Analizar la prescripción de fármacos antihipertensivos en pacientes con diabetes tipo 2 (DM2) en Andalucía, comparándola con las directrices SEH-LELHA 2022, y evaluar el coste directo de estos tratamientos.
Material y métodosEstudio multicéntrico, transversal y descriptivo de 385 pacientes con DM2. Los participantes fueron seleccionados aleatoriamente entre los cupos de 120 médicos de Atención Primaria de toda Andalucía. Los criterios de inclusión fueron: diagnóstico de DM2 y registros clínicos completos en 2022. Se recopilaron datos demográficos y de prescripción de fármacos, calculando el coste promedio por paciente.
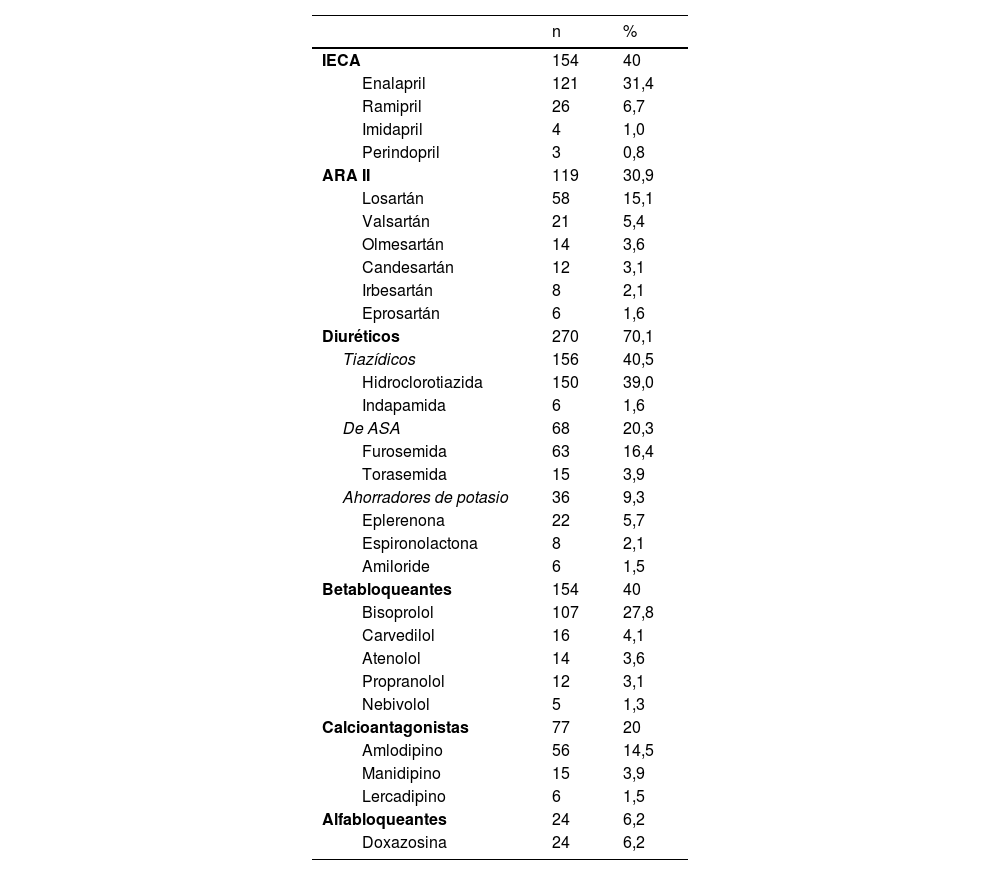
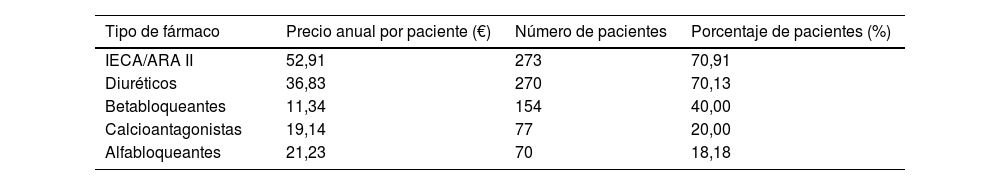
ResultadosLa edad media de los sujetos fue de 70,72 años y el 53,51% eran hombres. Un 70,9% de los pacientes tomaban antihipertensivos, siendo los más comunes IECA/ARA II (70,9%), diuréticos (70,1%), betabloqueantes (40,0%) y calcioantagonistas (20,0%). Cada uno de los pacientes tomaba una media de 2,46±1,06 antihipertensivos, y las asociaciones fijas de 2 o más antihipertensivos las utilizaban el 40,29% de los pacientes estudiados. El gasto anual por paciente fue de 141,45euros/año.
ConclusionesNuestros resultados revelan una sólida concordancia con las guías SEH-LELHA 2022 por parte de los médicos en Andalucía respecto a la prescripción de antihipertensivos en pacientes con DM2. Destaca una preferencia significativa hacia los bloqueadores del sistema renina-angiotensina, diuréticos y betabloqueantes. Sin embargo, apreciamos una notable desviación en las prácticas de prescripción con la elección frecuente de doxazosina, en lugar de espironolactona; a pesar de que esta última se recomienda, preferentemente, para casos de hipertensión arterial resistente. Aunque el gasto global en antihipertensivos es moderado, su relación costo-beneficio se ve reforzada por la efectividad de estos en la prevención de complicaciones cardiovasculares.
This study aims to analyze the prescription of antihypertensive drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Andalusia, comparing it with the SEH-LELHA 2022 guidelines, and to assess the direct cost of these treatments.
Materials and methodsA multicentric, cross-sectional, and descriptive study was conducted with 385 T2D patients. Participants were randomly selected from the patient lists of 120 primary care physicians from Andalusia. Inclusion criteria included a diagnosis of T2D and complete clinical records for the year 2022. Demographic data and drug prescription information were collected, with the average cost per patient being calculated.
ResultsThe mean age of the subjects was 70.72 years, with 53.51% being male. A total of 70.9% of the patients were taking antihypertensive drugs, the most common being ACE inhibitors/ARBs (70.9%), diuretics (70.1%), beta-blockers (40.0%), and calcium channel blockers (20.0%). Each patient took an average of 2.46±1.06 antihypertendsive, and fixed association of 2 or more antihypertensive drugs were used by 40.9% of the studied patients. The annual cost per patient was 141.45€/year.
ConclusionsThe study reveals strong adherence to the SEH-LELHA 2022 guidelines among physicians in Andalusia regarding the of antihypertensives for T2D patients, with a significant preference for Renin-Angiotensin System blockers, diuretics, and beta-blockers. However, a notable deviation in prescription practices was observed with the frequent choice of doxazosin over spironolactone, despite the latter being the recommended option for resistant hypertension. Although the overall expenditure on antihypertensives is moderate, their cost-effectiveness is enhanced by the efficacy of these treatments in preventing cardiovascular complications.