The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation is recommended by most scientific societies to calculate the estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Recently the group Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKP-EPI) has published a new, more precise and accurate equation. We have analysed its behaviour in a group of polypathological patients (PP) and compared it with the classic MDRD-4.version.
Patients and methodMulticenter, observational, descriptive and transversal study. We calculated GFR by MDRD-4 and CKD-EPI in 425 PP. Each stage was assigned according to the GFR: 1: >90; 2: 60–89; 3: 30–59; 4: 15–29; and 5 <15ml/min/1.73m2. We analysed the correlation between both and the patients reclassified by CKD-EPI.
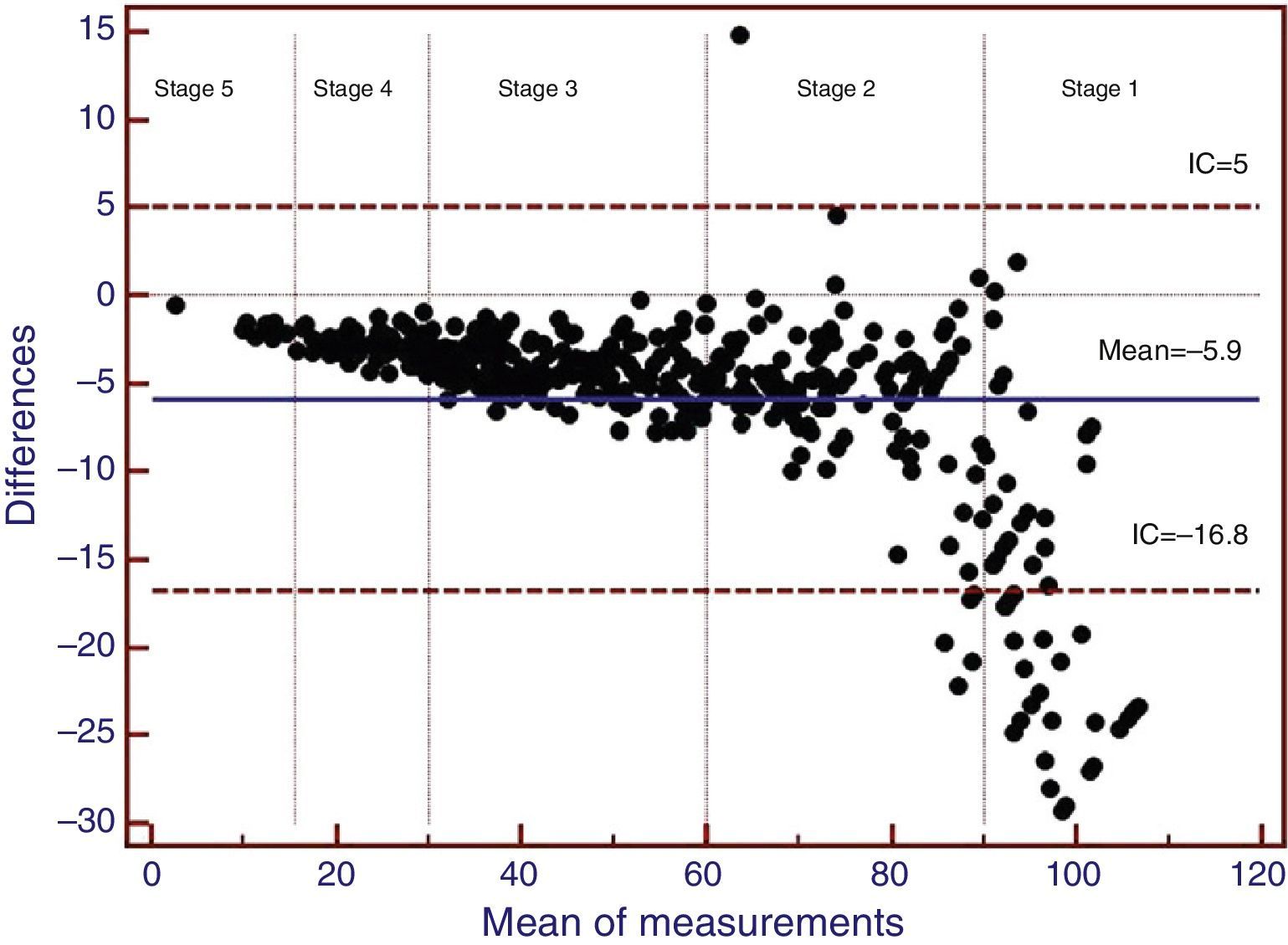
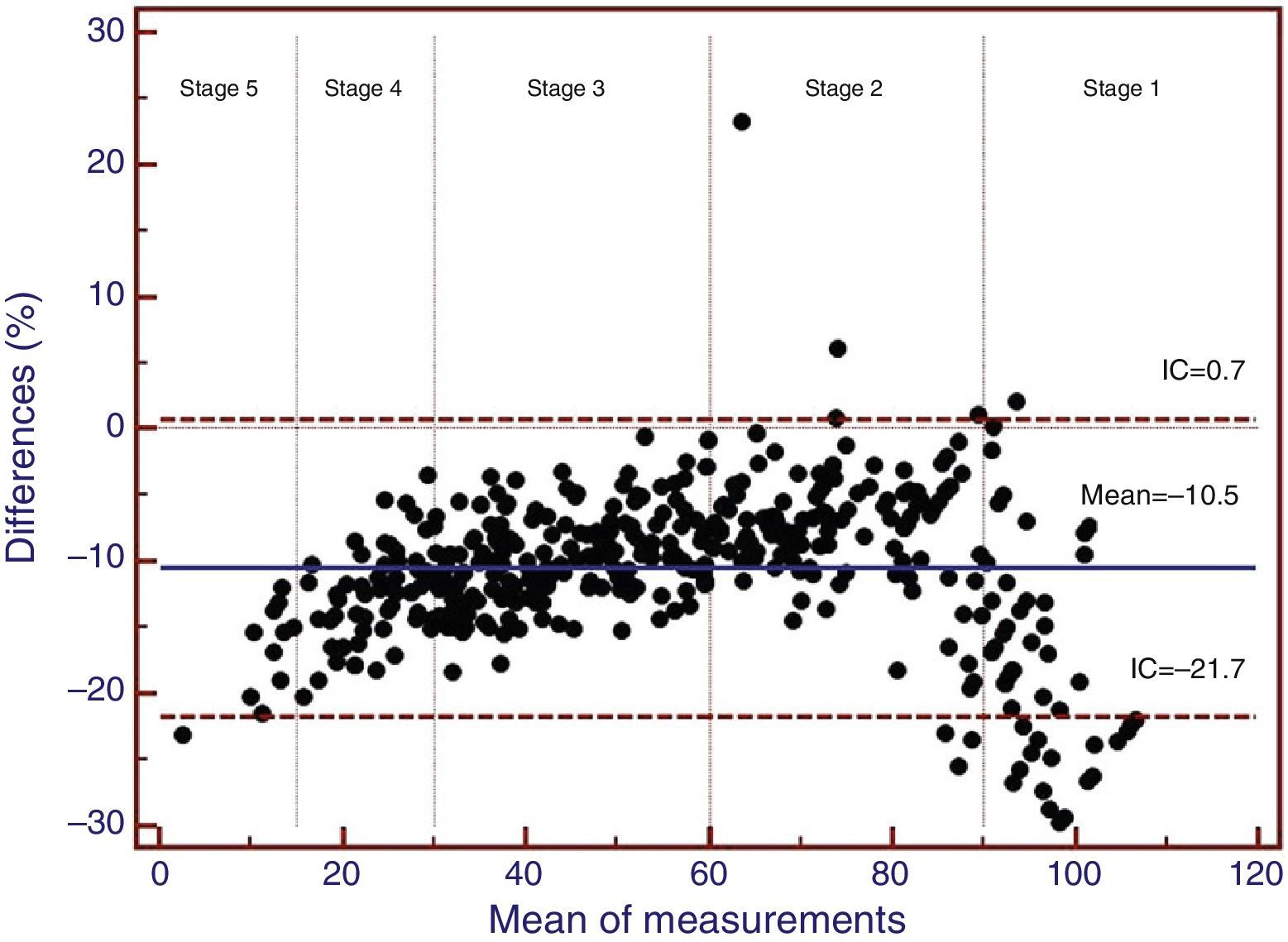
