Cardiovascular risk calculators (CRC) are not locally validated and calibrated. Surrogate biomarkers of insulin resistance had identified subjects at higher risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
AimEstablish the frequency of surrogate biomarkers of insulin resistance and their correlation with CRC in primary prevention non-diabetic hypertensive subjects.
MethodsThis is an observational registry with a prospective consecutive outpatient's sample. The TyG index (TyGi) was calculated as logarithm (Ln) of (fasting triglycerides [mg/dl]×fasting plasma glucose [mg/dl]/2). Patients were stratified according to quartiles of TyGi. Pearson correlation coefficient between TyGi and other relevant variables was evaluated.
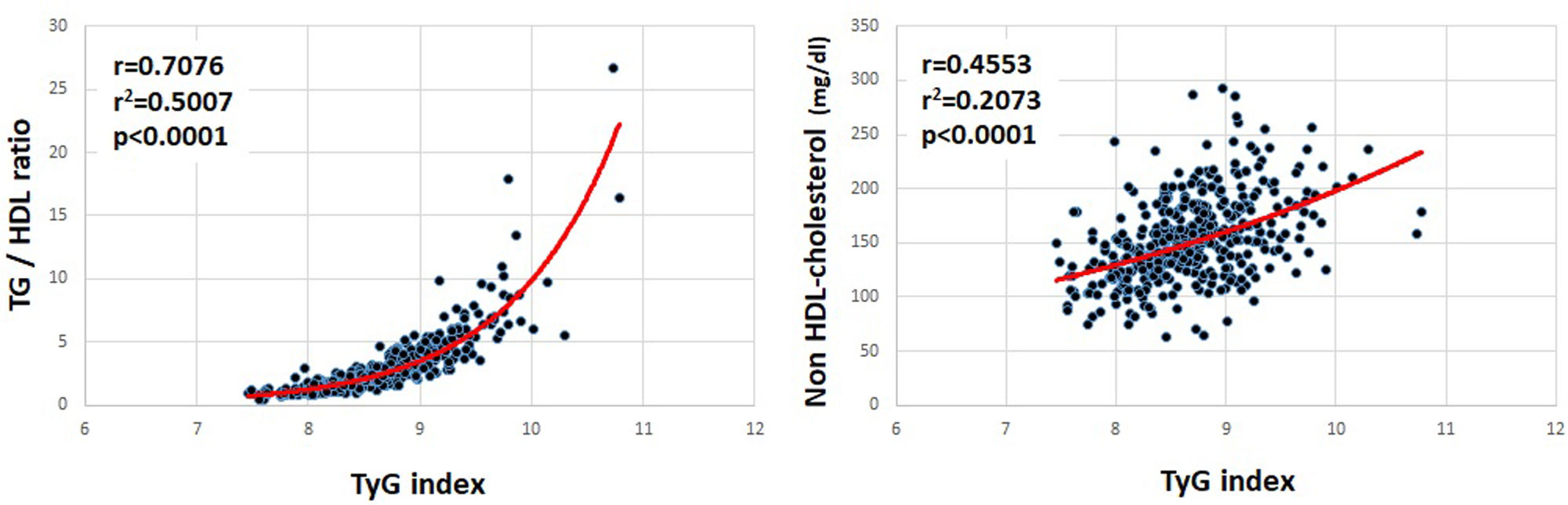
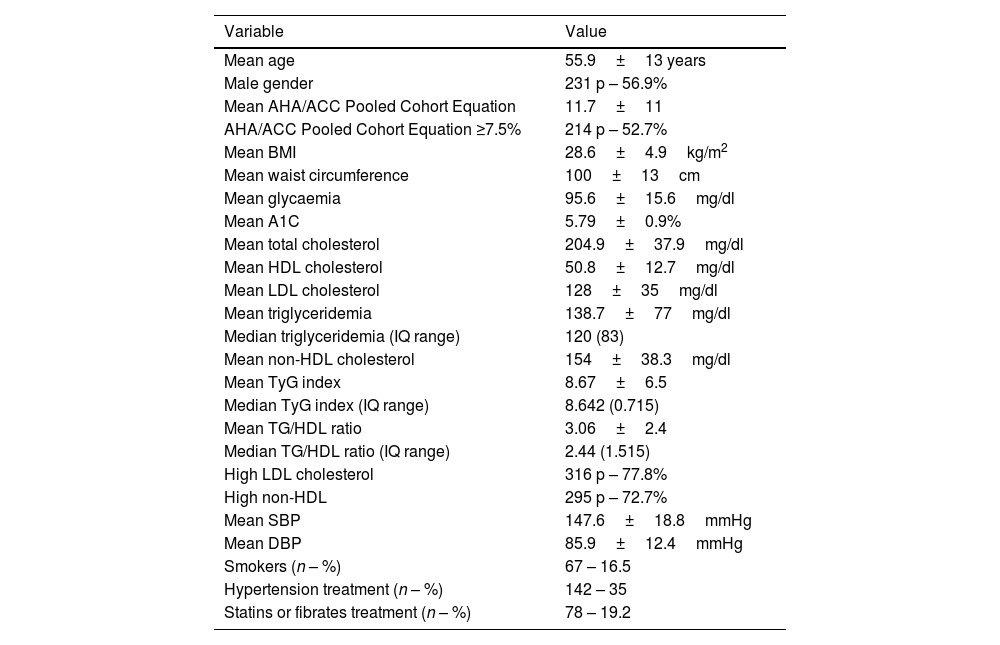
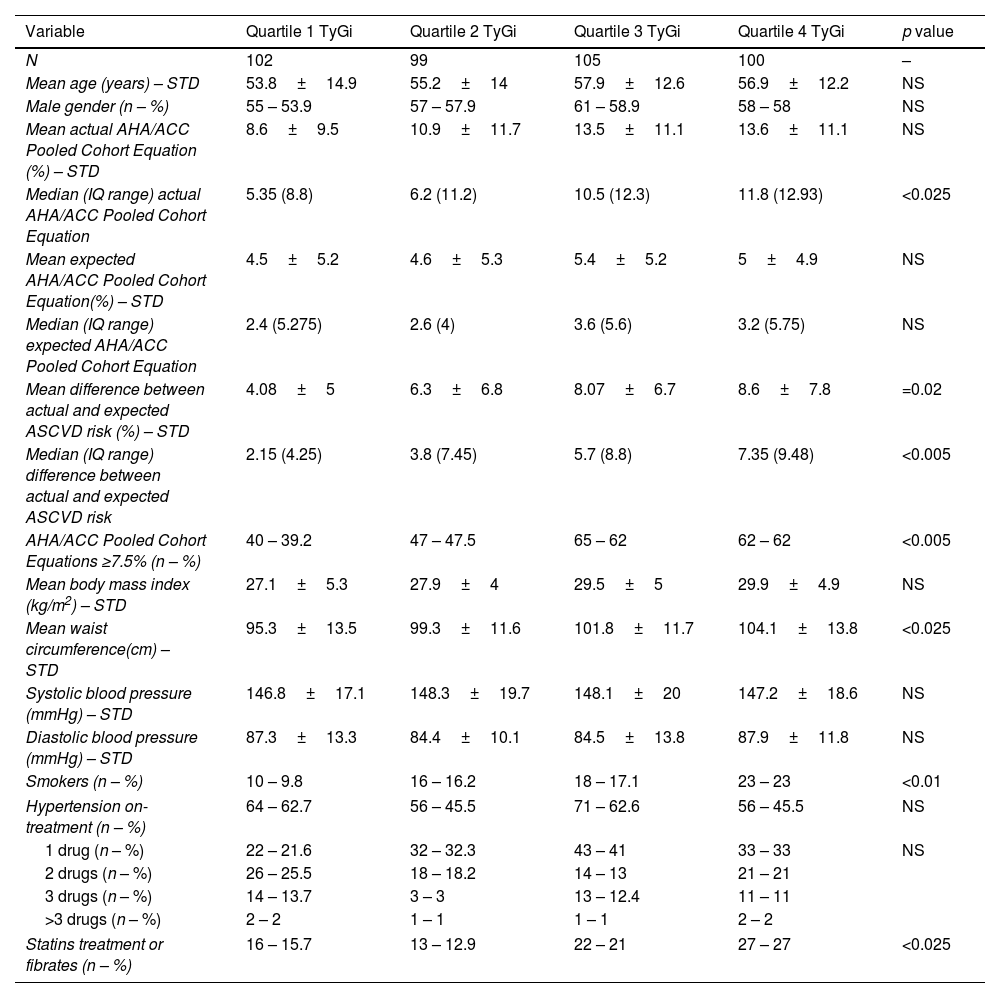
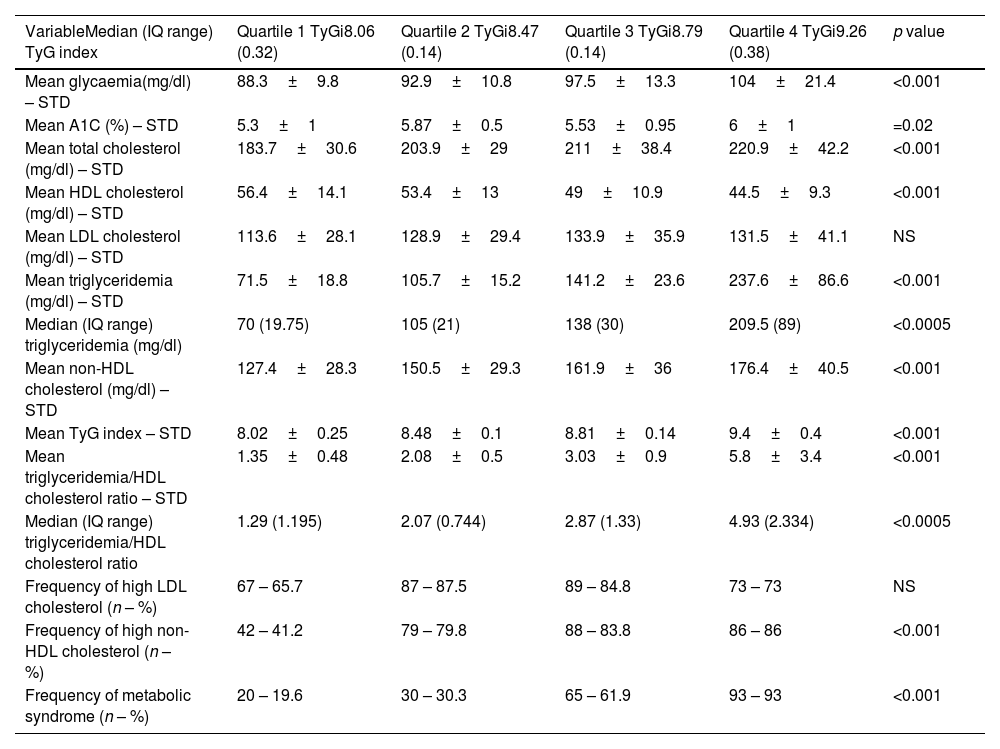
ResultsFour hundred six patients were included with a mean age 55.9±13 years, 231 p (56.9%) males. The mean TyGi was 8.667±0.53. Patients in the highest quartiles of TyGi had significantly higher median difference between expected and actual ASCVD risk (p=0.02), higher frequency of AHA/ACC Pooled Cohort Equation >7.5% (p<0.005), and higher levels of metabolic biomarkers such as median triglyceridemia/HDL cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL) (p<0.0005), glycaemia and A1C (p<0.001 and p=0.02, respectively). The correlation between TyGi and TG/HDL was highly significant (r=0.7076; r2=0.5007; p<0.0001), and intermediate with non-HDL cholesterol (r=0.4553, r2=0.2073; p<0.0001).
ConclusionsNon-diabetic hypertensive patients with high TyGi, a surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance, had a higher 10-year cardiovascular risk by AHA/ACC Pooled Cohort Equation. TyGi is statistically and significantly correlated with other biomarkers of insulin resistance. TyGi could be a reliable biomarker in clinical practice to stratify cardiovascular risk.
Las calculadoras de riesgo cardiovascular (CRC) no están validadas ni calibradas localmente. Otros tipos de biomarcadores de insulinorresistencia podrían identificar mayor riesgo de diabetes tipo 2 y enfermedades cardiovasculares.
ObjetivoEstablecer la frecuencia de biomarcadores de insulinorresistencia y su correlación con CRC en sujetos hipertensos no diabéticos en prevención primaria.
MétodosRegistro observacional con muestra prospectiva consecutiva de pacientes ambulatorios. El índice TyG (iTyG) se calculó como logaritmo (Ln) de (triglicéridos en ayunas [mg/dl]×glucemia en ayunas [mg/dl]/2). Los pacientes fueron estratificados según cuartiles de iTyG. Se evaluó el coeficiente de correlación de Pearson entre iTyG y variables relevantes.
ResultadosUn total de 406 pacientes, edad media 55,9±13 años, 231 (56,9%) hombres. iTyG medio 8,667±0,53. Los pacientes en cuartiles elevados de iTyG tuvieron una diferencia mediana más significativa entre riesgo esperado y real (p<0,005), mayor frecuencia de la CRC AHA/ACC >7,5% (p<0,005) y biomarcadores metabólicos: mediana relación trigliceridemia/cHDL (TG/cHDL) (p<0,0005), glucemia y A1C (p<0,001 y p=0,02, respectivamente). La correlación iTyG y TG/cHDL fue altamente significativa (r=0,7076; r2=0,5007; p<0,0001), e intermedia con colesterol no HDL (r=0,4553; r2=0,2073; p<0,0001).
ConclusionesLos pacientes hipertensos no diabéticos con iTyG elevado tuvieron mayor riesgo cardiovascular a 10años según la CRC AHA/ACC. El iTyG se correlaciona estadísticamente con otros biomarcadores de resistencia a la insulina. El iTyG podría ser un biomarcador fiable en la práctica clínica para estratificar el riesgo cardiovascular.