Poor adherence to oral antidiabetic drugs (Adh-OAD) is a risk factor for poor control of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Therefore, it is necessary to quantify the Adh-OAD. This quantification is possible through electronic dispensing records from the community pharmacy.
The objective was to evaluate the influence of the Adh-OAD on the control of T2DM and the percentage of glycosylated hemoglobin (%HbA1c) in the patient.
Materials and methodsA cross-sectional descriptive observational study was conducted in 8 community pharmacies in Granada (Spain). Patients older than 18 years with T2DM and on oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs) for at least 6 months were included. The main study variables were the control of T2DM, %HbA1c, and the Adh-OAD considering three cut-off points (≥80%, ≥70%, ≥60%). This relationship was studied using multivariate binary logistic regression and multivariate linear regression, respectively.
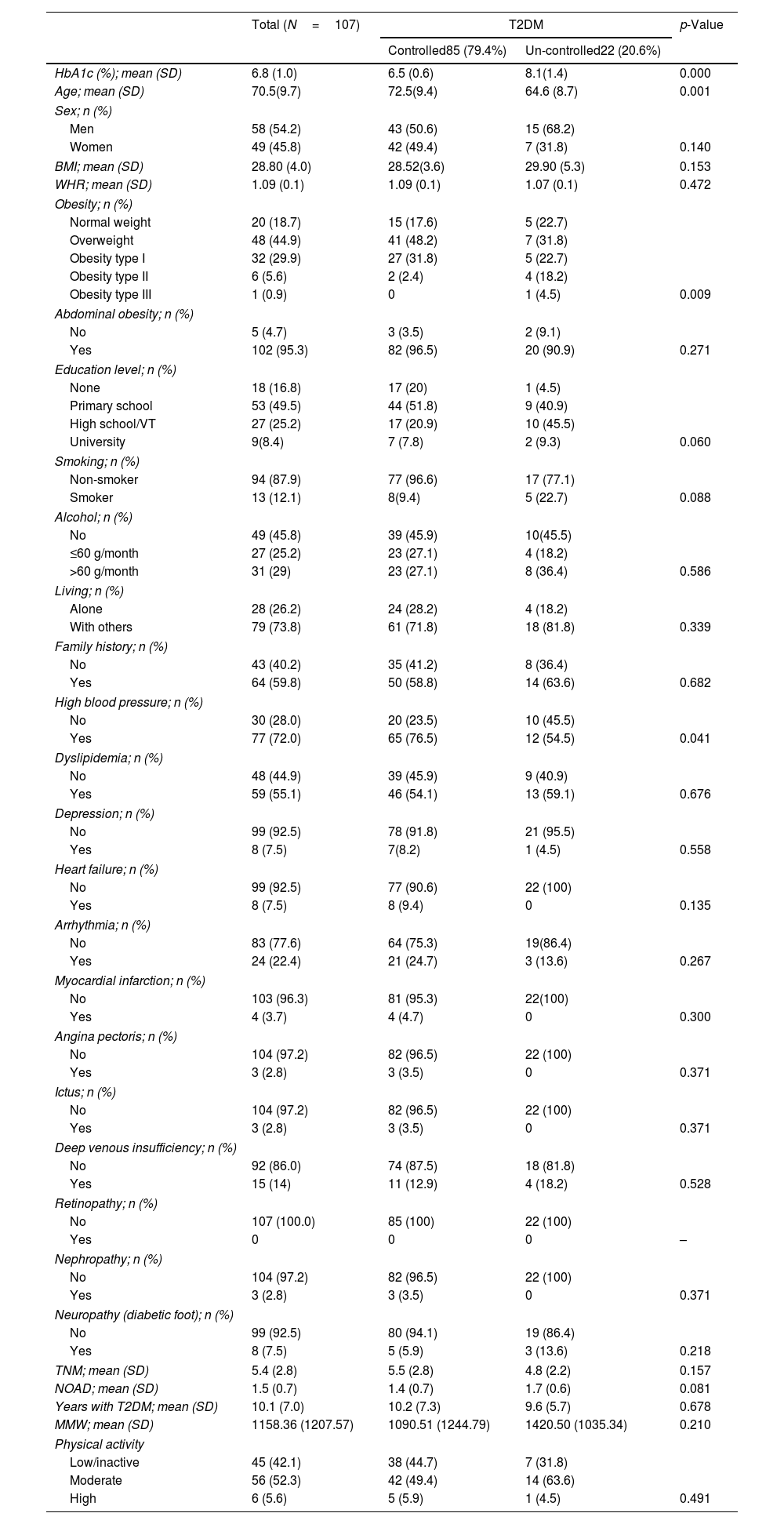
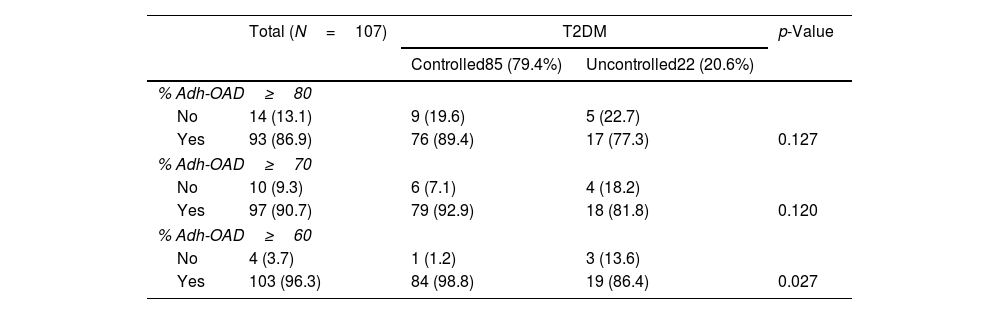
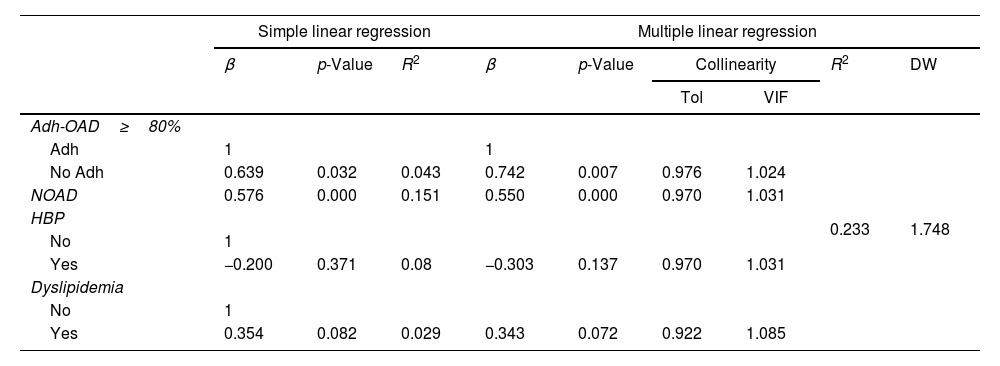
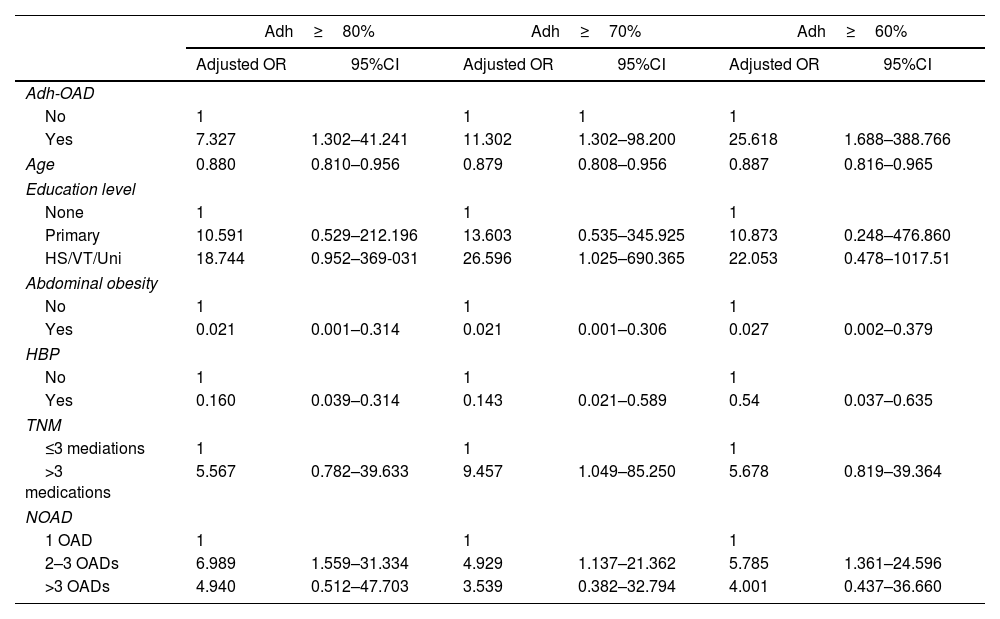
ResultsA total of 107 patients were included. The mean age was 70.5 years (SD: 9.7), and 54.2% were men. Eighty-five patients (79.4%) had well-controlled T2DM (mean %HbA1c: 6.5%; SD=0.6). Considering Adh-OAD≥80%, 13.1% (n=14) had a poor adherence and was related to the %HbA1c (β=0.742; p=0.007) and the control of T2DM (OR: 7.327; 95% CI: 1.302–41.241). Poor adherence was found in 9.3% (n=10) considering Adh-OAD≥70% and in 3.7% (n=4) considering Adh-OAD≥60%. In both cases, a statistically significant relationship was found between Adh-OAD and the %HbA1c and between Adh-OAD and the control of T2DM.
ConclusionsAdh-OAD influenced the %HbA1c in patients with T2DM and the control of their disease.
La falta de adherencia al tratamiento antidiabético oral (Adh-ADO) es factor de riesgo de la falta de control de la diabetes mellitus 2 (DM2). Por tanto, es necesario cuantificar la Adh-ADO. Desde la farmacia comunitaria esto es posible mediante los registros electrónicos de dispensación.
El objetivo fue evaluar la influencia de la Adh-ADO sobre el control de la DM2 y sobre el porcentaje de hemoglobina glicosilada (%HbA1c) del paciente.