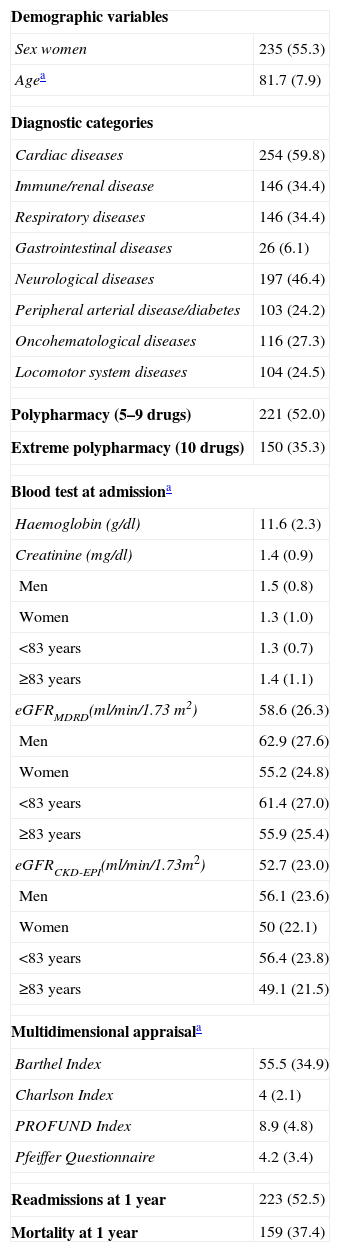
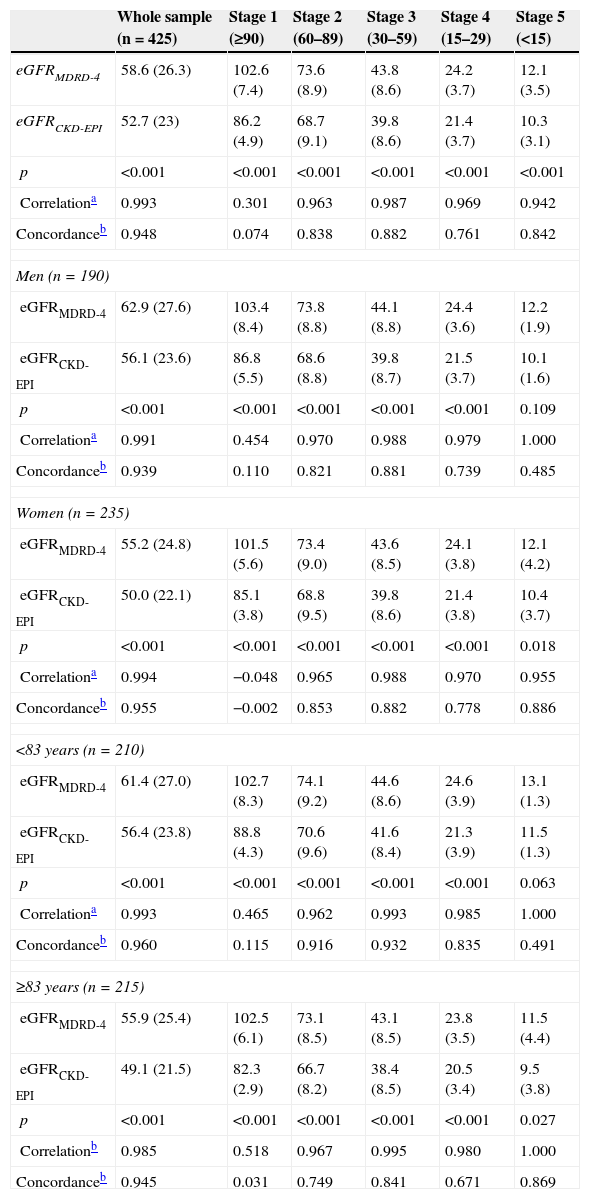
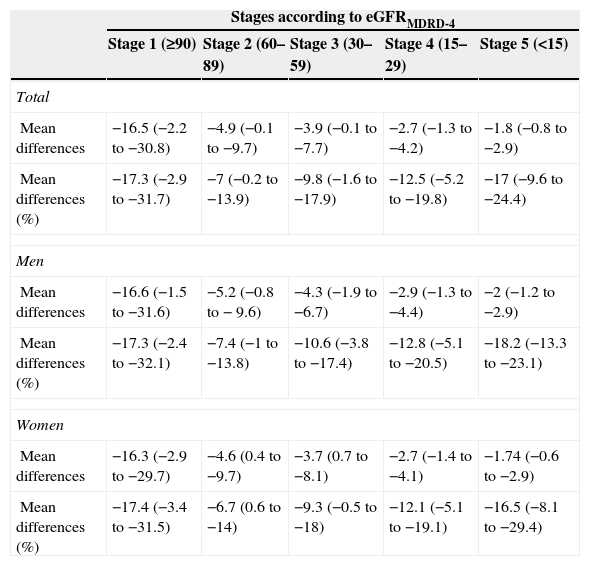
ResultsMean age was (mean [SD]) 81.7 (7.9) years. 55.3% were women. The mean estimated GFR was 58.6 (26.3)ml/min/1.73m2 by MDRD-4 and 52.7 (23.0)ml/min/1.73m2 by CKD-EPI (p<.001; Spearman's Rho correlation and Lin concordance coefficients: 0.993 and 0.948). The Bland–Altman plots reflected lower values for GFR for CKD-EPI equation. In the stage 2, 21.2% were reclassified by CKD-EPI to the stage 3, with women older than 83 years being the more disadvantaged subgroup with 27.3% or reclassification.
ConclusionCKD-EPI equation applied to PP worsens the results of MDRD-4. In general, it originates low values of GFR and increases the degree of renal insufficiency, especially in older women.
La fórmula Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) es la recomendada por la mayoría de las sociedades científicas para el cálculo del filtrado glomerular estimado (FGe). Recientemente el grupo Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) ha publicado una nueva ecuación con mayor exactitud y precisión. Hemos analizado su comportamiento en un grupo de pacientes pluripatológicos (PP) comparándola con la versión clásica MDRD-4.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio multicéntrico, observacional, descriptivo y transversal. Se calculó el FGe por MDRD-4 y CKD-EPI en 425 PP. A cada uno se le asignó un estadio según su FGe: 1: >90; 2: 60-89; 3: 30-59; 4: 15-29; y 5: <15ml/min/1,73 m2. Se analizó la concordancia entre ambas y la reclasificación de pacientes por CKD-EPI.
ResultadosLa edad media (DE) fue de 81,7 (7,9) años. El 55,3% eran mujeres. La media del FGe fue de 58,6 (26,3) ml/min/1,73 m2 según MDRD-4 y de 52,7 (23,0) ml/min/1,73 m2 según CKD-EPI (p<0,001; coeficientes de correlación Rho de Spearman y de concordancia de Lin: 0,993 y 0,948, respectivamente). Los gráficos de Bland-Altman reflejaban valores inferiores de FGe para la ecuación CKD-EPI. En el estadio 2, el 21,2% eran reasignados por CKD-EPI al estadio 3, siendo las mujeres mayores de 83 años el subgrupo más desfavorecido, con el 27,3% de reclasificación.
ConclusionesLa CKD-EPI aplicada al cálculo del FGe en PP empeora los resultados de la estimación mediante MDRD-4. Origina, de forma general, valores de FGe inferiores e incrementa el grado de insuficiencia renal, en especial en mujeres más añosas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora