La receta electrónica es el sistema de prescripción que permite a los profesionales sanitarios enviar directamente a las oficinas de farmacia comunitarias y a la unidad de pacientes externos de los servicios de farmacia hospitalaria, las prescripciones de medicamentos para su dispensación. Sin embargo, existe dificultad para la obtención de una historia farmacoterapéutica fiable en el paciente crónico a través de la receta electrónica al ingreso hospitalario como punto crítico para la adecuada adaptación del tratamiento. Por tanto, el farmacéutico como miembro del equipo multidisciplinar debe asegurar, a través de la conciliación de la medicación, una adecuada transición asistencial mediante el manejo correcto del tratamiento que requiere el paciente crónico durante su hospitalización.
ObjetivosEvaluar la calidad de los registros de prescripción electrónica del tratamiento crónico habitual analizando la concordancia de la receta electrónica.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, transversal y retrospectivo en el Hospital General Universitario de Elche. Se incluyeron los pacientes hospitalizados a cargo de los servicios de cirugía ortopédica y traumatología, urología y neurocirugía en los que el médico responsable solicitó la conciliación de la medicación por parte del servicio de farmacia entre enero 2022/diciembre 2022.
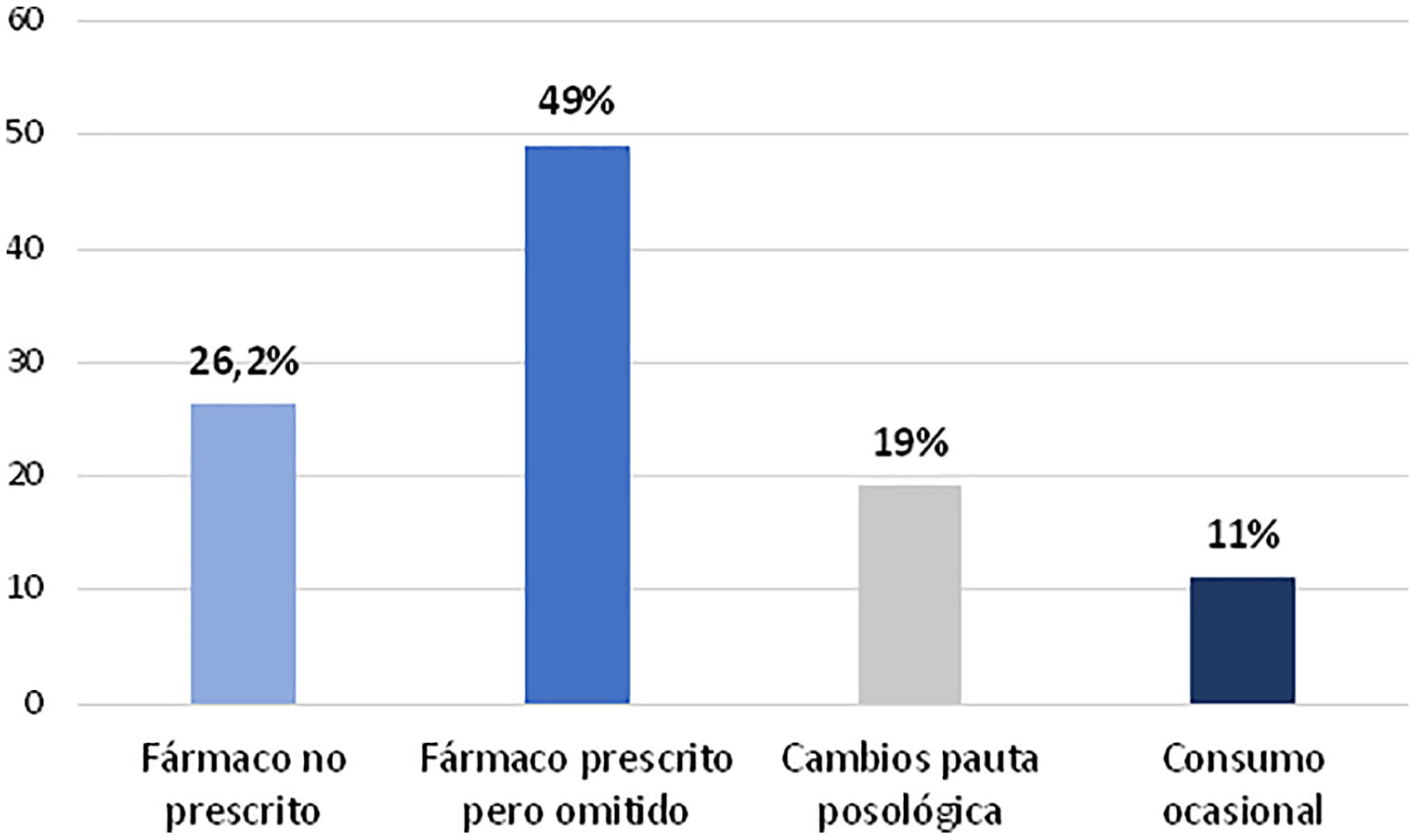
ResultadosTrescientos setenta y ocho pacientes, 209 (55,3%) mujeres y 169 (44,7%) varones, con una edad media±desviación estándar de 71,0±11,6 años y 69,0±11,8 años, respectivamente. El porcentaje total de pacientes con discrepancias en la prescripción electrónica respecto al tratamiento crónico habitual fue del 60,6%, reflejando que tan solo el 39,4% de los pacientes presentaban prescripciones electrónicas no discordantes.
ConclusionesMás de la mitad de los pacientes quirúrgicos hospitalizados presentan discrepancias en los medicamentos prescritos en la receta electrónica domiciliaria, lo cual justifica la importancia de la conciliación del tratamiento al ingreso llevada a cabo por los farmacéuticos del hospital.
Electronic prescription is the prescription system that allows healthcare professionals to send medication prescriptions directly to community pharmacies and the outpatient unit of Hospital Pharmacy Services for dispensing. However, there is difficulty in obtaining a reliable pharmacotherapeutic history in chronic patients through electronic prescription upon hospital admission as a critical point for adequate treatment adaptation. Therefore, the pharmacist as a member of the multidisciplinary team must ensure, through medication conciliation, an adequate transition of care through the correct management of the treatment that the chronic patient requires during their hospitalization.
ObjectivesTo evaluate the quality of electronic prescription records for routine chronic treatment by analyzing the concordance of the electronic prescription.
Material and methodsObservational, cross-sectional and retrospective study at the General University Hospital of Elche. Hospitalized patients in charge of the Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Urology and Neurosurgery Services in which the responsible doctor requested medication reconciliation by the Pharmacy Service between January 2022 - December 2022 were included.
Results378 patients, 209 (55.3%) women and 169 (44.7%) men, with a mean age±standard deviation of 71.0±11.6 years and 69.0±11.8 years, respectively. The total percentage of patients with discrepancies in the electronic prescription with respect to the usual chronic treatment was 60.6%, reflecting that only 39.4% of the patients had non-discordant electronic prescriptions.
ConclusionsMore than half of hospitalized surgical patients present discrepancies in the medications prescribed in the home electronic prescription, which justifies the importance of treatment reconciliation upon admission carried out by hospital pharmacists.