Analizar los datos, según lugar de reclutamiento y sexo, de la encuesta (May Measure Month) en 2018 (MMM18) en España, promovida por la International Society of Hypertension.
MétodosSe estudiaron sujetos ≥ 18 años. Se realizó protocolo MMM18. Los sujetos fueron reclutados desde la Sociedad Española de Farmacia Comunitaria (SEFAC) y la Sociedad Española de Hipertensión (SEH-LELHA). Se realizaron modelos lineales generalizados de la presión arterial (PA), en sujetos con y sin tratamiento, y ajustados por edad, sexo, tabaquismo, obesidad y lugar de reclutamiento.
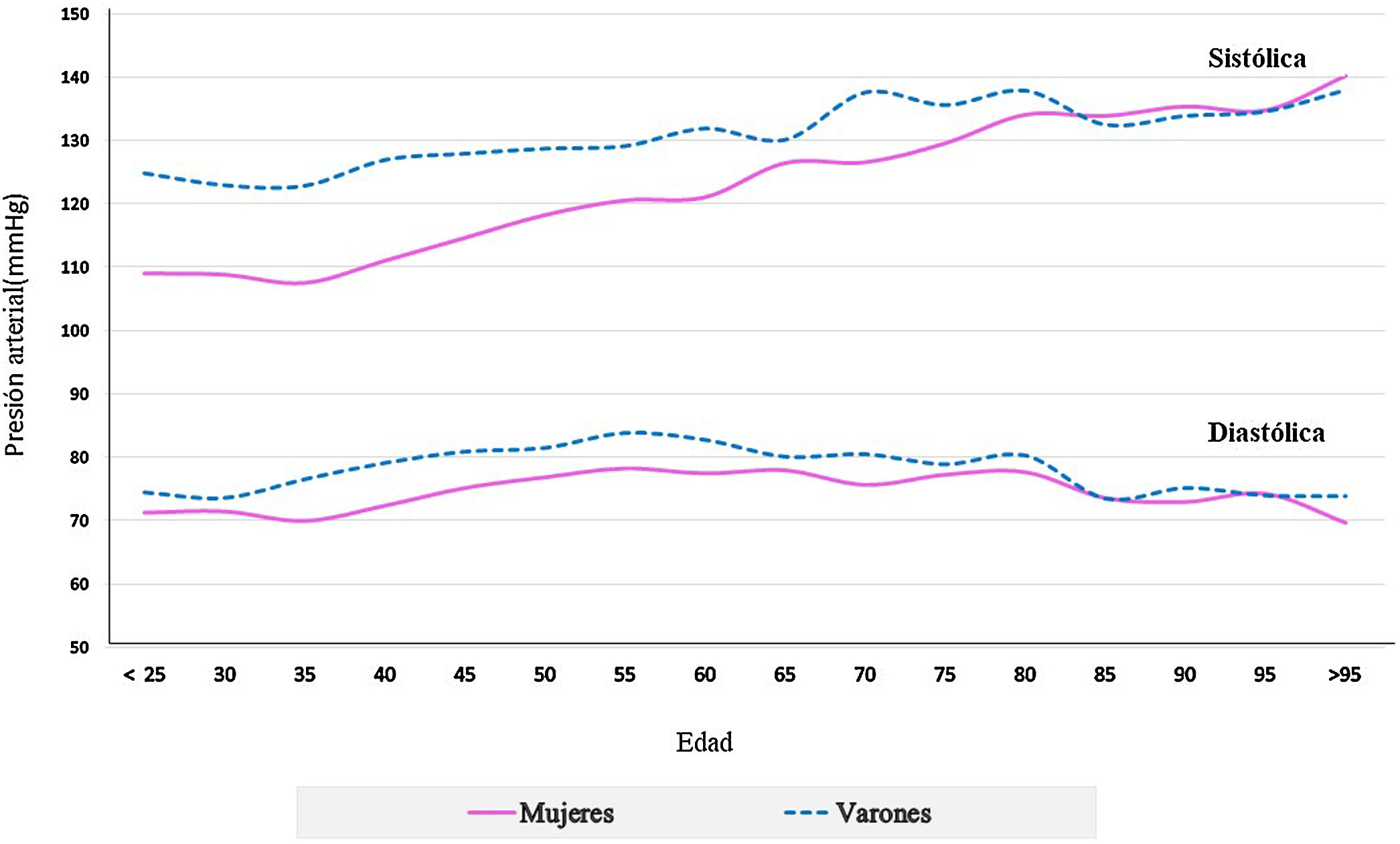
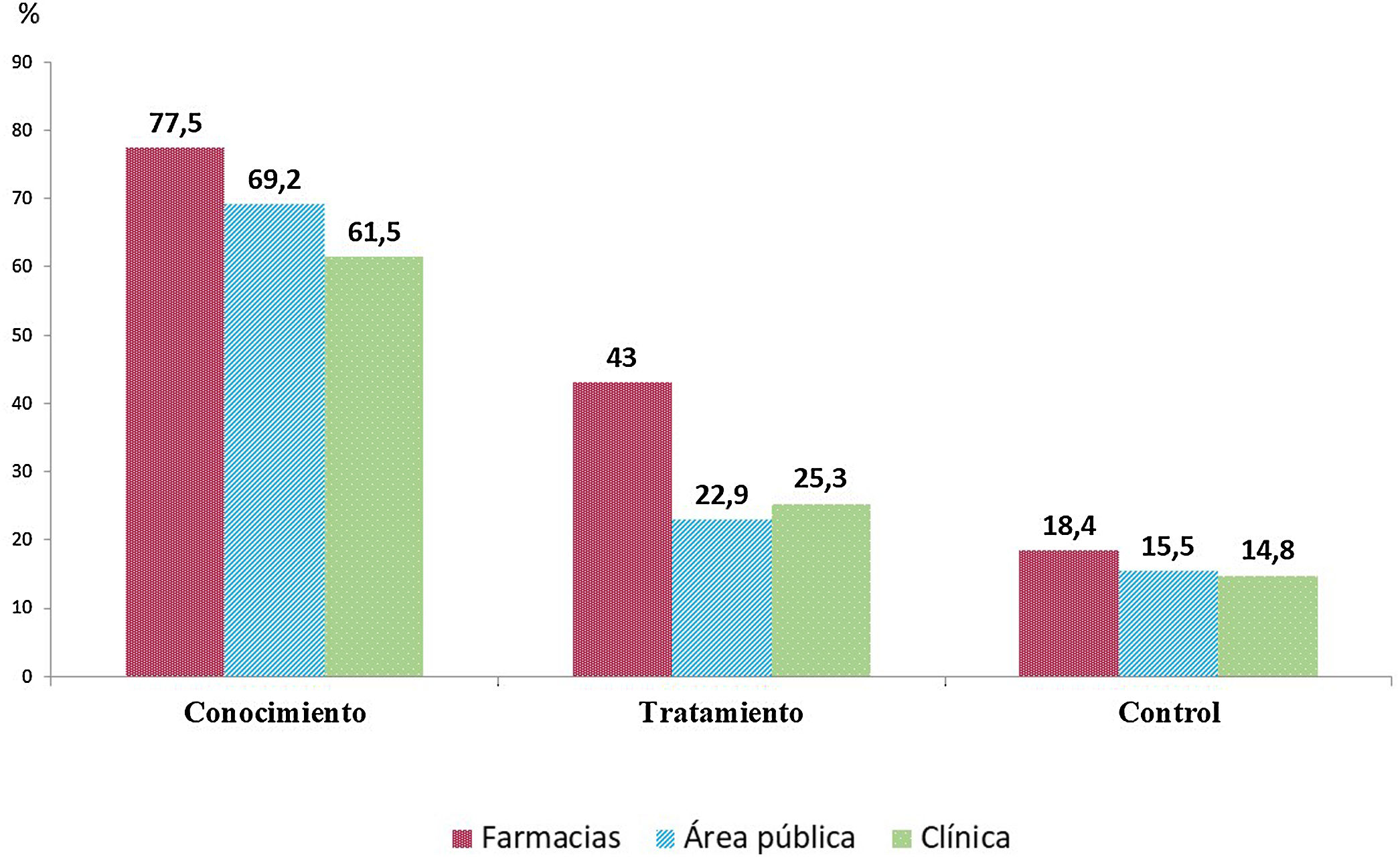
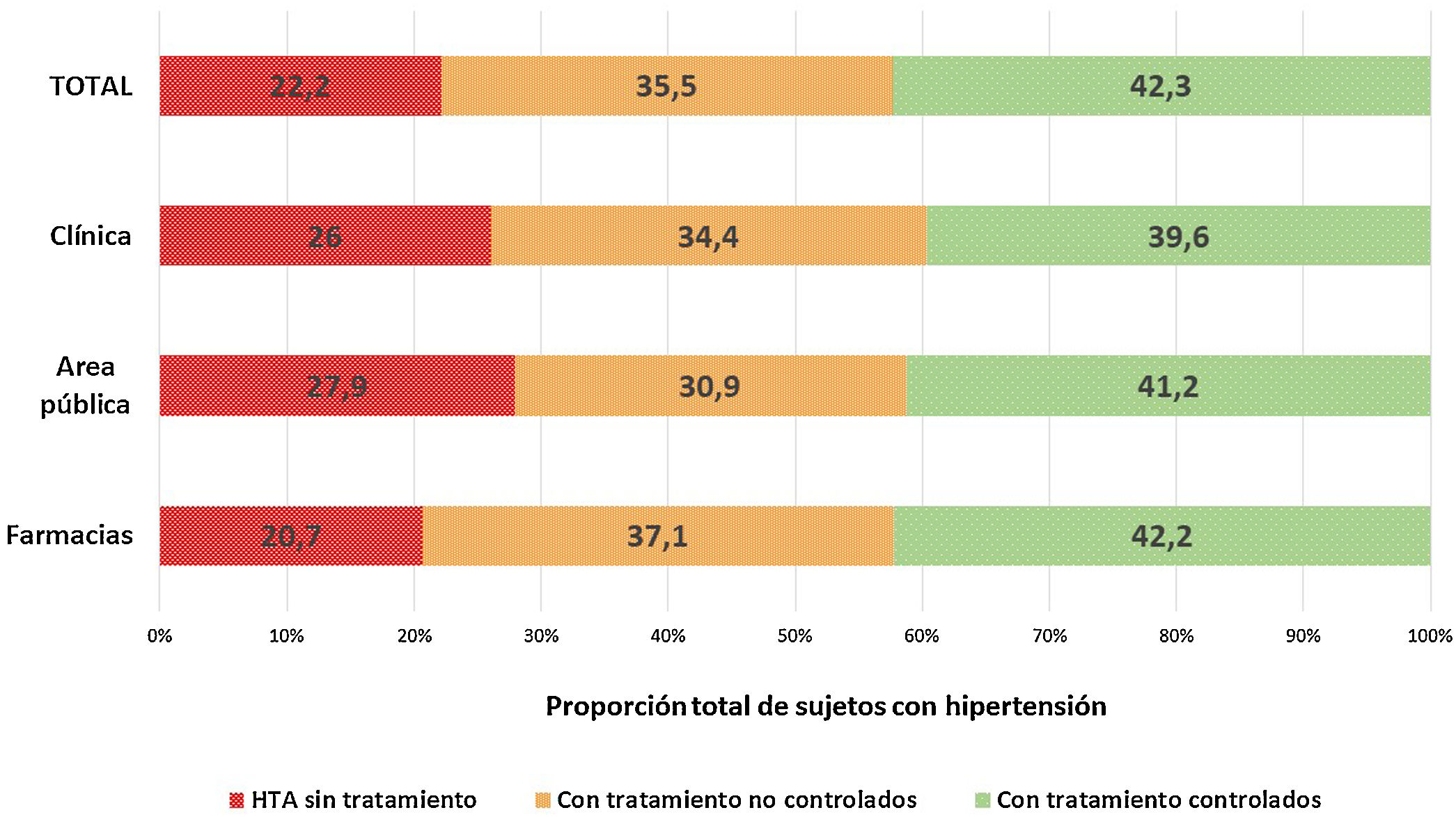
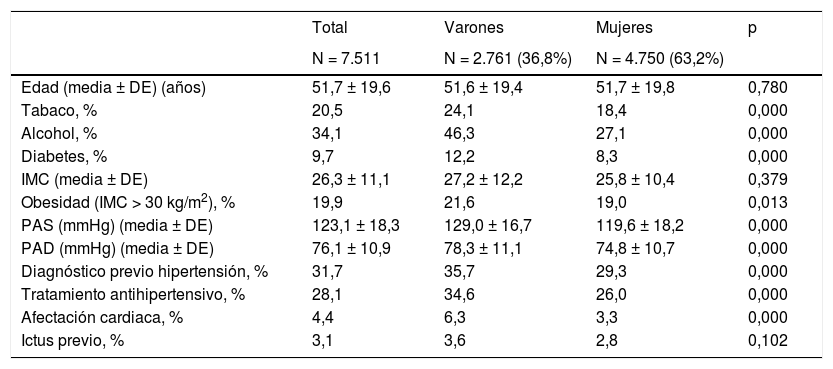
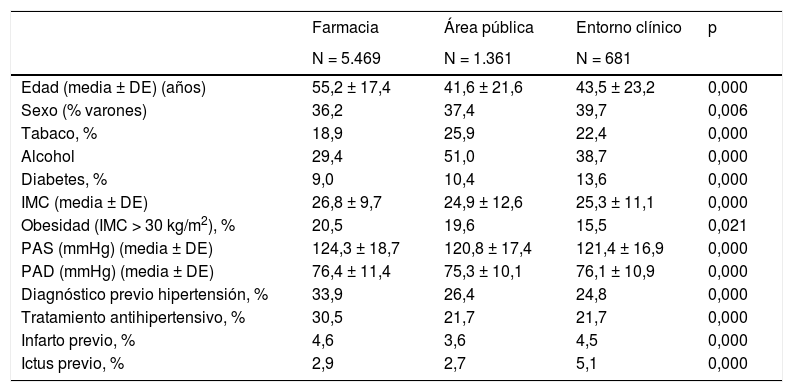
