To evaluate the prognostic performance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) for mortality in patients with acute stroke treated at a Peruvian hospital.
DesignRetrospective cohort study.
SettingTertiary care hospital.
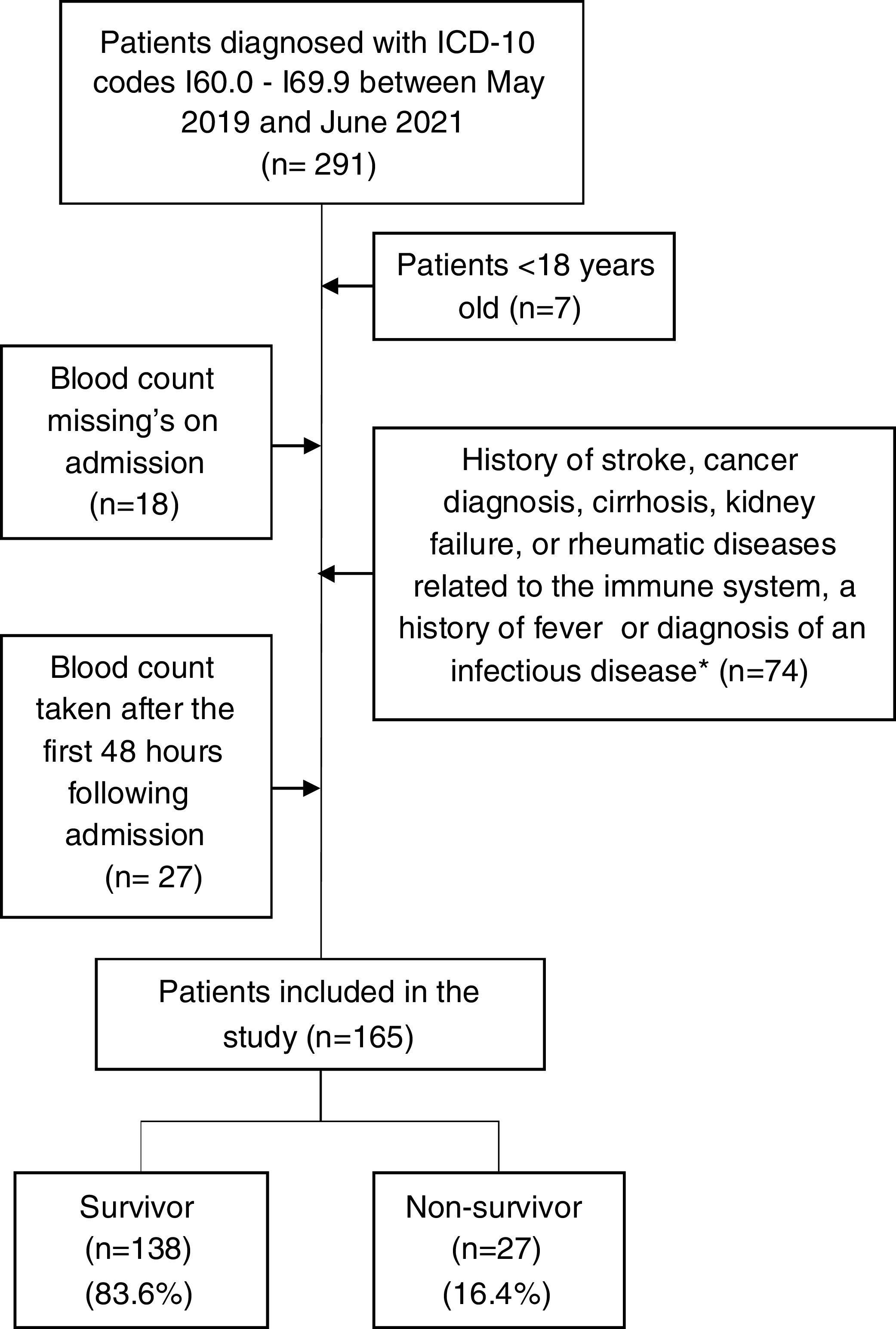
PatientsPatients aged ≥18 years with a diagnosis of acute stroke and admitted to the hospital from May 2019 to June 2021.
InterventionsNone.
Main variables of interestsNeutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and mortality.
