To present methodical approach of preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) as an option for an unaffected pregnancy in reproductive-age couples who have a genetic risk of the X-linked dominant peripheral neuropathy Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1 disease.
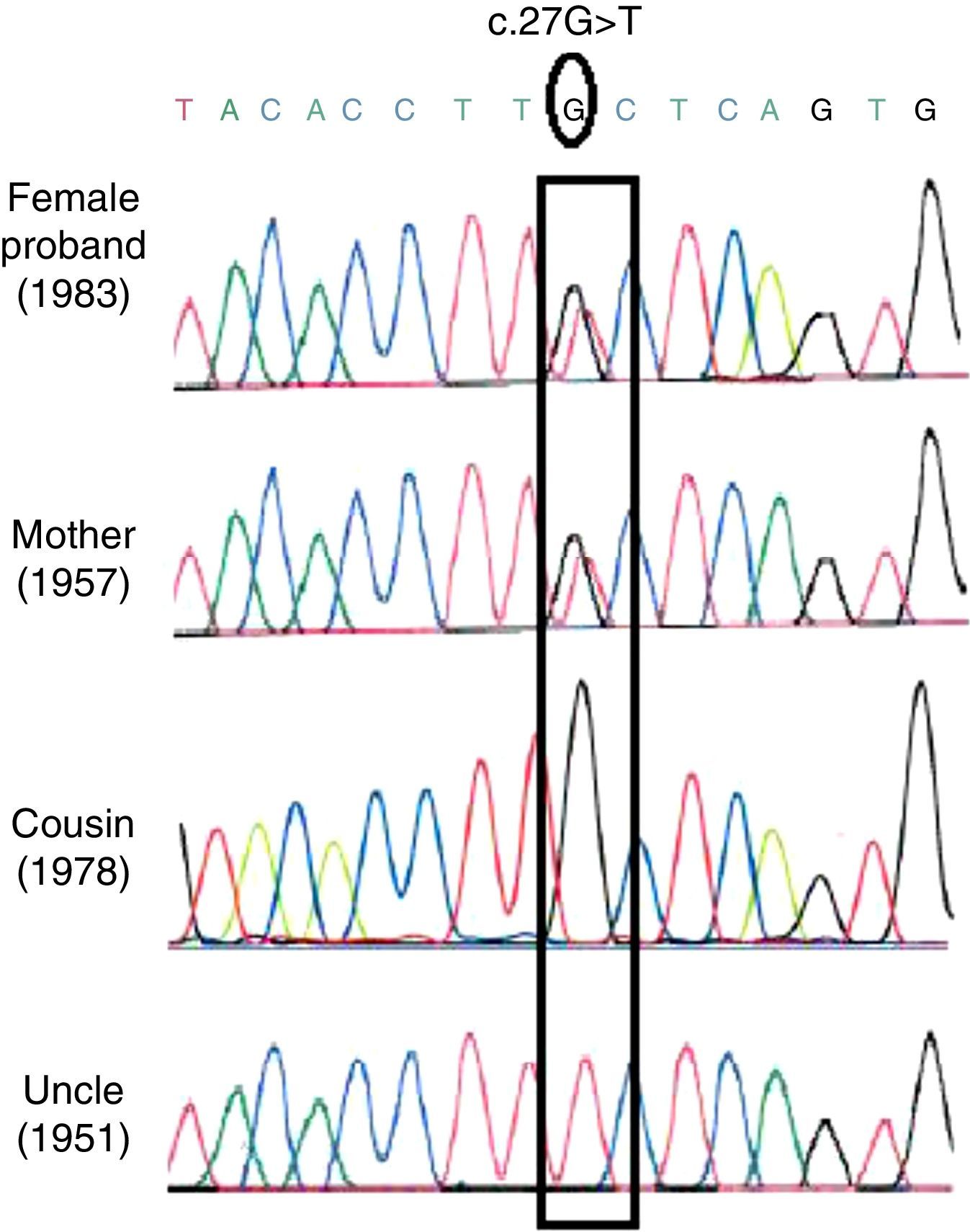
