Endoscopy is the gold standard to assess disease severity in inflammatory bowel disease, although it is an invasive procedure. Clinical activity and biological markers have been routinely used to determine disease activity in a non-invasive manner. The aim of this study was to determine concordance between common biological markers (C reactive protein, orosomucoid, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, fibrinogen, platelets, leukocytes, neutrophils and haemoglobin) and clinical activity in inflammatory bowel disease.
Patients and methodConsecutive patients with inflammatory bowel disease were included. Clinical activity was evaluated according to the Harvey–Bradshaw index in Crohn's disease and to the partial Mayo score in ulcerative colitis. Serum concentrations of the different biomarkers were analysed. Concordance between clinical activity and elevation of the serological biomarkers was determined using the kappa statistic.
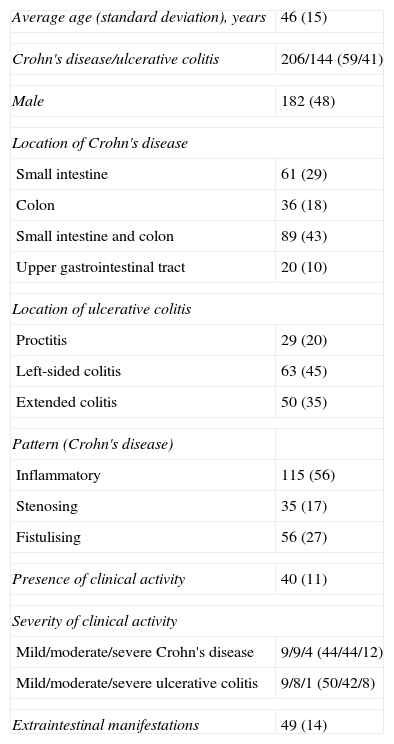
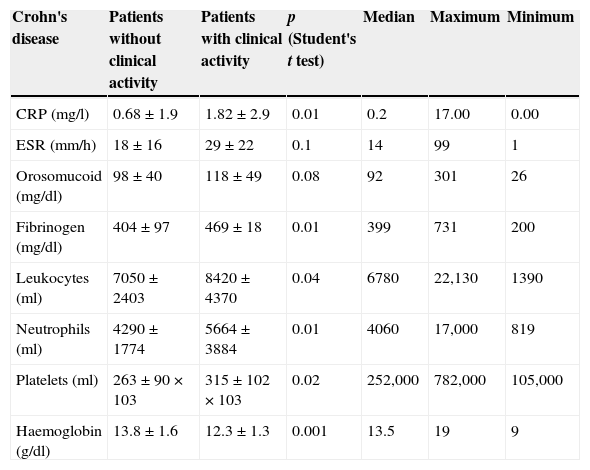
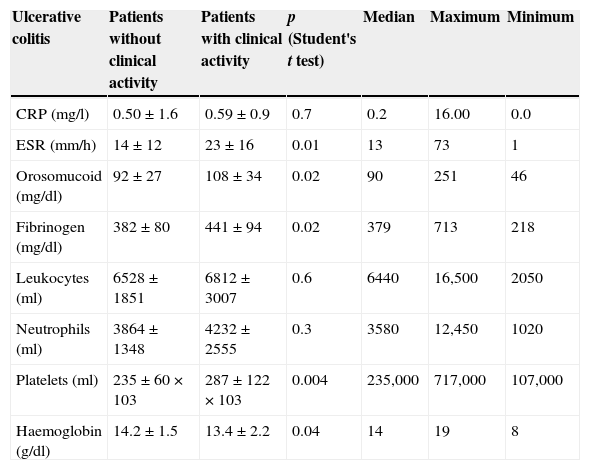
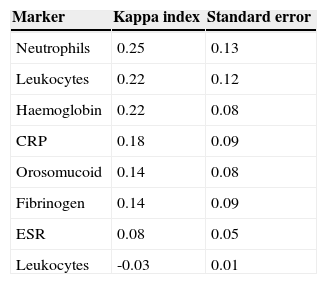
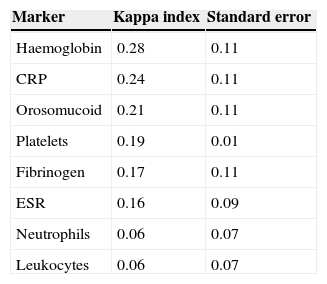
ResultsIn total, 350 patients were included (median age 46 years, Crohn's disease 59%). Eleven percent of patients had clinical activity. Crohn's disease patients had mild clinical activity in 44% of cases, moderate disease in 44% and only 12% of patients had severe clinical activity. In ulcerative colitis, patients had mild, moderate and severe clinical activity in 50%, 42% and 8% of cases, respectively. None of the biomarkers included had an acceptable concordance with clinical activity (kappa statistic≤0.30).
ConclusionsConcordance between serological biomarkers and clinical activity in inflammatory bowel disease is remarkably low.
La ileocolonoscopia es el patrón oro para determinar el grado de actividad de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Sin embargo, es una técnica invasiva. La actividad clínica y los marcadores biológicos se han empleado como indicadores indirectos para determinar, de forma no invasiva, el grado de actividad inflamatoria. El objetivo de este estudio fue determinar la concordancia entre los marcadores biológicos séricos más utilizados (proteína C reactiva, orosomucoide, velocidad de sedimentación globular, fibrinógeno, plaquetas, leucocitos, neutrófilos, hemoglobina) y la actividad clínica de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal.
Pacientes y métodoSe incluyeron prospectivamente pacientes consecutivos en los que se evaluó la actividad clínica medida mediante el índice de Harvey–Bradshaw en la enfermedad de Crohn, y mediante el índice de Mayo parcial en la colitis ulcerosa. Se cuantificaron los valores de los diversos marcadores biológicos. Se determinó la concordancia de la actividad clínica con la elevación de los marcadores biológicos mediante el estadístico kappa.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 350 pacientes (edad media 46 años, enfermedad de Crohn 59%). El 11% presentaba actividad clínica. De los pacientes con enfermedad de Crohn, el 44% tenía un brote leve, un 44% un brote moderado y un 12% un brote grave. Los pacientes con colitis ulcerosa presentaban actividad leve, moderada y grave en un 50, 42 y 8% de los casos, respectivamente. Ninguno de los marcadores biológicos estudiados se correlacionó aceptablemente con la actividad clínica (índices kappa≤0,30 en todos los casos).
ConclusionesLa concordancia de los marcadores biológicos con la actividad clínica de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal es notablemente baja.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora