A low socioeconomic status (SES) has been associated with poor health results. The present study aimed to investigate if SES of older patients attending the emergency department is associated with the use of healthcare resources and outcomes.
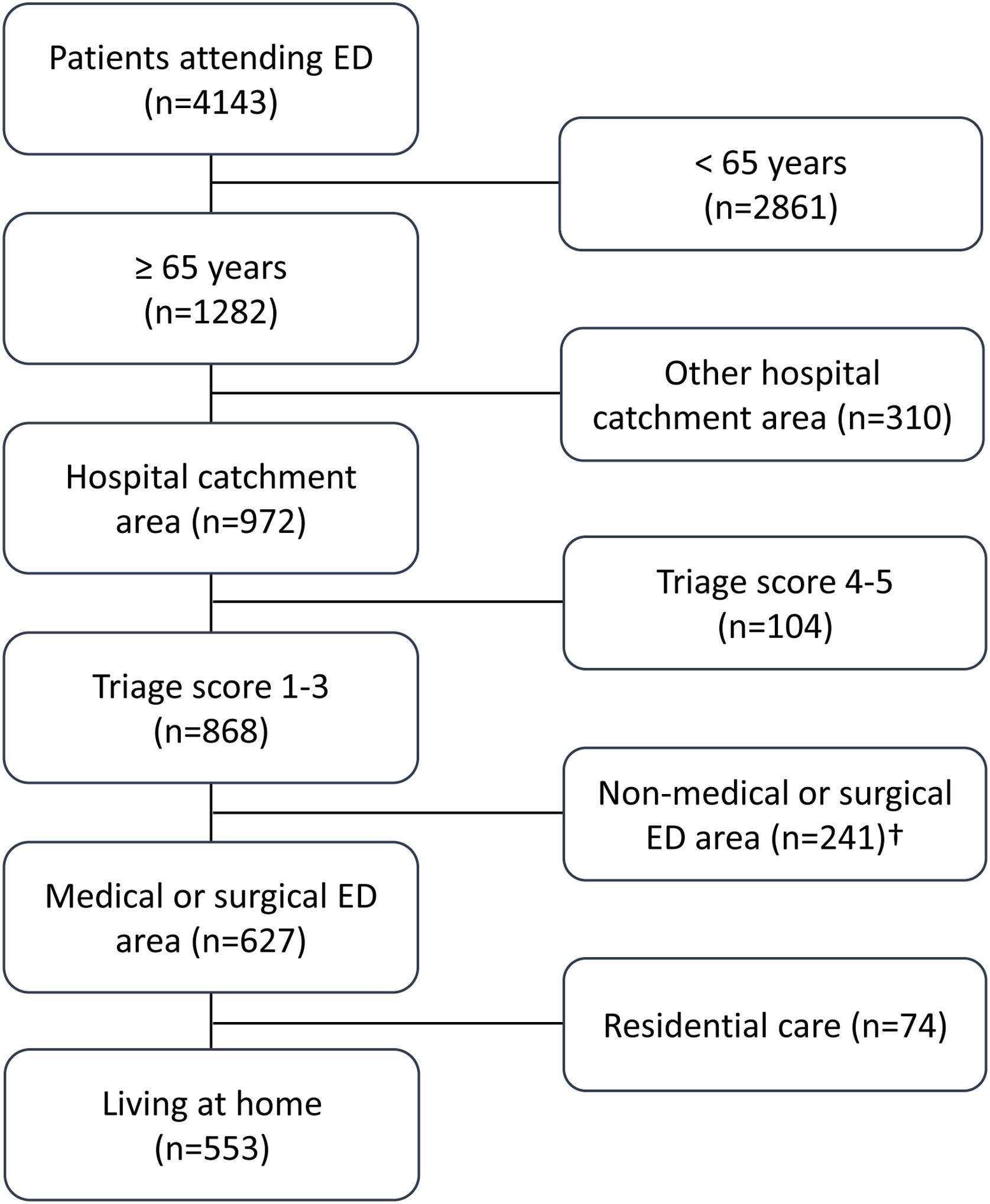
Patients and methodsObservational, retrospective study including consecutive patients 65 years or older admitted to the emergency department. Variables at baseline, index episode, and follow-up were recorded. SES was measured using an indirect theoretical index and patients were categorised into two groups according to whether they lived in a neighbourhood with a low or high SES. Primary outcomes included hospitalisation after the emergency department visit and prolonged hospitalisation (>7 days) at index episode. Secondary outcomes included emergency department re-consultant and hospital admission in the following 3 months after the index episode, and all-cause mortality after long-term follow-up. Logistic regression and cumulative hazards regression models were used to investigate associations between SES and outcomes.
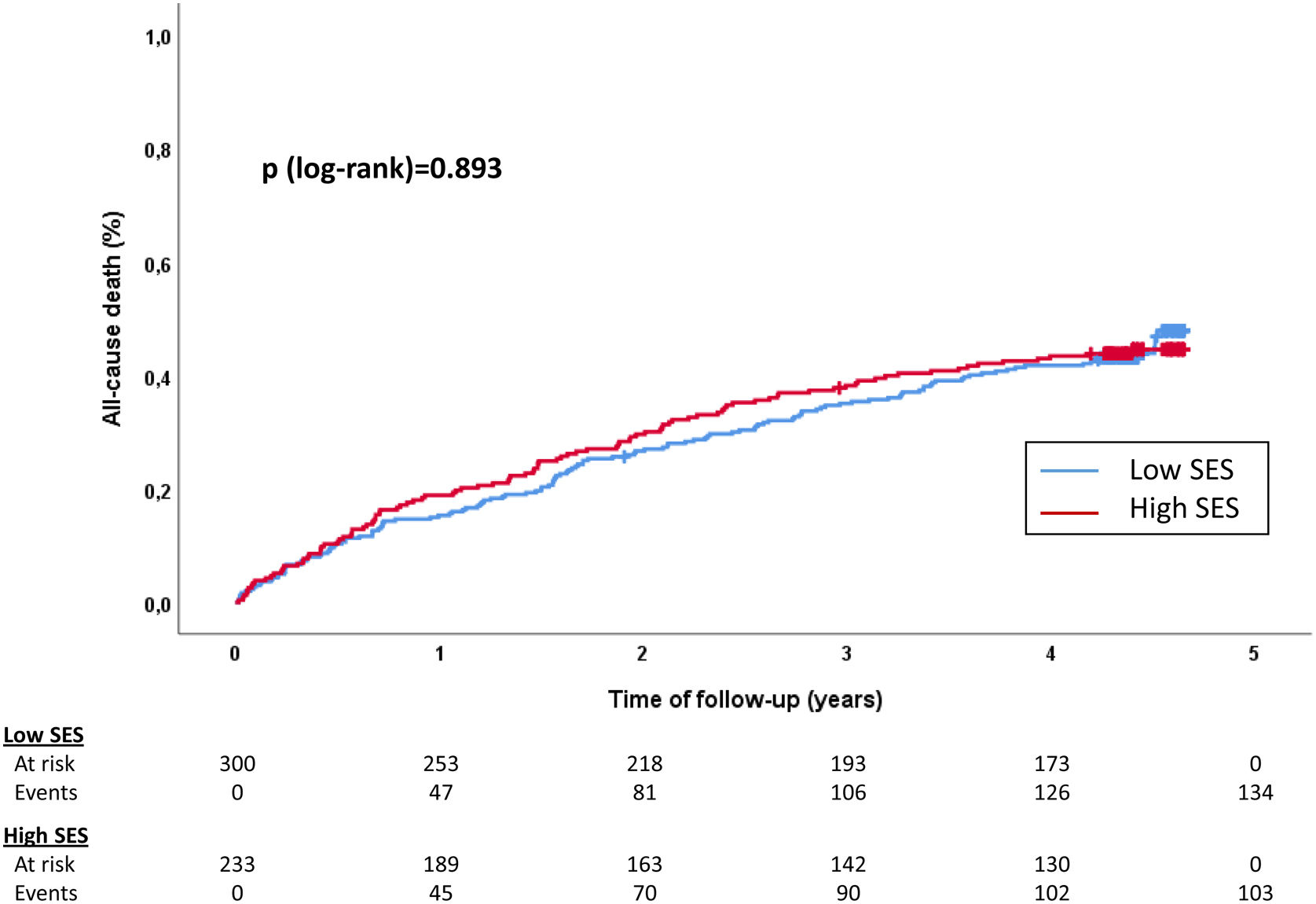
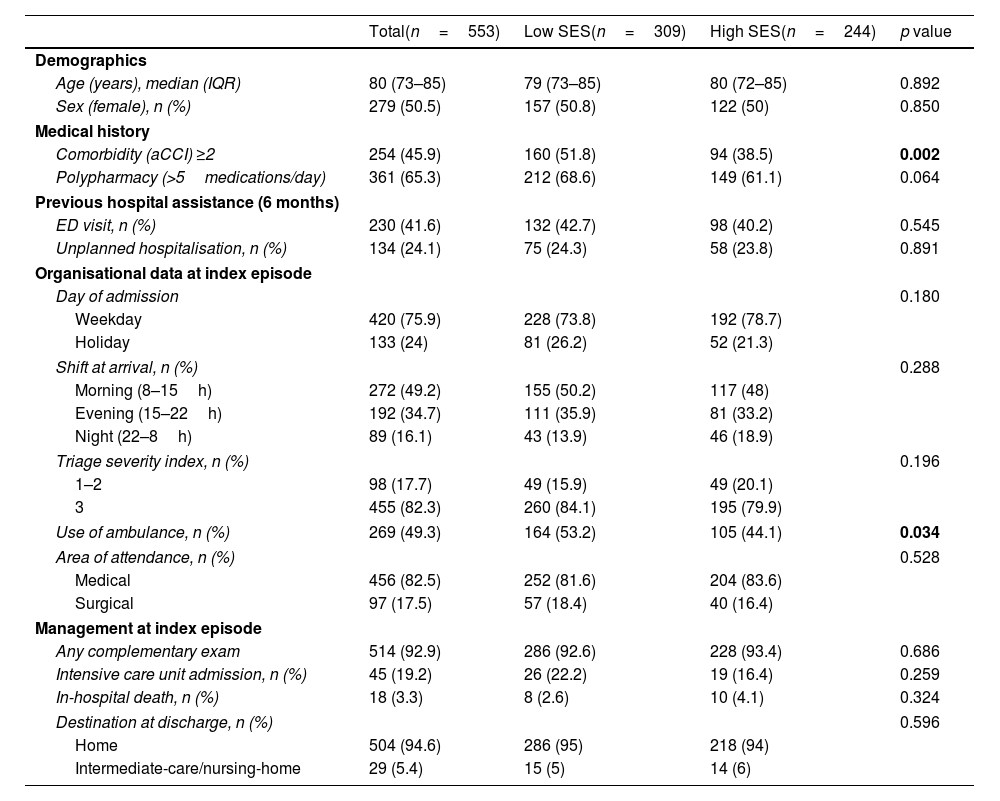
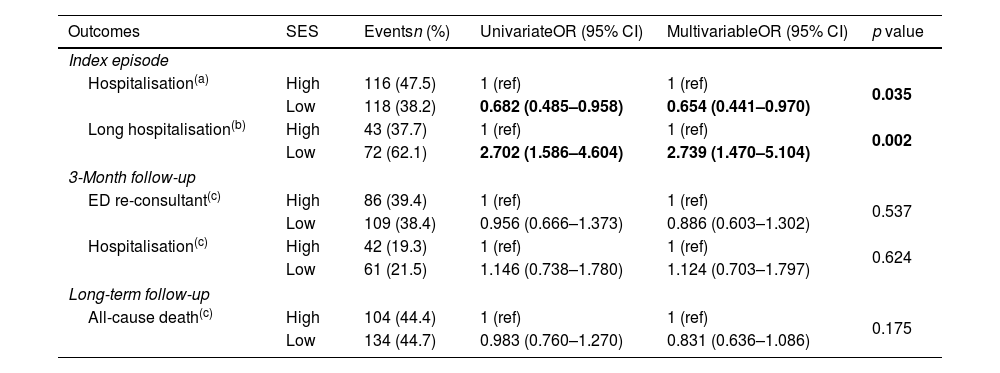
ResultsThe cohort included 553 patients (80 years [73–85], 50.5% female, 55.9% with low SES). After the emergency department visit, 234 patients (42.3%) required hospital admission. A low SES was inversely associated with hospitalisation with an adjusted odds ratio=0.654 (95% CI 0.441–0.970). Among hospitalised patients, a low SES was associated with prolonged hospitalisation (adjusted odds ratio=2.739; 95% CI 1.470–5.104). Follow-up outcomes, including all-cause mortality, were not associated with SES.
ConclusionsOlder patients living in more deprived urban areas were hospitalised less often after emergency department care, but hospital stays were longer. Understanding the effect of social determinants in healthcare use is mandatory to tailor resources to patient needs.
El nivel socioeconómico (NSE) se asocia con los resultados en salud. El objetivo del estudio fue investigar si el NSE de los pacientes de edad avanzada que acuden a un servicio de urgencias hospitalario influye en el uso de recursos sanitarios y en el pronóstico clínico.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, retrospectivo que incluyó pacientes consecutivos de 65 años o más atendidos en urgencias. Se registraron las características basales de los pacientes, del episodio índice y del seguimiento. El NSE se midió utilizando un índice