Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is the most dominant cause of neuropathy worldwide, and there has been no specific treatment until now. The aim of the current study was to assess the probable protective effect of empagliflozin in type 2 diabetics who are suffering from DPN.
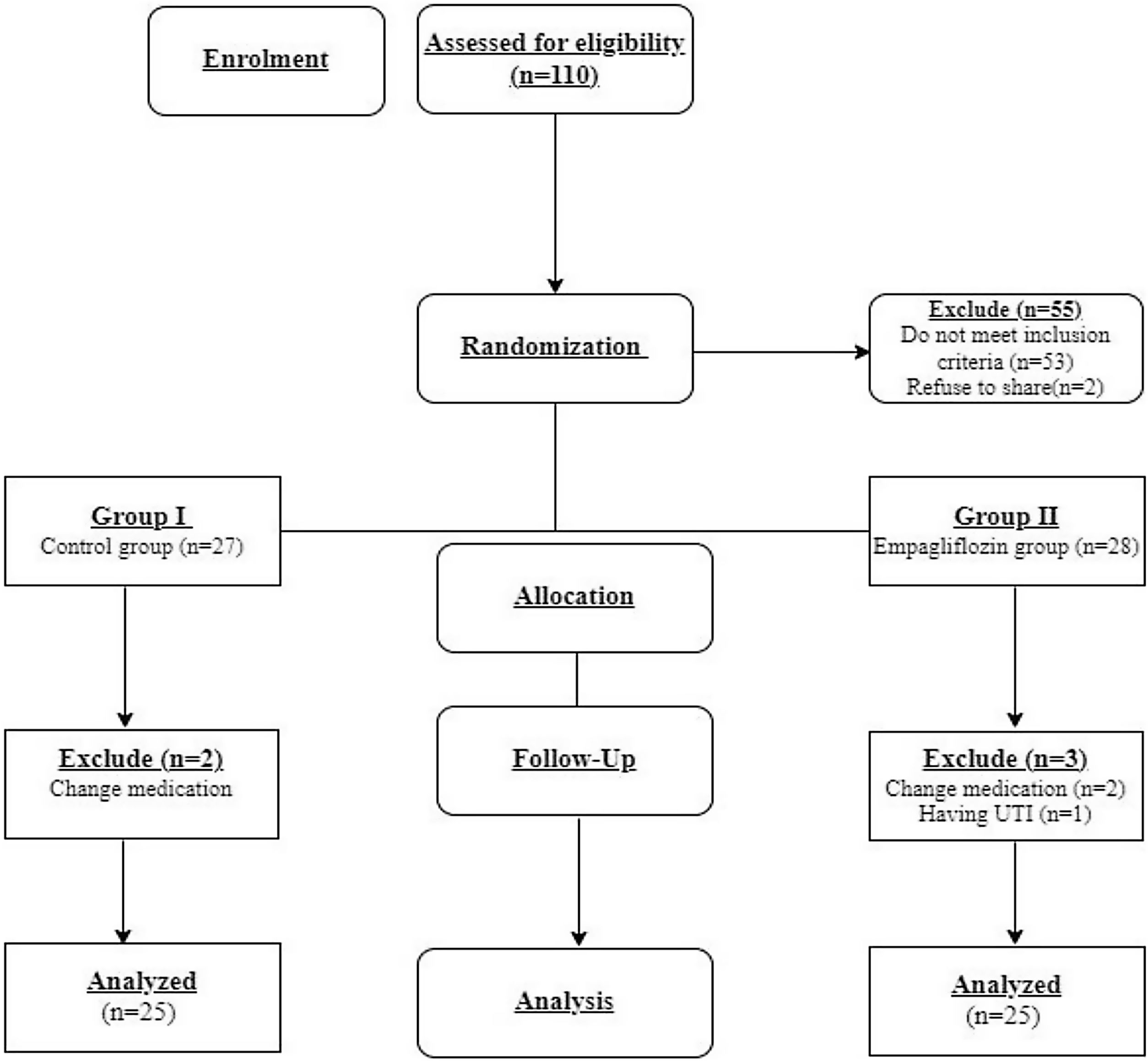
MethodsFifty eligible type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) cases with diabetic peripheral neuropathy were recruited in this study and classified into 2 groups. Group I (n=25) (control group) received placebo tablets once daily. Group II (n=25) (empagliflozin group) received empagliflozin 25mg once daily for three months. Empagliflozin efficacy was evaluated using electrophysiological studies, and HbA1c levels, the brief pain inventory short-form item (BPI-SF) score, the diabetic neuropathy symptom (DNS) score, the atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score, and the serum levels of neuron-specific enolase (NSE), malondialdehyde (MDA) and calprotectin (Calpro), lipid profile, and random blood glucose level (RBG).
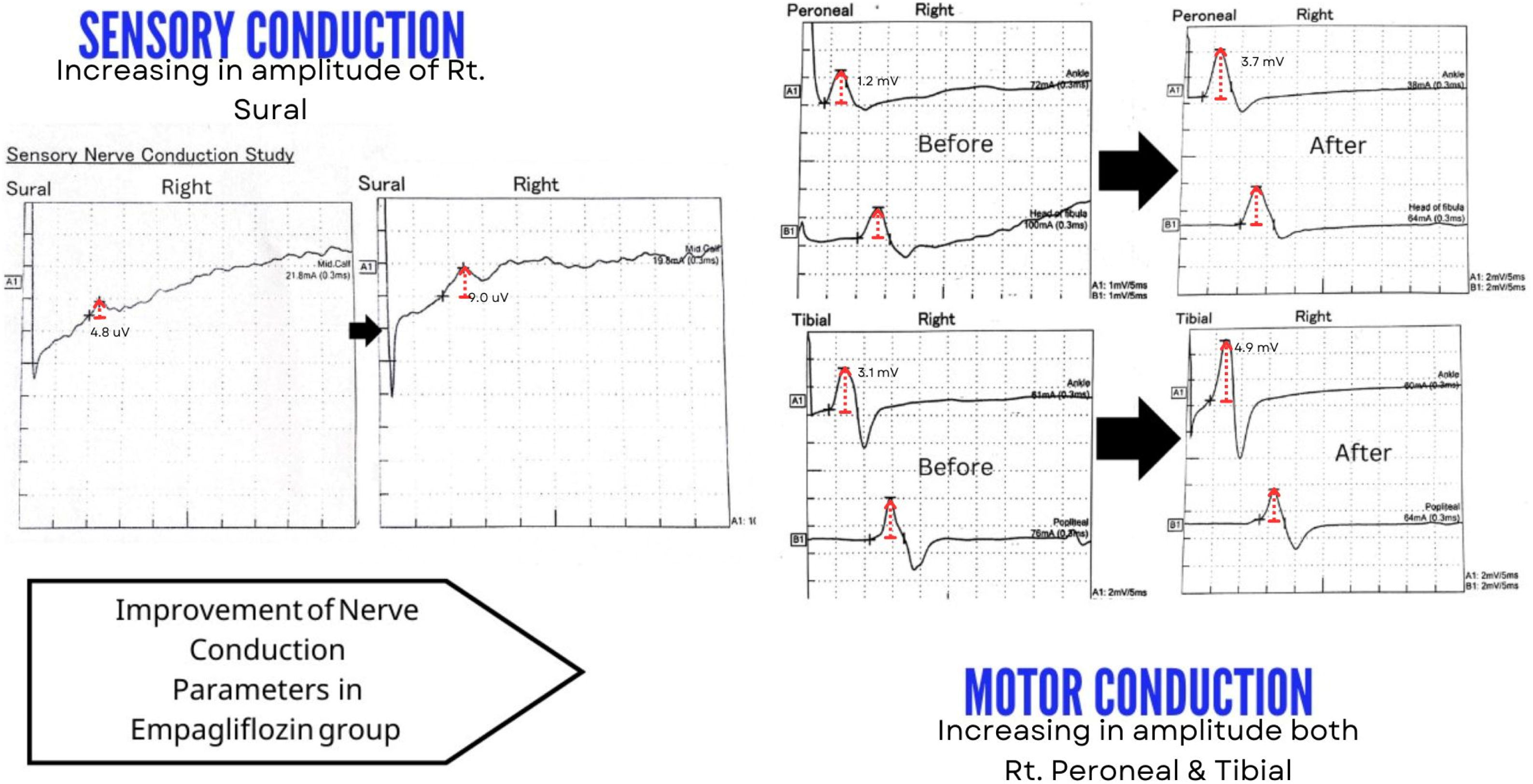
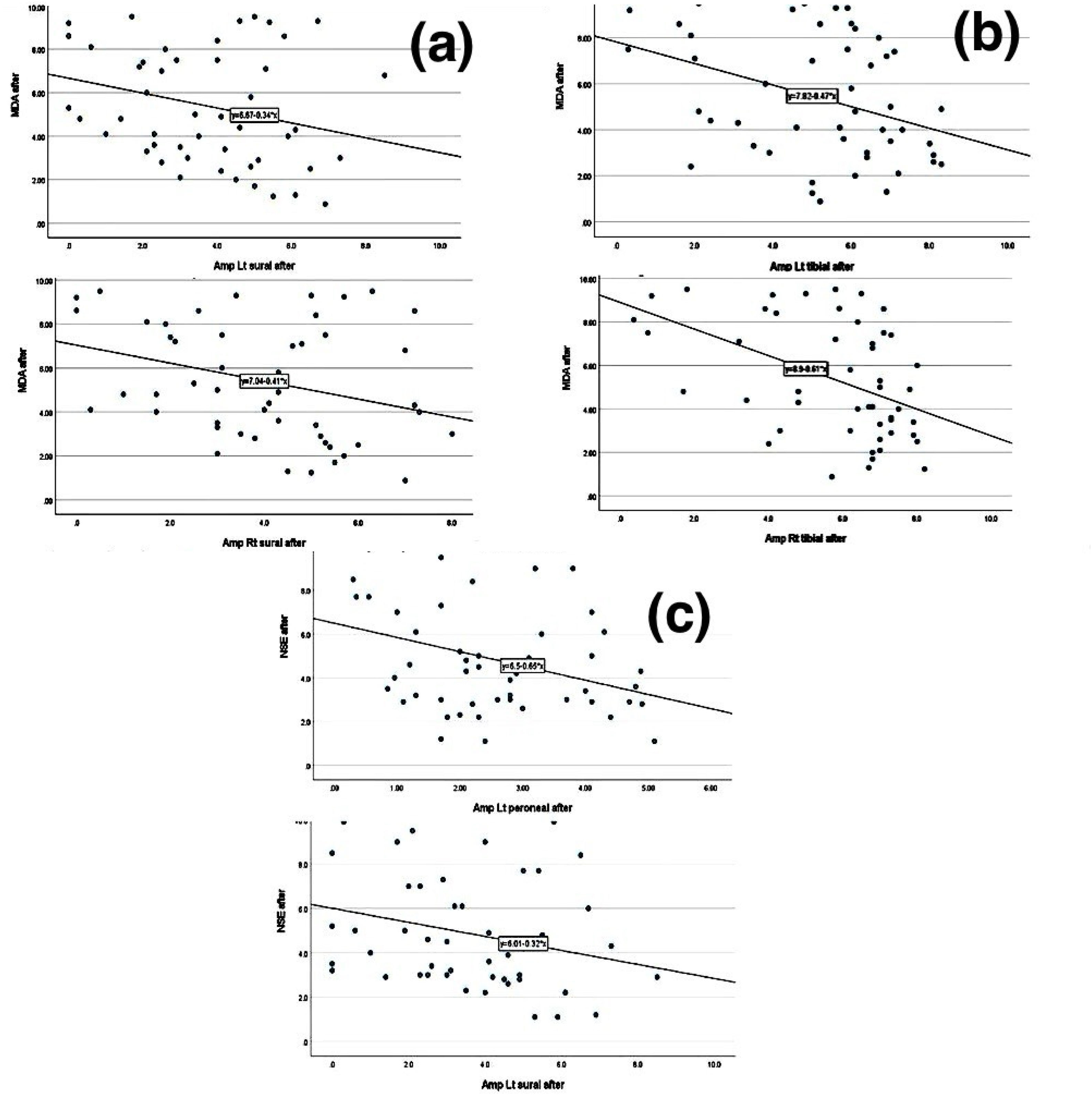
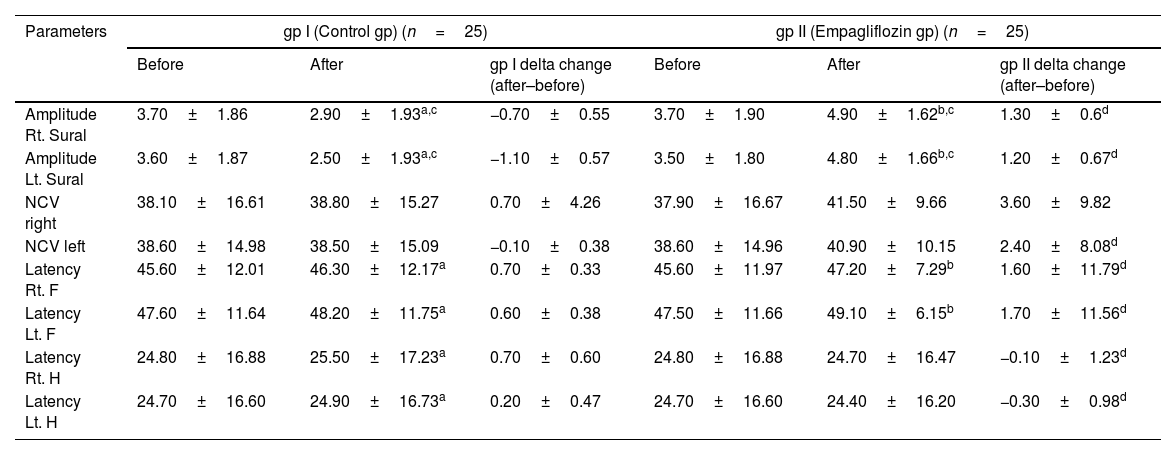
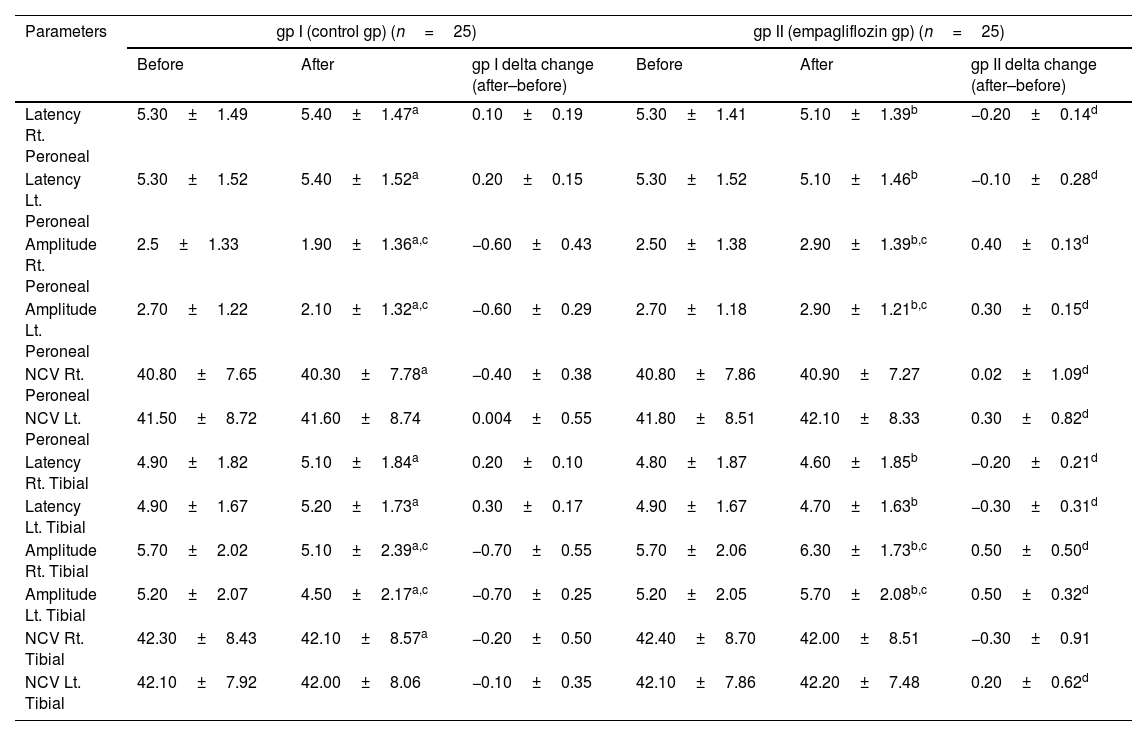
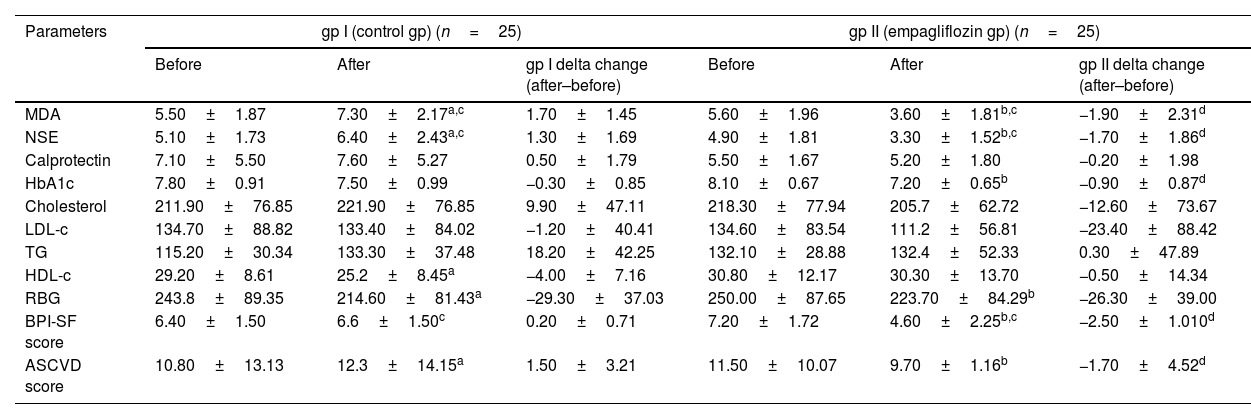
ResultsAfter three months, comparing the results of the empagliflozin arm to the control arm showed a significant improvement in the electrophysiological studies and a significant decrease in the BPI-SF score and the mean serum levels of NSE and MDA. However, no significant difference was determined in HbA1c, Calpro, lipid profile, and RBG levels. In addition, the DNS and ASCVD risk scores were not significantly different. The NSE and MDA levels were significantly negatively correlated with the electrophysiological parameters. However, the BPI-SF score showed a non-significant difference.
