Presentar nuestra experiencia y analizar la supervivencia de los pacientes hospitalizados con covid-19 y que desarrollaron algún proceso trombótico vascular.
Material y métodosSe incluyó a todos los pacientes consecutivos con covid-19 que fueron atendidos durante los meses de marzo y abril de 2020 en nuestra institución. Se incluyó a pacientes sintomáticos con trombosis venosa profunda (TVP), tromboembolia pulmonar (TEP), ictus isquémico y trombosis arterial periférica (TAP) confirmados objetivamente. Se analizaron las curvas de supervivencia de todos los grupos mediante Kaplan-Meier, test de log rank y regresión de Cox.
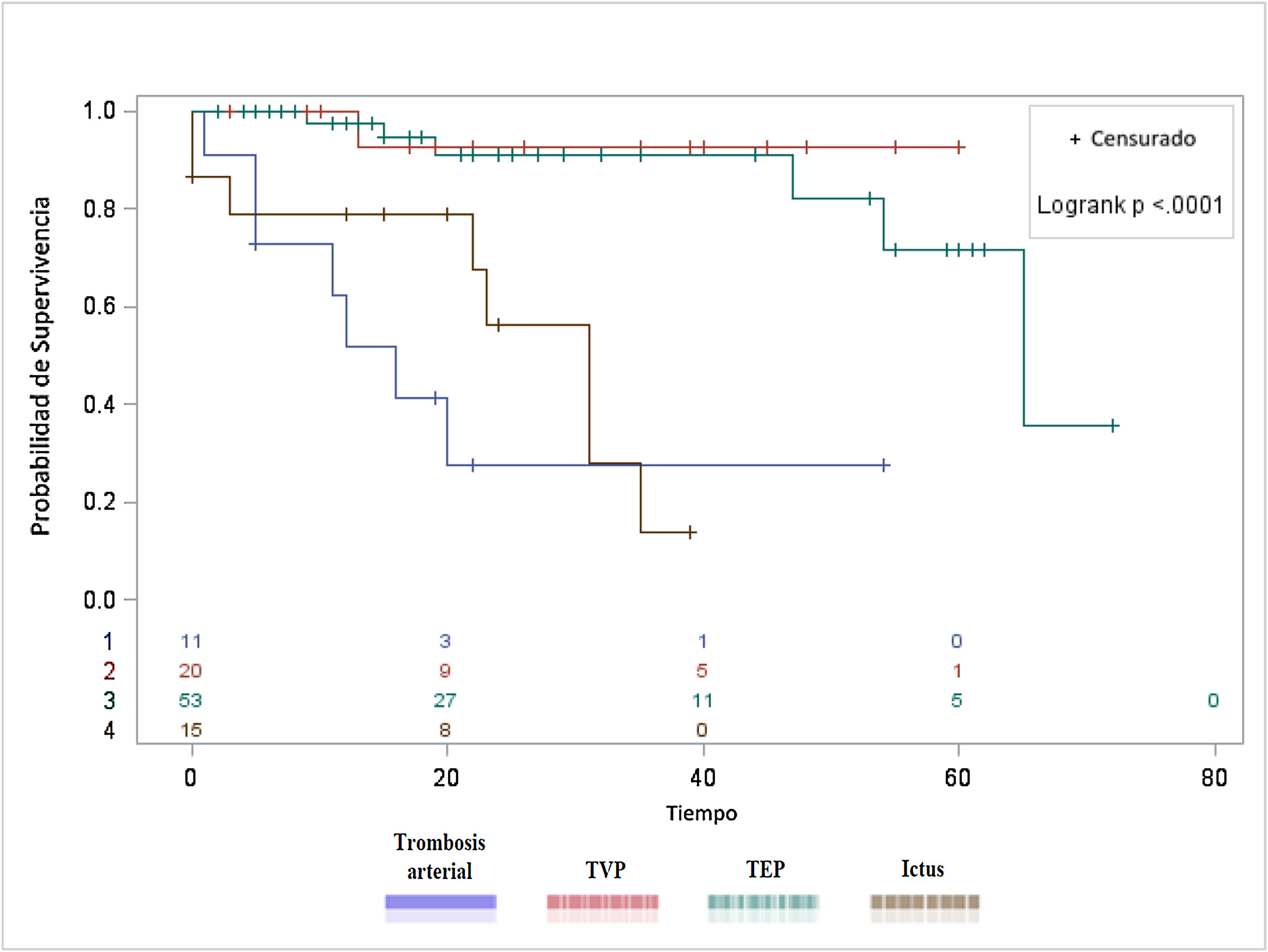
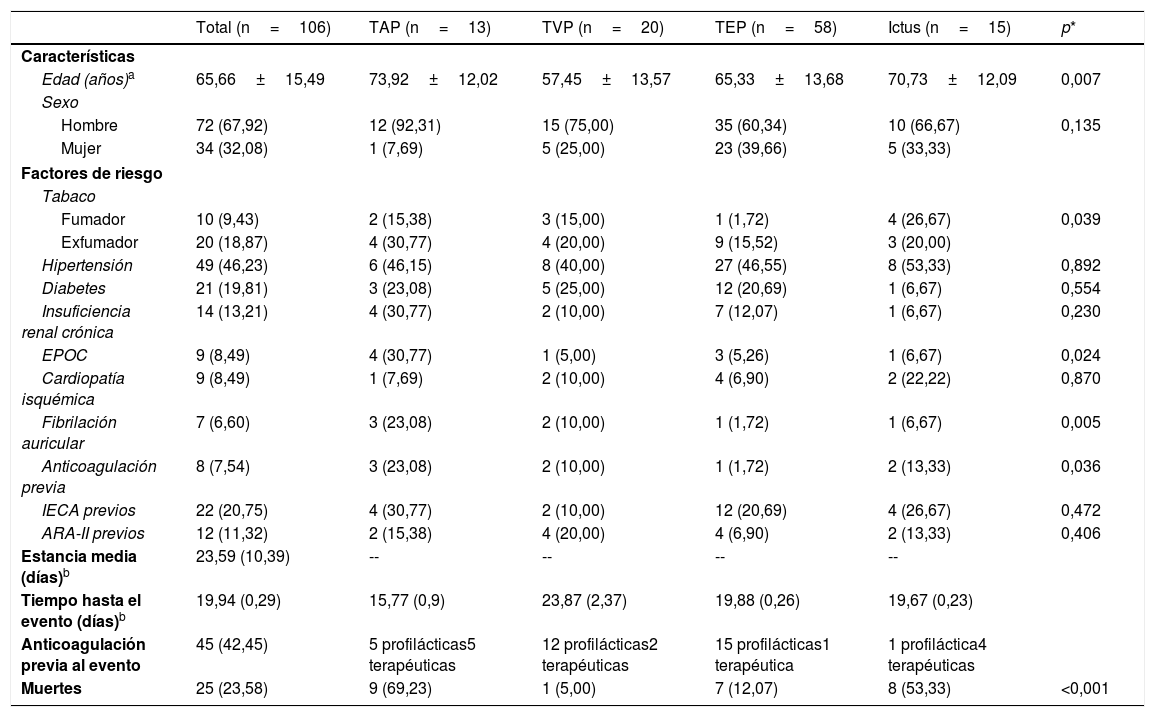
ResultadosDurante el periodo pandémico del 1 de marzo al 30 de abril, fueron atendidos 2.943 pacientes con covid-19 en nuestro centro. De ellos, 106 presentaron algún proceso trombótico vascular sintomático: 13 pacientes tuvieron TAP, 15 ictus, 20 TVP y 58 TEP; otros 11 pacientes mostraron trombosis vasculares múltiples. Aunque la edad media fue de 65 años, fueron de edad más avanzada los que mostraron trombosis arteriales que los que mostraron procesos tromboembólicos venosos. El 67,92% fueron hombres. En total, 25 pacientes murieron durante su ingreso hospitalario (23,58%), con diferencias entre grupos: fue más común en pacientes con TAP (9 pacientes de 13) e ictus isquémico (8 pacientes de 15), que en los de TVP (1 paciente de 20) o TEP (7 pacientes de 58).
