Non-adherence to antihypertensive medication is a key factor contributing to uncontrolled blood pressure and the subsequent complications of hypertension. Despite its importance, there is a lack of data regarding the prevalence of and factors associated with non-adherence to medication among individuals with hypertension in India. This review aimed to assess medication adherence rates among hypertensive patients in India and identify the factors influencing non-adherence.
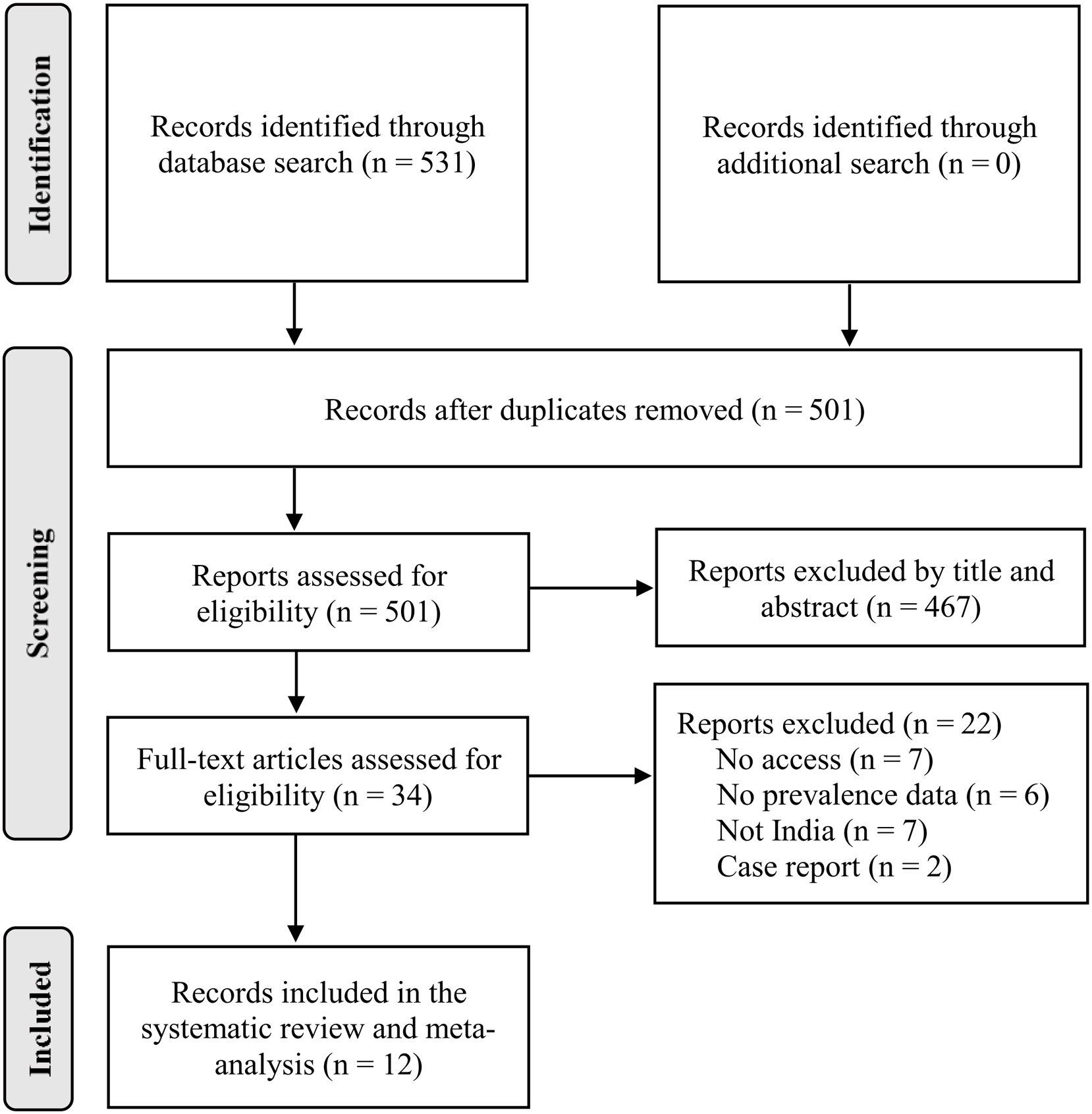
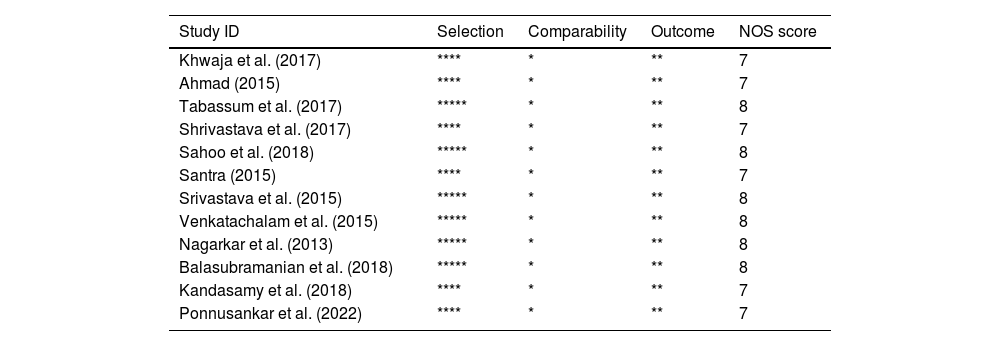
MethodsA comprehensive search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar. Studies reporting medication adherence/non-adherence to antihypertensive medications in India, using the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS), with publication dates up to July 2023, were included.