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional descriptivo transversal realizado en ocho farmacias comunitarias de Granada (España). Se incluyeron pacientes mayores de 18 años con DM2 y en tratamiento con antidiabéticos orales durante mínimo seis meses. Las variables principales fueron el control de DM2, %HbA1c y Adh-ADO teniendo en cuenta tres puntos de corte (≥ 80%, ≥ 70%, ≥ 60%). Esta relación se estudió mediante regresión logística binaria multivariante y regresión lineal multivariante respectivamente.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 107 pacientes. La edad media fue 70,5 (DE = 9,7) años y el 54,2% fueron hombres; 85 pacientes (79,4%) tuvieron controlada la DM2 (%HbA1c medio 6,5%; DE=0,6). Considerando Adh-ADO ≥ 80%, el 13,1% (n=14) tuvo falta de adherencia y se relacionó con %HbA1c (β = 0,742; p=0,007) y con el control de la DM2 (OR = 7,327; IC 95%: 1,302-41,241). El 9,3% (n=10) tuvo falta de adherencia considerando Adh-ADO ≥ 70% y el 3,7% (n=4) considerando Adh-ADO ≥ 60. En ambos casos hubo relación estadísticamente significativa con %HbA1c y con el control de la DM2.
ConclusionesLa Adh-ADO influyó sobre el %HbA1c en los pacientes con DM2 y sobre el control de su enfermedad.