teórico indirecto y los pacientes se clasificaron en dos grupos según vivían en un vecindario de NSE bajo o alto. El objetivo primario incluyó la hospitalización en el episodio índice y la hospitalización prolongada (>7 días). Los objetivos secundarios incluyeron reconsultas a urgencias e ingresos hospitalarios no planificados en los 3 meses siguientes al episodio índice, y mortalidad por cualquier causa a largo plazo. Se utilizaron modelos de regresión logística y de riesgos acumulados para investigar las asociaciones entre el NSE y los resultados.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 553 pacientes (80 años [73-85], 50,5% mujeres, 55,9% NSE bajo). Tras la visita en urgencias, 234 pacientes (42,3%) requirieron ingreso. El NSE bajo se asoció inversamente con la hospitalización (odds ratio ajustada=0,654; IC 95%: 0,441-0,970; p=0,035). Sin embargo, un NSE bajo se asoció con hospitalización prolongada (odds ratio ajustada=2,739; IC 95%: 1,470-5,104; p=0,002). El NSE no se relacionó con los resultados durante el seguimiento, incluida la mortalidad.
ConclusionesLos pacientes de edad avanzada que vivían en áreas urbanas más desfavorecidas fueron hospitalizados con menos frecuencia después de la atención en urgencias, pero las estancias hospitalarias fueron más largas. Comprender el efecto de los determinantes sociales en el uso de la atención sanitaria es obligatorio para adaptar los recursos a las necesidades de los pacientes.