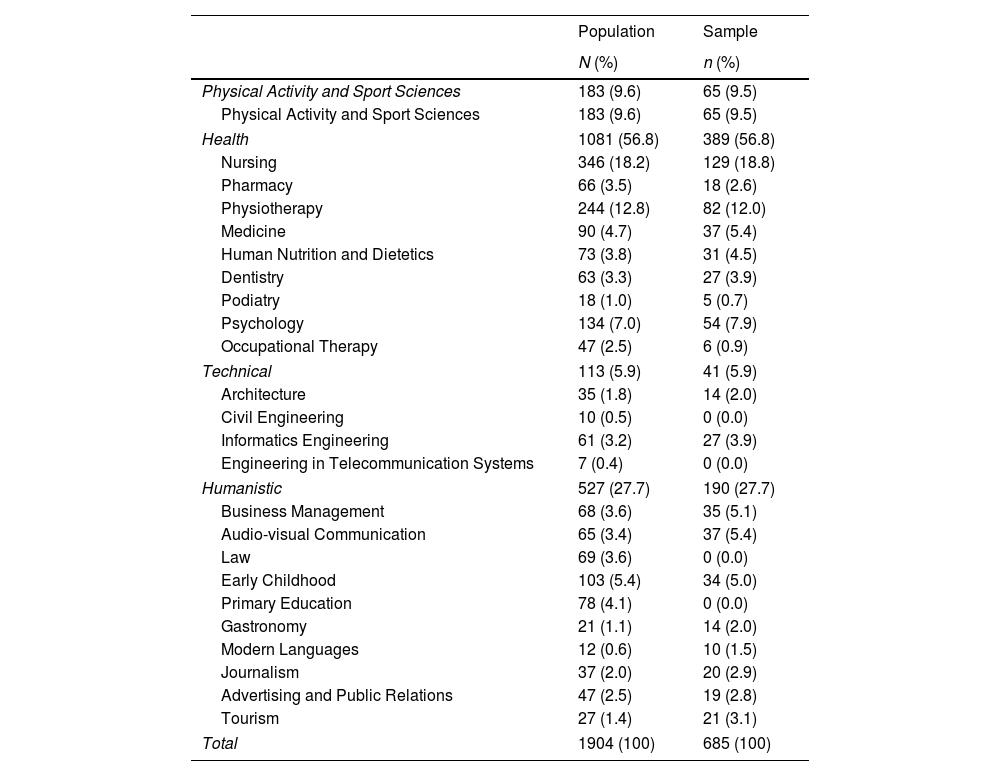
Material and methodsA descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted with 685 university students who completed a self-report questionnaire. The data collected included demographic characteristics, dietary habits, smoking habits, alcohol consumption and physical activity. Mediterranean diet adherence was assessed by measuring the consumption of the foods that compose this type of diet through a score (range 0–10). Adherence to the Mediterranean diet was considered poor, average, or good.
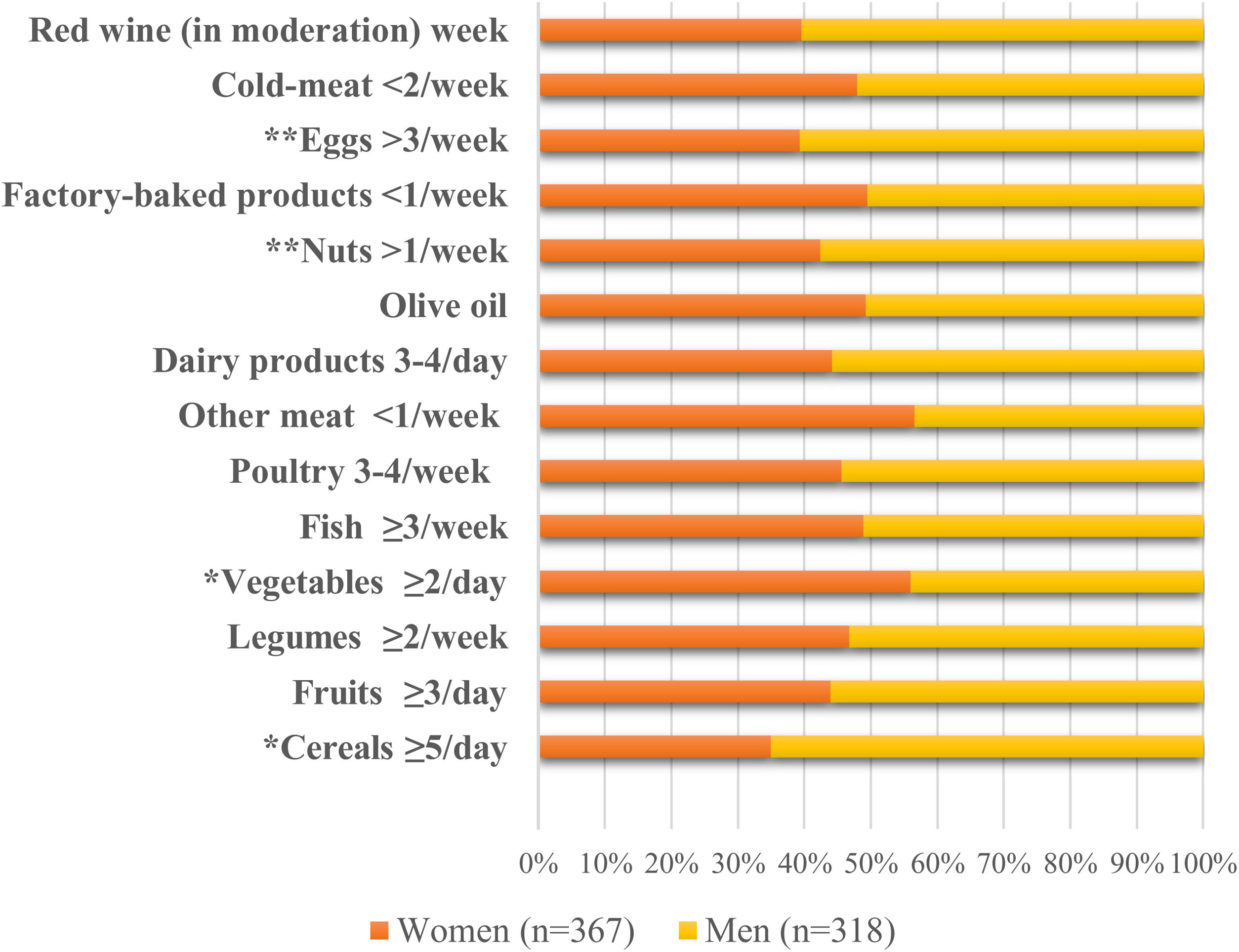
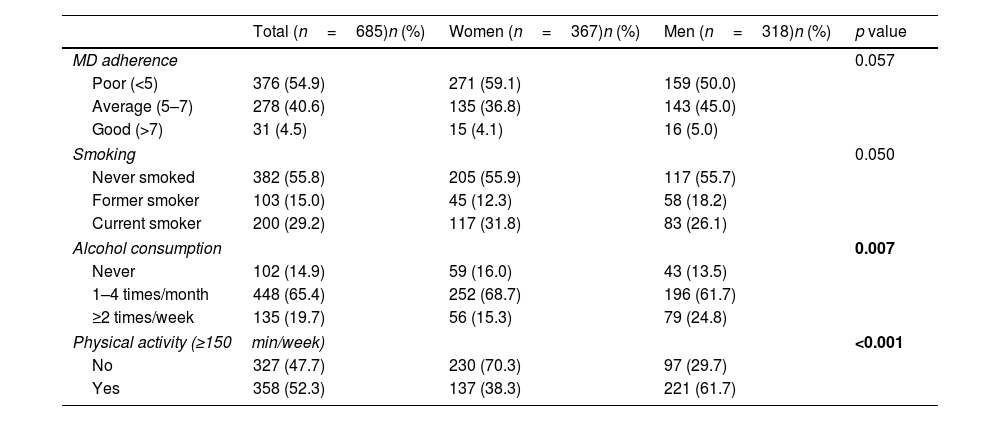
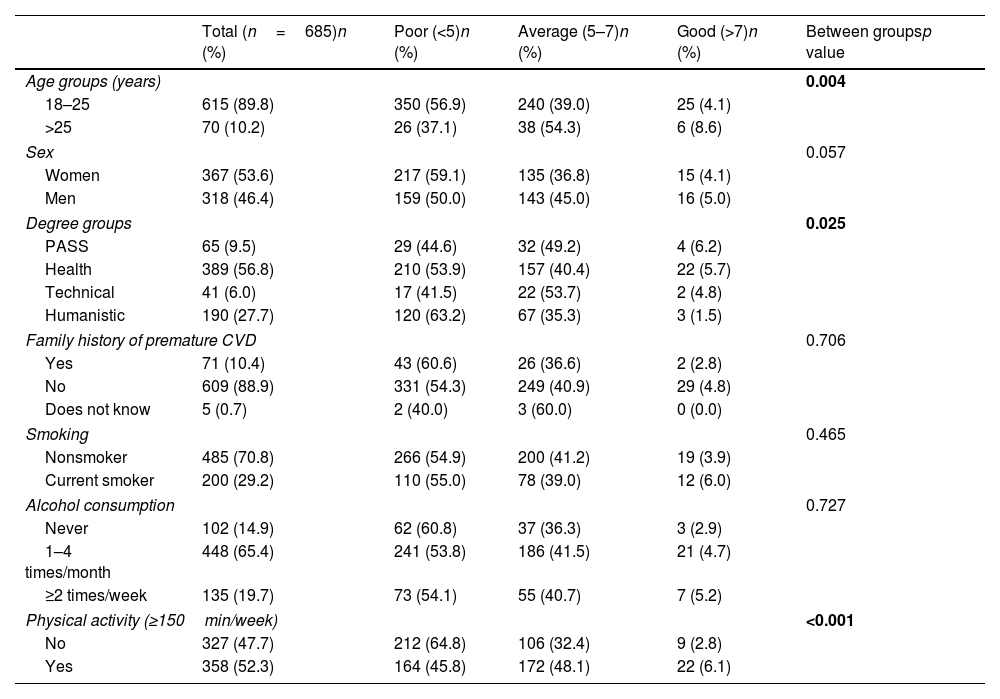
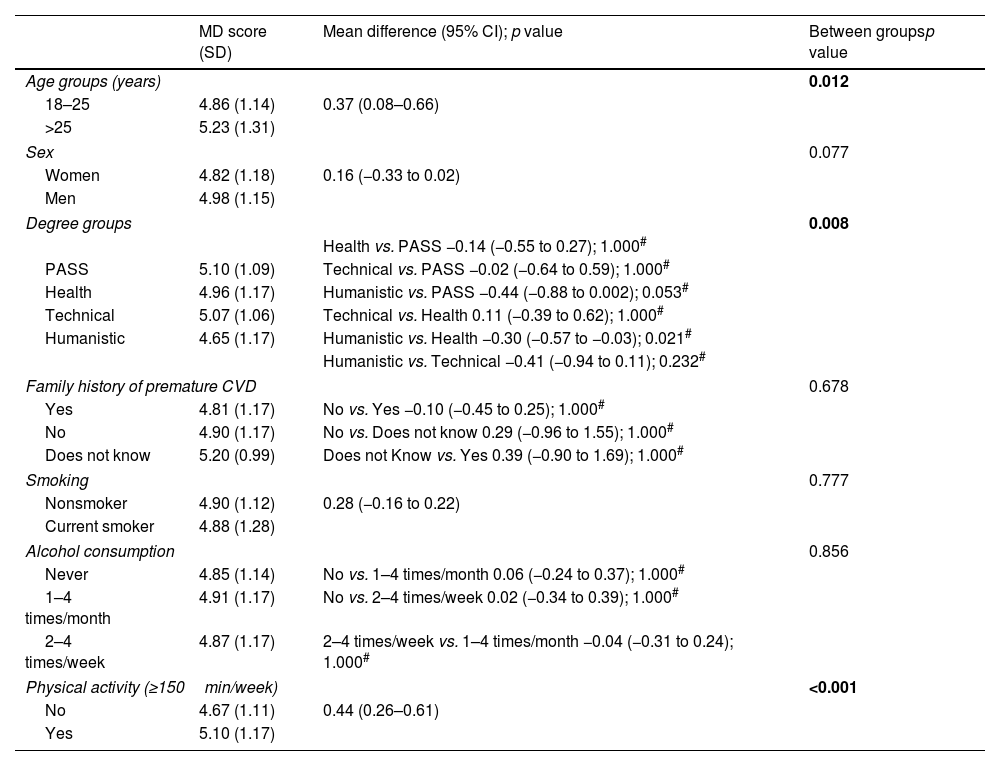
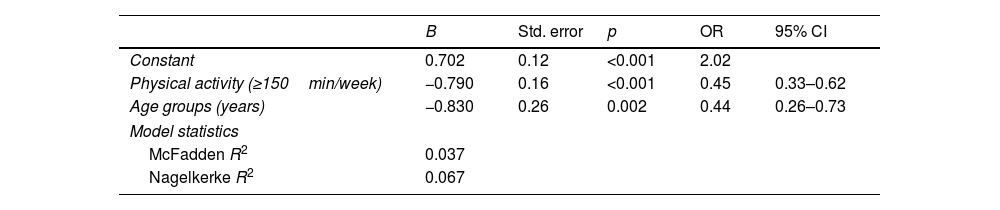
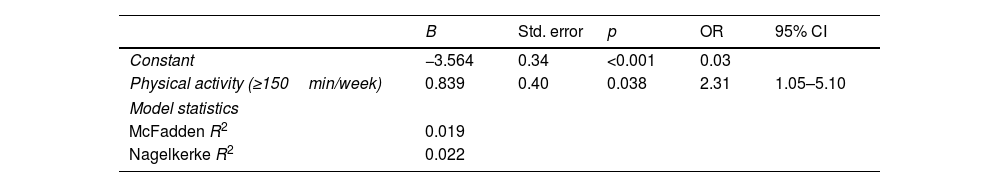
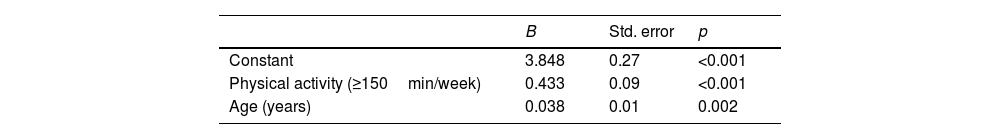