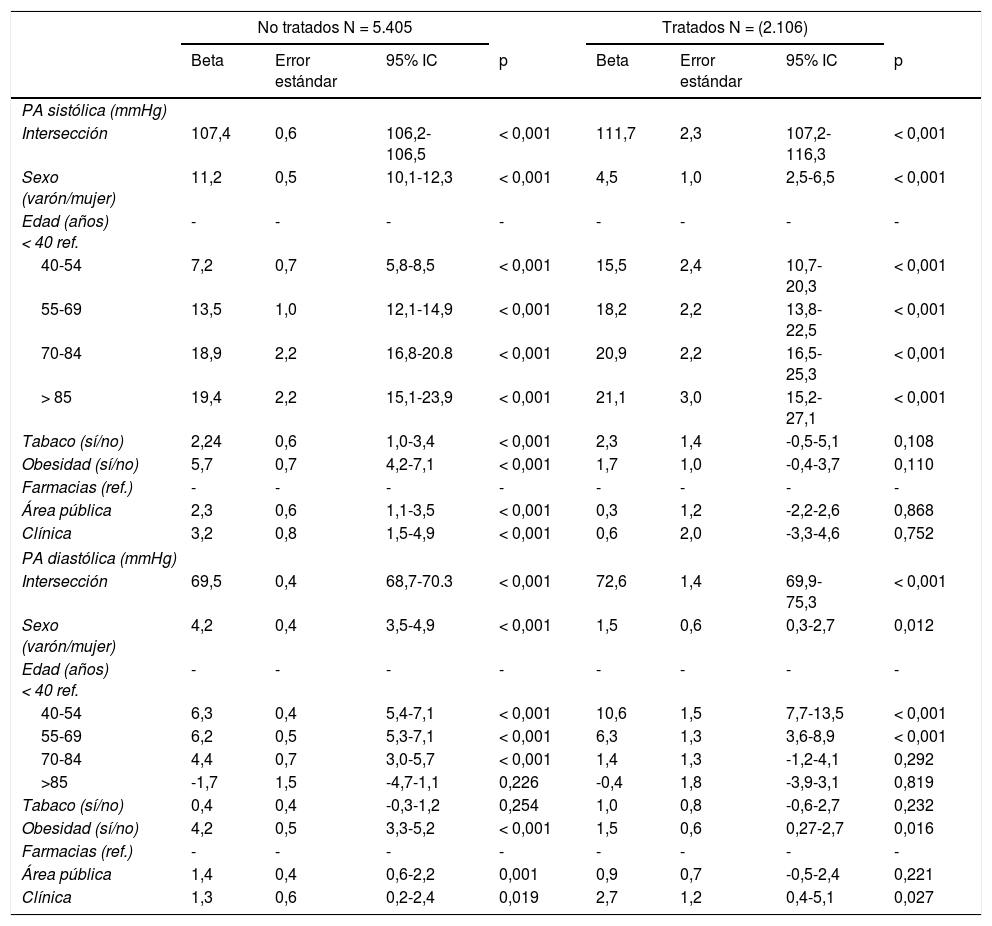
ResultadosSe analizaron 7.511 sujetos (edad media 51,7 ± 19,6 años, 36,8% varones). Las PA sistólica y diastólica fue más elevada en varones (129,0 ± 16,7/119,6 ± 18,2 mmHg) (78,3 ± 11,1/74,8 ± 10,7 mmHg) (p < 0,001). Hubo relación lineal entre PA sistólica, edad y sexo, con valores mayores en varones (11,2 mmHg en no tratados y 4,5 mmHg en tratados) (p < 0,001). La PA diastólica tenía distribución en U invertida, con cifras más elevadas en varones entre 50-55 años. La proporción de sujetos con hipertensión (farmacias; área publica y clínica) fue 47,2% (54,2; 34,1 y 34,8%). El 75% eran hipertensos conocidos (77,5; 61,5 y 69,2%), estando el 22% de los mismos sin tratamiento farmacológico (20,7; 26,0 y 27,9%). El 64,5% de los tratados cumplían objetivos (62,9; 65,6 y 69,1%) (p < 0,001).
ConclusionesHay amplio margen de mejora en los indicadores del MMM en España. Casi la mitad de sujetos son hipertensos, uno de cada cinco de los conocidos no seguían tratamiento farmacológico y, de los tratados, uno de cada tres no cumplían objetivos. Las cifras de PA son significativamente mayores en varones. Nuestro estudio sugiere que los umbrales de PA deberían contemplar las diferencias de género descritas.
To analyse the data, according to recruiting place and sex, of the survey May Measure Month in 2018 (MMM18) in Spain, promoted by the International Society of Hypertension.
MethodsSubjects more than 18 years old were studied. MMM18 protocol was performed. Volunteers were recruited through the Spanish Society of Community Pharmacy (SEFAC) and the Spanish Society of Hypertension (SEH-LELHA). General linear models of blood pressure (BP) were carried out in subjects with and without treatment, and adjusted by age, sex, tobacco use, obesity and recruitment site.
Results7 511 individuals (mean age 51.7 ± 19.6 years, 36.8% males) were screened. Systolic and diastolic BP was higher in males (129.0-16.7/119.6-18.2 mmHg) (78.3-11.1/74.8-10.7 mmHg) (p < 0.001). There was a linear relationship between systolic BP, age and sex, with higher values in males (11.2 mmHg in untreated and 4.5 mmHg in treated) (p < 0.001). Diastolic BP was inverted U-shaped, with highest level in males and between 50-55 years. The proportion of individuals with hypertension (pharmacies; public and clinical area) was 47.2% (54.2; 34.1 and 34.8%). Seventy-five percent were aware of their diagnosis (77.5; 61.5 and 69.2%), with 22% of them without pharmacological treatment (20.7; 26.0 and 27.9%). Sixty-four point five percent of those under antihypertensive treatment met targets (62.9; 65.6 and 69.1%) (p < 0.001).
ConclusionsThere is big room for improvement in MMM indicators in Spain. Nearly half of subjects are hypertensive. Of those aware of their condition, 1 in 5 did not follow pharmacological treatment and of those treated, 1 in 3 did not meet targets. BP levels were significantly higher in males. Our study suggests that gender differences described should be considered in the BP thresholds established.