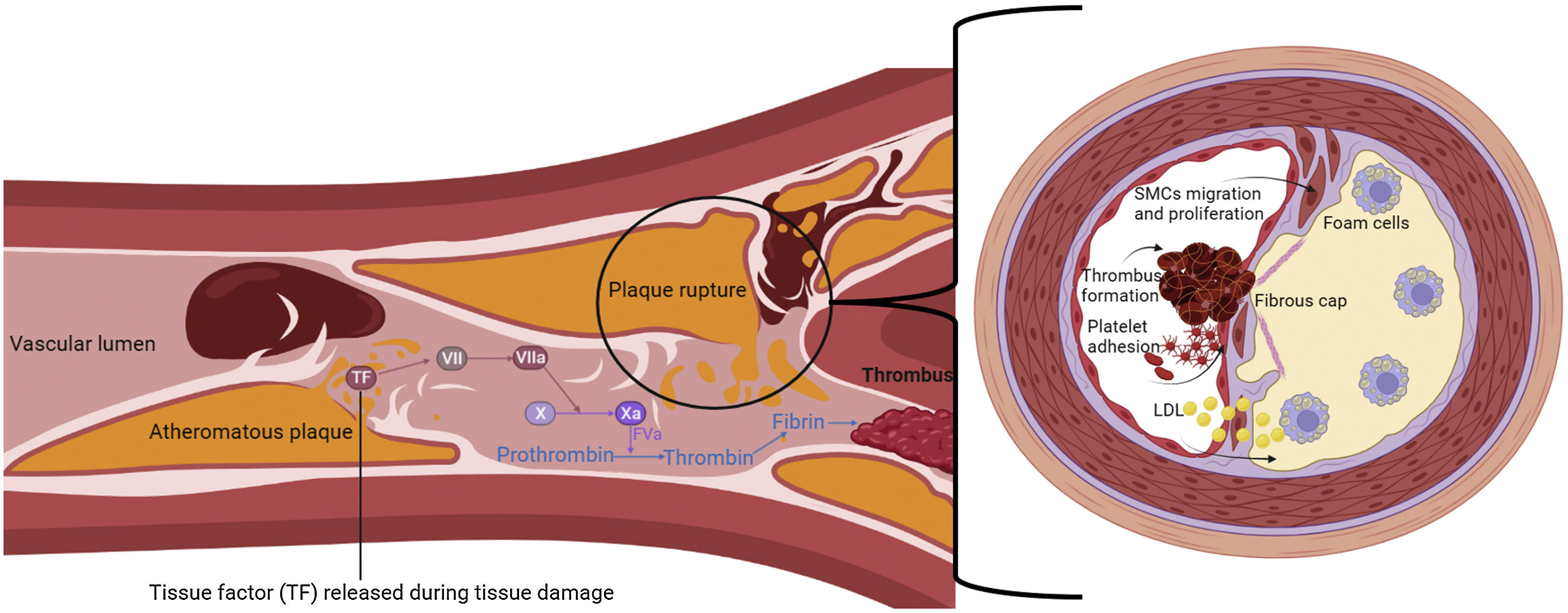
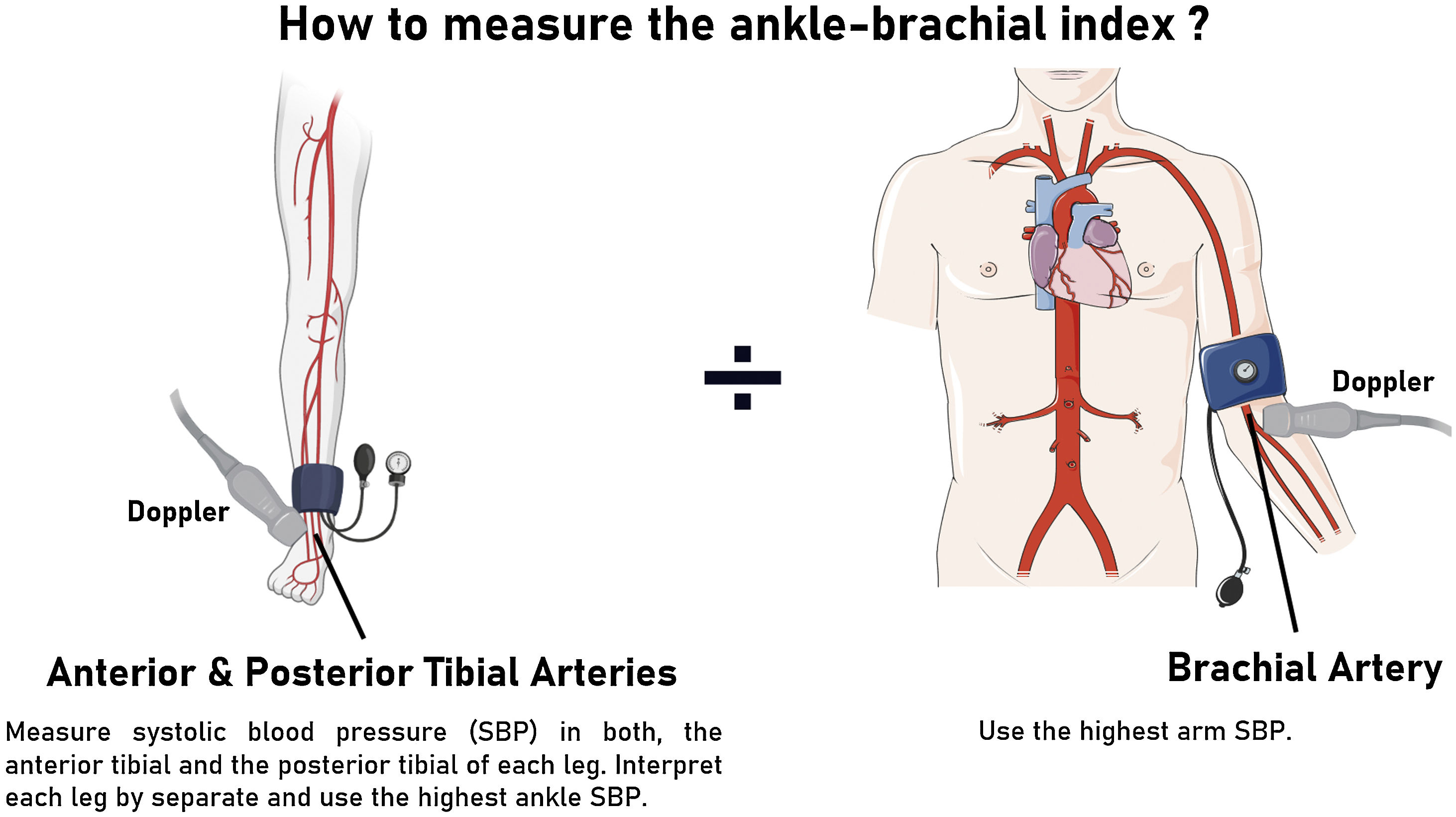
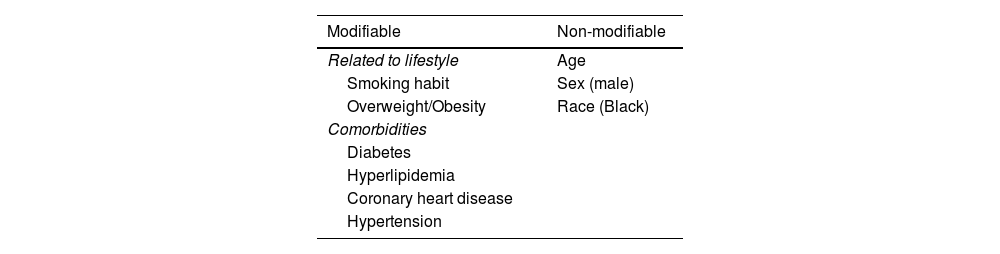
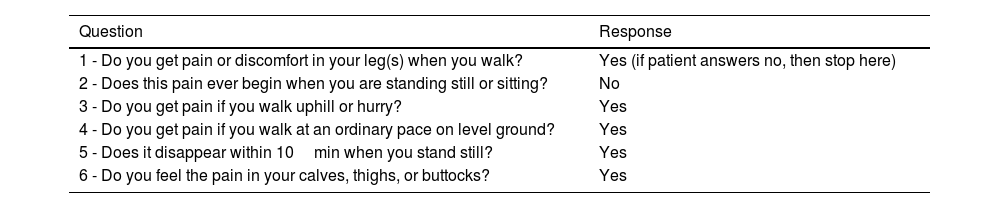
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition related to atherosclerosis affecting >200 million people worldwide, and it increases cardiovascular morbidity (mainly from myocardial infarction and stroke) and mortality. Indeed, PAD patients are classified as patients at very high cardiovascular risk. The most common manifestation of PAD is intermittent claudication, which is associated with reduced mobility and leg pain. Nevertheless, asymptomatic PAD is the most frequent form of PAD worldwide; therefore, it remains underdiagnosed and undertreated. The major risk factors for PAD are smoking, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, overweight/obesity, age, male sex, and black race. Hence, the first and most relevant approach in PAD treatment is lifestyle management, with measures such as smoking cessation, healthy diet, weight loss, and regular physical exercise. This should also be supported by an optimal pharmacological approach including lipid-lowering drugs, antihypertensive drugs, antidiabetic agents, and antithrombotics.
La enfermedad arterial periférica (EAP) es una afección relacionada con la aterosclerosis que afecta a más de 200 millones de personas en todo el mundo y aumenta la morbilidad cardiovascular (principalmente por infarto de miocardio e ictus) y la mortalidad. De hecho, los pacientes con EAP se clasifican como pacientes de muy alto riesgo cardiovascular. La manifestación más común de la EAP es la claudicación intermitente, que se asocia con movilidad reducida y dolor en las piernas. No obstante, la EAP asintomática es la forma más frecuente de EAP en todo el mundo, razón por la cual esta continúa estando infradiagnosticada e infratratada. Los principales factores de riesgo de la EAP son el tabaquismo, la diabetes mellitus, la hiperlipidemia, la hipertensión, el sobrepeso/obesidad, la edad, el sexo masculino y la raza negra. Por lo tanto, el primer enfoque y el más relevante en el tratamiento de la EAP es el manejo del estilo de vida, con medidas como el abandono del hábito tabáquico, una dieta saludable, la pérdida de peso y el ejercicio físico regular. Esto también debe estar respaldado por un enfoque farmacológico óptimo que incluya medicamentos hipolipemiantes, medicamentos antihipertensivos, agentes antidiabéticos y antitrombóticos.