ResultsThe mean adherence score for the Mediterranean diet was 4.9 (1.2) points out of 10. A higher degree of adherence to the Mediterranean diet was observed in physically active students (OR=2.31, 95% CI: 1.05–5.10; p=0.038). Students who performed ≥150min/week of physical activity (OR=0.45, 95% CI: 0.33–0.62; p<0.001) and those over 25 years old (OR=0.44, 95% CI: 0.26–0.73; p=0.002) were less prone to low adherence to the Mediterranean diet than sedentary and younger students.
ConclusionThe university students have poor adherence to the Mediterranean diet. The results of the current study indicate that age and physical activity are associated with Mediterranean diet adherence. It is urgent to raise awareness among university students and implement intervention programmes promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Los hábitos alimentarios de los estudiantes universitarios se están alejando de las pautas de la dieta mediterránea hacia patrones de alimentación poco saludables. El objetivo de este estudio fue determinar la adherencia a la dieta mediterránea en una muestra de estudiantes universitarios españoles y su asociación con factores del estilo de vida.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio descriptivo transversal con 685 universitarios que cumplimentaron un cuestionario autoinformado. Los datos recogidos incluyeron características demográficas, hábitos alimentarios, hábito tabáquico, consumo de alcohol y actividad física. La adherencia a la dieta mediterránea fue evaluada midiendo el consumo de alimentos que componen este tipo de dieta a través de una escala (rango 0-10). La adherencia a la dieta mediterránea se consideró pobre, media y buena.
ResultadosLa puntuación media de adherencia a la dieta mediterránea fue de 4,9 (1,2) puntos de 10. Se observó un mayor grado de adherencia a esta dieta en los estudiantes físicamente activos (OR=2,31; IC95%: 1,05-5,10; p=0,038). Los estudiantes que realizaban ≥150min/semana de actividad física (OR=0,45; IC95%: 0,33-0,62; p<0,001) y los mayores de 25 años (OR=0,44; IC95%: 0,26-0,73; p=0,002) fueron menos propensos a una baja adherencia a la dieta mediterránea que los estudiantes sedentarios y los más jóvenes.
ConclusiónLos estudiantes universitarios tienen una pobre adherencia a la dieta mediterránea. Los resultados del presente estudio indican que la edad y la actividad física están asociadas con la adherencia a la dieta mediterránea. Es urgente concienciar a los universitarios e implementar programas de intervención que promuevan un estilo de vida saludable.