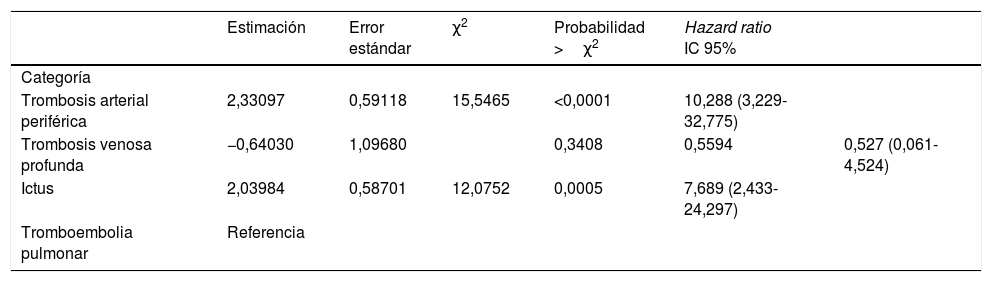
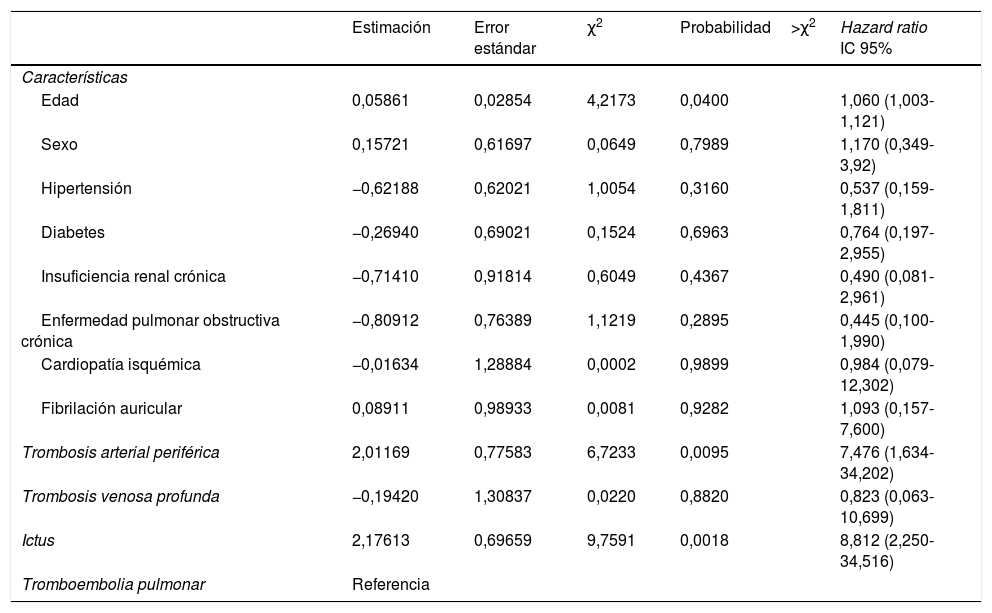
ConclusionesEl riesgo tromboembólico venoso en estos pacientes es mayor que el arterial, pero la trombosis arterial cuando aconteció estuvo asociada a altas tasas de mortalidad. La supervivencia fue mejor en los pacientes con TVP y TEP que en los pacientes con ictus isquémico o TAP.
To analyze the survival of patients hospitalized with covid-19 and who presented some vascular thrombotic complication.
Material and methodsAll consecutive patients with covid-19 who were treated during the months of March and April 2020 at our institution were included. All patients were symptomatic and the thrombotic event objectively confirmed. Patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), ischemic stroke, and peripheral arterial thrombosis (PAT) were included. Survival curves for all groups were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier with log rank test, and Cox regression.
ResultsDuring the pandemic period from March-1 to April-30, 2943 patients were treated with confirmed covid-19 in our center. Of them, 106 patients showed some symptomatic vascular thrombosis: 13 patients had PAT, 15 ischemic stroke, 20 DVT and 58 PE. Another 11 patients presented multiple vascular thrombosis. Although the mean age was 65 years, there were differences between groups being older those patients with arterial thrombosis. A 67.92% were men. In total, 25 patients died during their hospital admission (23.58%), with differences between groups, being more common in patients with PAT (9 patients out of 13) and ischemic stroke (8 patients out of 15), than in those with DVT (1 patient out of 20) or PE (7 patients out of 58).
ConclusionsThe venous thromboembolic risk in these patients is greater than the arterial, but arterial thrombosis when it occurs was associated with high mortality rates. Survival was better in patients with DVT and PE than in patients with ischemic stroke or PAT.