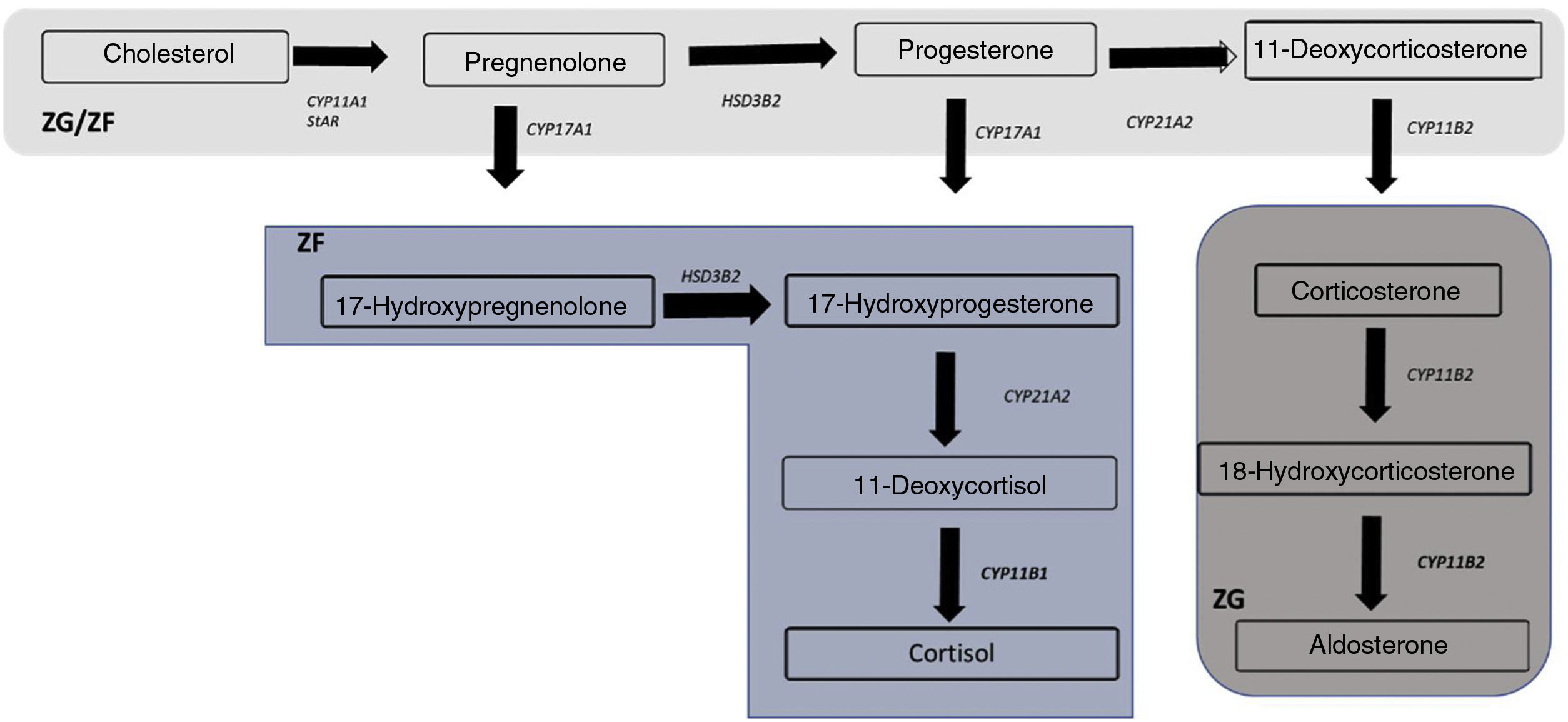
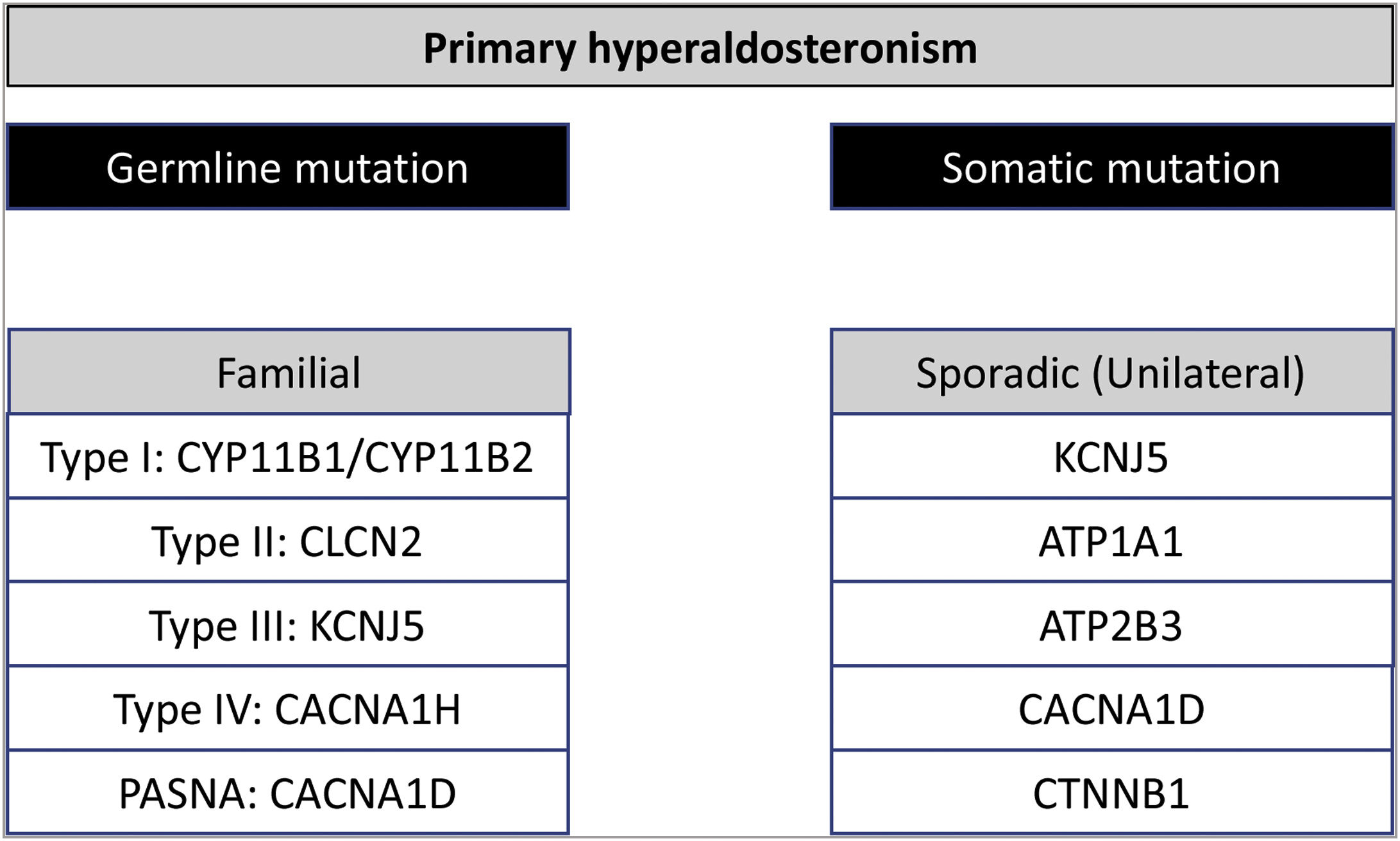
Primary hyperaldosteronism (PAH) is the most frequent cause of secondary arterial hypertension. Most PAHs occur sporadically, but 5% of cases have a hereditary origin (familial PAH). Four forms of familial PAH have been described. Type I familial PAH is produced by a fusion of the CYP11B2 and CYP11B1 genes, in this way the synthesis of aldosterone becomes to be regulated by ACTH instead of by angiotensin II. In type II, III and IV familial PAH there is an increase in the transcription and expression of CYP11B2 responsible for aldosterone synthesis due to a germinal mutation in CLCN2, KCNJ5 and CACNA1H, respectively. On the other hand, somatic mutations have been identified in 50% of sporadic PAHs, with gain-of-function mutations at the level of KCNJ5, ATP1A1, ATP2B3 and CACNA1D being the most common. This review provides a detailed description of the different forms of familial PAH and the molecular profile of patients with sporadic PAH.
El hiperaldosteronismo primario (HAP) es la causa más frecuente de hipertensión arterial secundaria. La mayor parte de los HAP ocurren de forma esporádica, pero un 5% de los casos tienen un origen hereditario (HAP familiar). Se conocen 4 formas de HAP familiares. El HAP familiar tipo I se produce por una fusión de los genes CYP11B2 y CYP11B1, de esta forma la síntesis de aldosterona pasa a estar regulada por la ACTH en vez de por la angiotensina II. En el HAP familiar tipo II, III y IV se produce un aumento de la transcripción y expresión de CYP11B2, responsable de la síntesis de aldosterona debido a una mutación germinal en CLCN2, KCNJ5 y CACNA1H, respectivamente. Por otra parte, se han identificado mutaciones somáticas en un 50% de los HAP esporádicos, siendo las mutaciones de ganancia de función a nivel de KCNJ5, ATP1A1, ATP2B3 y CACNA1D las más frecuentes. En esta revisión se ofrece una descripción detallada de las distintas formas de HAP familiar y sobre el perfil molecular de los pacientes con HAP esporádico.