ConclusionsEmpagliflozin may be a promising neuroprotective and therapeutic agent for diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Trial registration Identifier: NCT05977465.
La neuropatía periférica diabética (NPD) es la causa más dominante de neuropatía en todo el mundo y hasta ahora no ha existido un tratamiento específico. El objetivo del presente estudio fue evaluar el probable efecto protector de la empagliflozina en diabéticos tipo 2 que padecen NPD.
MétodosEn este estudio se reclutaron 50 casos elegibles de diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2) con NPD y se clasificaron en dos grupos. El grupo I (n=25) (grupo de control) recibió comprimidos de placebo una vez al día. El grupo II (n=25) (grupo de empagliflozina) recibió 25mg de empagliflozina una vez al día durante tres meses. La eficacia de la empagliflozina se evaluó mediante estudios electrofisiológicos y los niveles de hemoglobina A1c (HbA1c), la puntuación del ítem breve del inventario de dolor (BPI-SF), la puntuación de los síntomas de neuropatía diabética (DNS), la puntuación de riesgo de enfermedad cardiovascular aterosclerótica (ASCVD) y los niveles séricos de enolasa neuronal específica (NSE), malondialdehído (MDA) y calprotectina (Calpro), perfil lipídico y nivel aleatorio de glucosa en sangre (RBG).
ResultadosDespués de tres meses, la comparación de los resultados del grupo de empagliflozina con los del grupo de control mostró una mejora significativa en los estudios electrofisiológicos y una disminución significativa en la puntuación BPI-SF y los niveles séricos medios de NSE y MDA. Sin embargo, no se determinaron diferencias significativas en los niveles de HbA1c, Calpro, perfil lipídico y RBG. Además, las puntuaciones de riesgo de DNS y ASCVD no fueron significativamente diferentes. Los niveles de NSE y MDA se correlacionaron significativa y negativamente con los parámetros electrofisiológicos. Sin embargo, la puntuación BPI-SF mostró una diferencia no significativa.
ConclusionesLa empagliflozina puede ser un agente neuroprotector y terapéutico prometedor para la NPD.