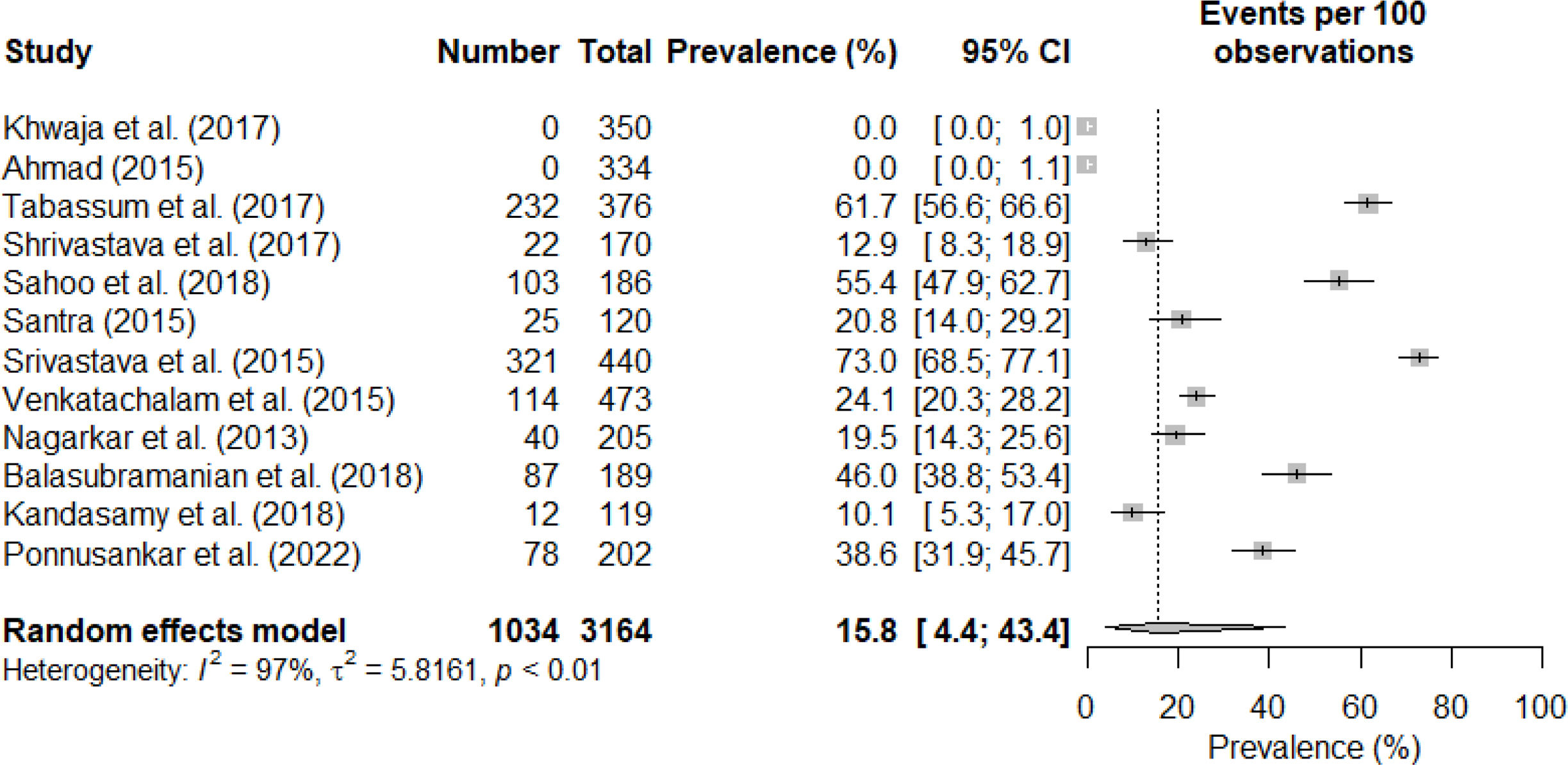
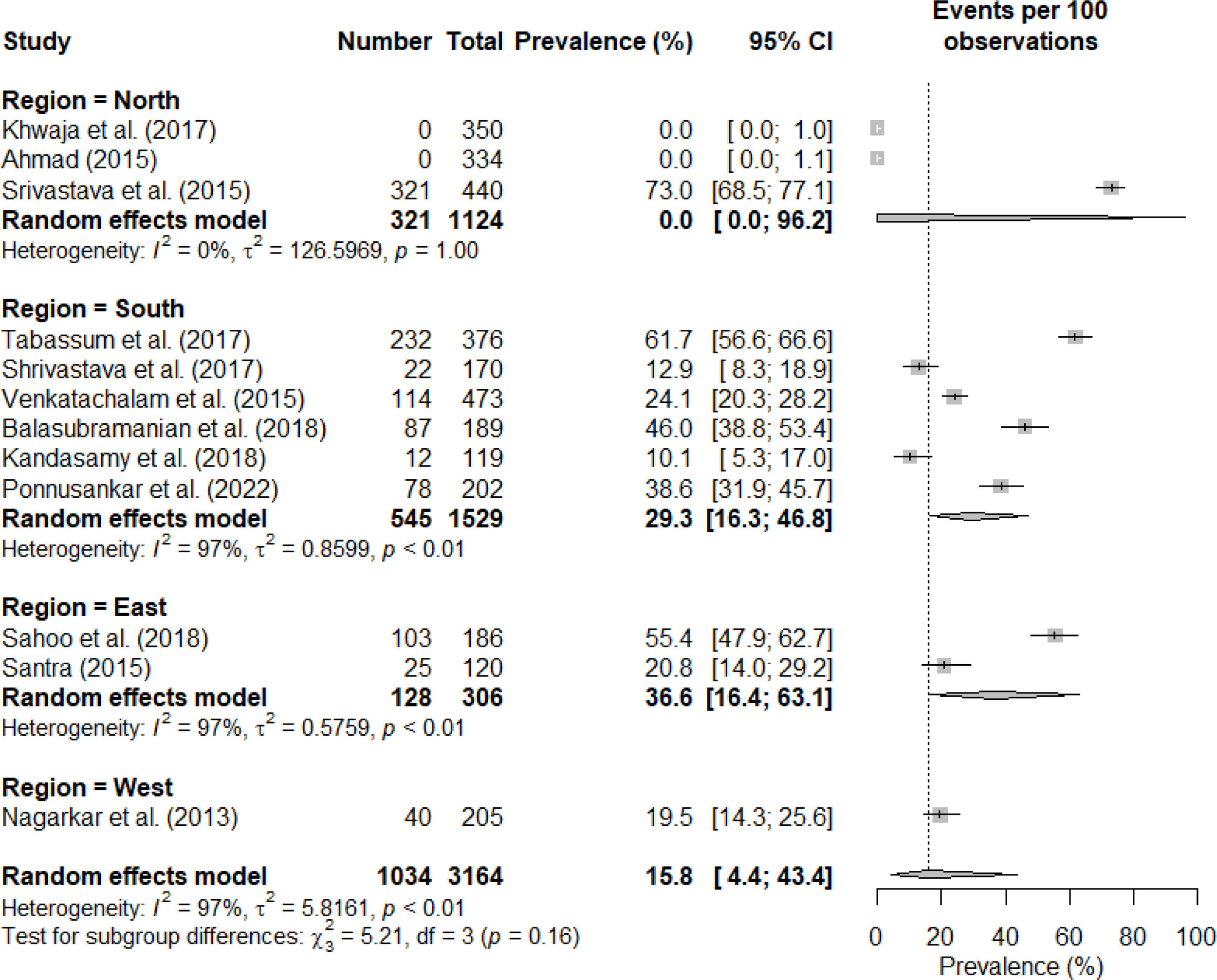
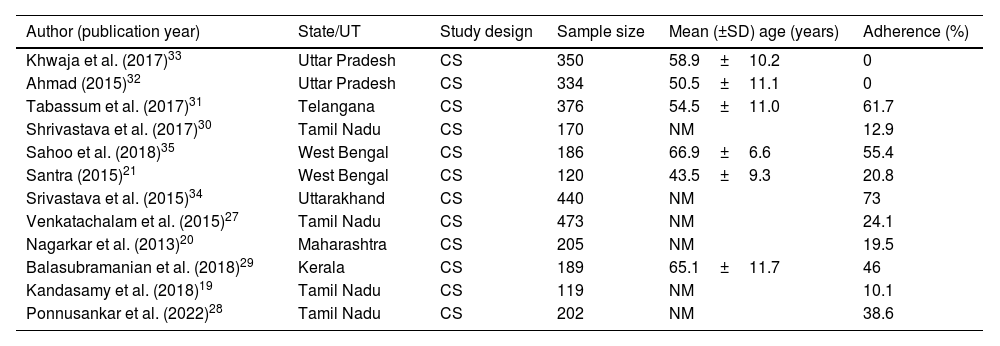
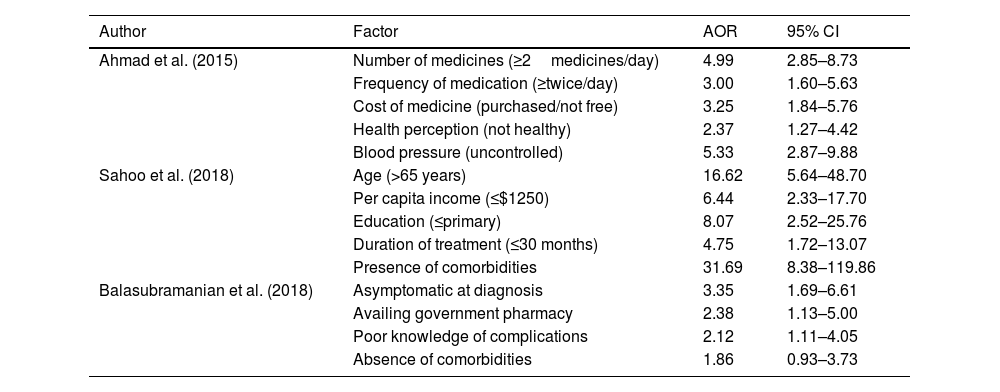
ResultsTwelve studies were included, involving a total of 3164 participants. The pooled rate of medication adherence to antihypertensive medications in India was determined to be 15.8% (95% CI: 4.4; 43.4). The important factors associated with non-adherence included higher age, medication regimen complexity, low socioeconomic status, low education levels, uncontrolled blood pressure, and comorbidities.
ConclusionsThe adherence rate to antihypertensive medication was observed to be quite low. Therefore, it is imperative to enhance the rate of medication adherence among individuals with hypertension in order to attain effective blood pressure control and reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases.
La falta de adherencia a la medicación antihipertensiva es un factor clave que contribuye a la presión arterial descontrolada y las complicaciones posteriores de la hipertensión. A pesar de su importancia, hay una falta de datos sobre la prevalencia y los factores asociados con la falta de adherencia a la medicación entre las personas con hipertensión en la India. Esta revisión tuvo como objetivo evaluar las tasas de adherencia a la medicación entre los pacientes hipertensos en la India e identificar los factores que influyen en la falta de adherencia.
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda exhaustiva en PubMed, Scopus, Embase y Google Scholar. Se incluyeron estudios que informaban sobre la adherencia/no adherencia a la medicación antihipertensiva en la India, utilizando la Escala de adherencia a la medicación de Morisky (MMAS), con fechas de publicación hasta julio de 2023.
ResultadosSe incluyeron doce estudios, con un total de 3164 participantes. Se determinó que la tasa combinada de adherencia a la medicación antihipertensiva en la India era del 15,8% (IC del 95%: 4,4; 43,4). Entre los factores importantes asociados con la falta de adherencia se encuentran la edad avanzada, la complejidad del régimen de medicación, el bajo nivel socioeconómico, los bajos niveles de educación, la presión arterial no controlada y las comorbilidades.
ConclusionesSe observó que la tasa de adherencia a la medicación antihipertensiva era bastante baja. Por lo tanto, es imperativo mejorar la tasa de adherencia a la medicación entre las personas con hipertensión para lograr un control eficaz de la presión arterial y reducir la carga de enfermedades no transmisibles.