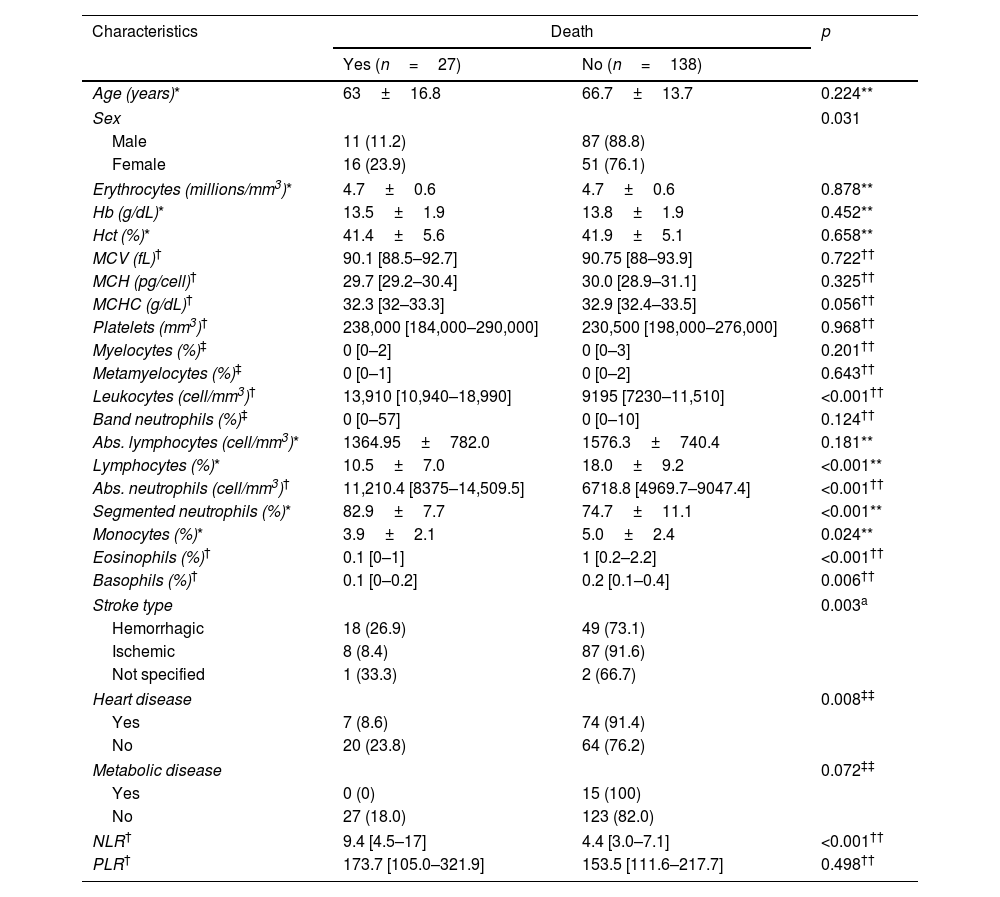
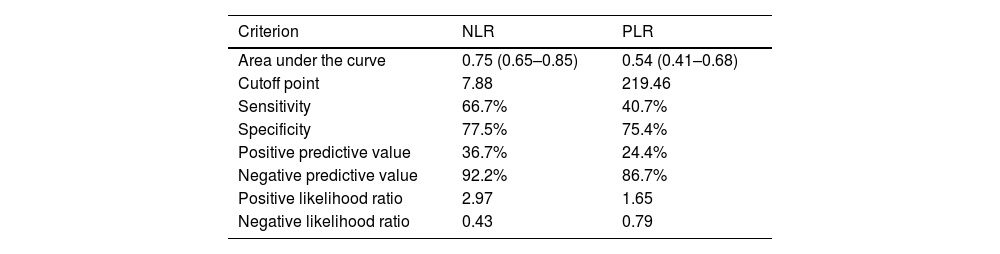
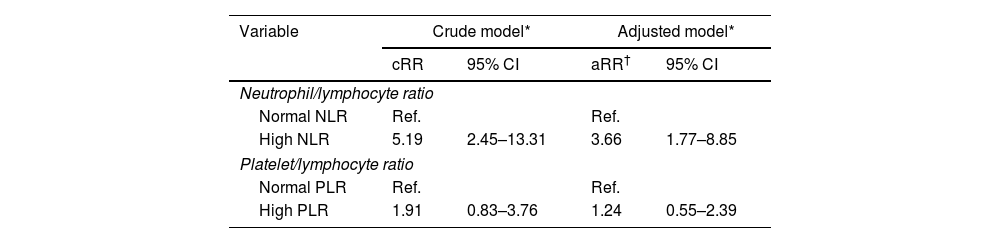
ResultsA total of 165 patients were included. The mean age was 66.1±14.2 years, and 59.4% were male. Only NLR had a performance superior to 0.7 (AUC: 0.75; 95%CI: 0.65–0.85), and its elevated levels were associated with an increased risk of mortality (aRR: 3.66; 95%CI: 1.77–8.85) after adjusting for confounders.
ConclusionThe neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio has an acceptable prognostic performance for mortality in patients with acute stroke. Its use may be considered to stratify patients’ risk and to consider timely alternative care and management.
Evaluar el desempeño pronóstico de la relación neutrófilos-linfocitos (NLR) y la relación plaquetas-linfocitos (PLR) para la mortalidad en pacientes con stroke agudo tratados en un hospital peruano.
DiseñoEstudio de cohorte retrospectivo.
ÁmbitoHospital de atención terciaria.
ParticipantesPacientes ≥18 años con diagnóstico de stroke agudo e ingresados en el hospital entre mayo de 2019 y junio de 2021.
IntervencionesNinguna.
Variables de interés principalesRazón neutrófilos/linfocitos, razón plaquetas/linfocitos y mortalidad.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 165 pacientes. La edad media fue de 66,1±14,2 años, y el 59,4% eran varones. Sólo el NLR tuvo un rendimiento superior a 0,7 (AUC: 0,75; IC95%: 0,65-0,85), y sus niveles elevados se asociaron con un mayor riesgo de mortalidad (RRa: 3,66; IC95%: 1,77-8,85) tras ajustar por factores de confusión.
ConclusionesLa razón neutrófilos/linfocitos tiene un rendimiento pronóstico aceptable para la mortalidad en pacientes con stroke. Su uso puede ser considerado para estratificar el riesgo de los pacientes y considerar oportunamente cuidados y manejo alternativos.