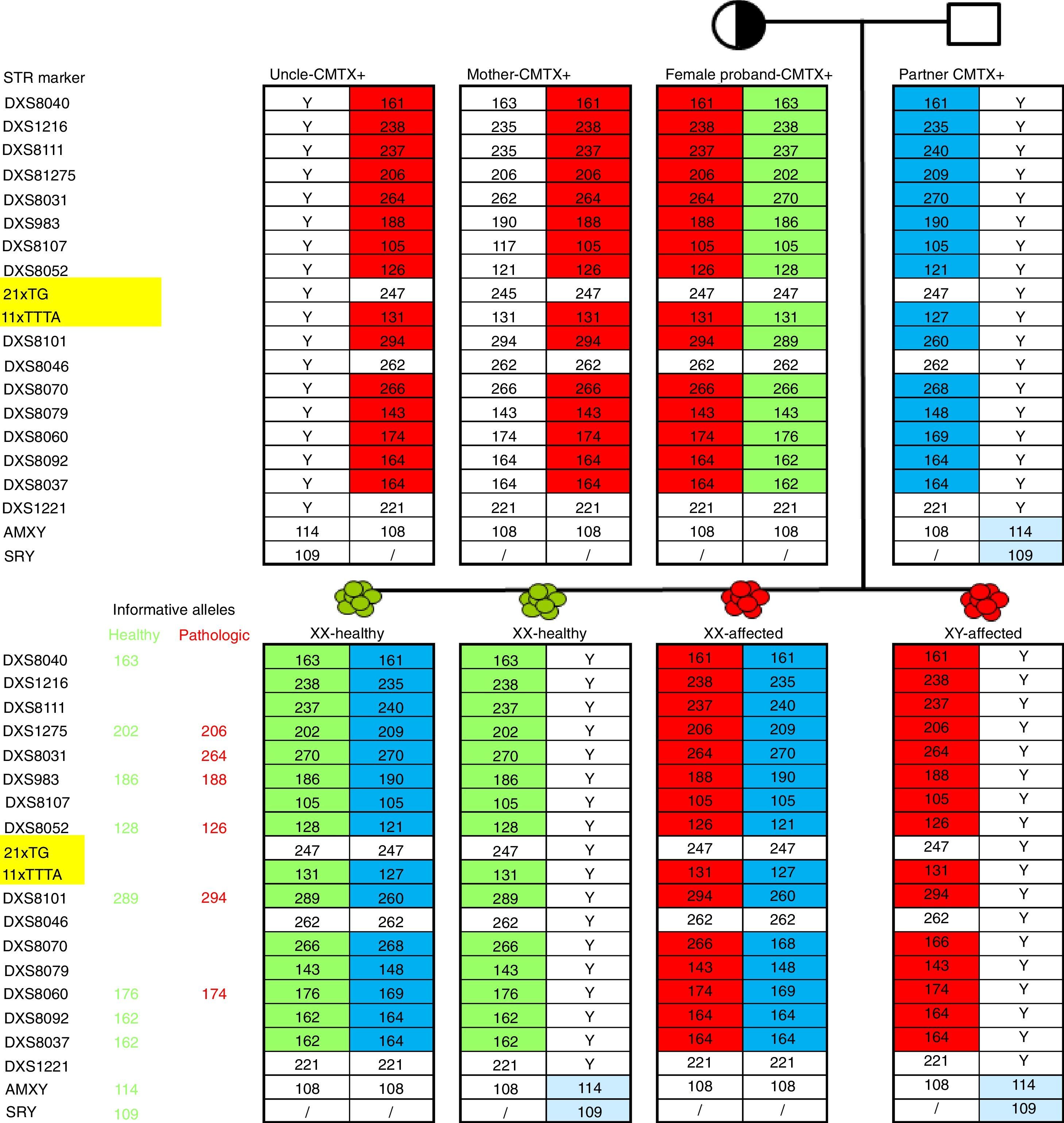
Patients and methodsWe performed PGD of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1 disease using haplotyping/indirect linkage analysis, when during analysis we reach to exclude embryos that carry a high-risk haplotype linked to the causal mutation p.Leu9Phe in the GJB1 gene.
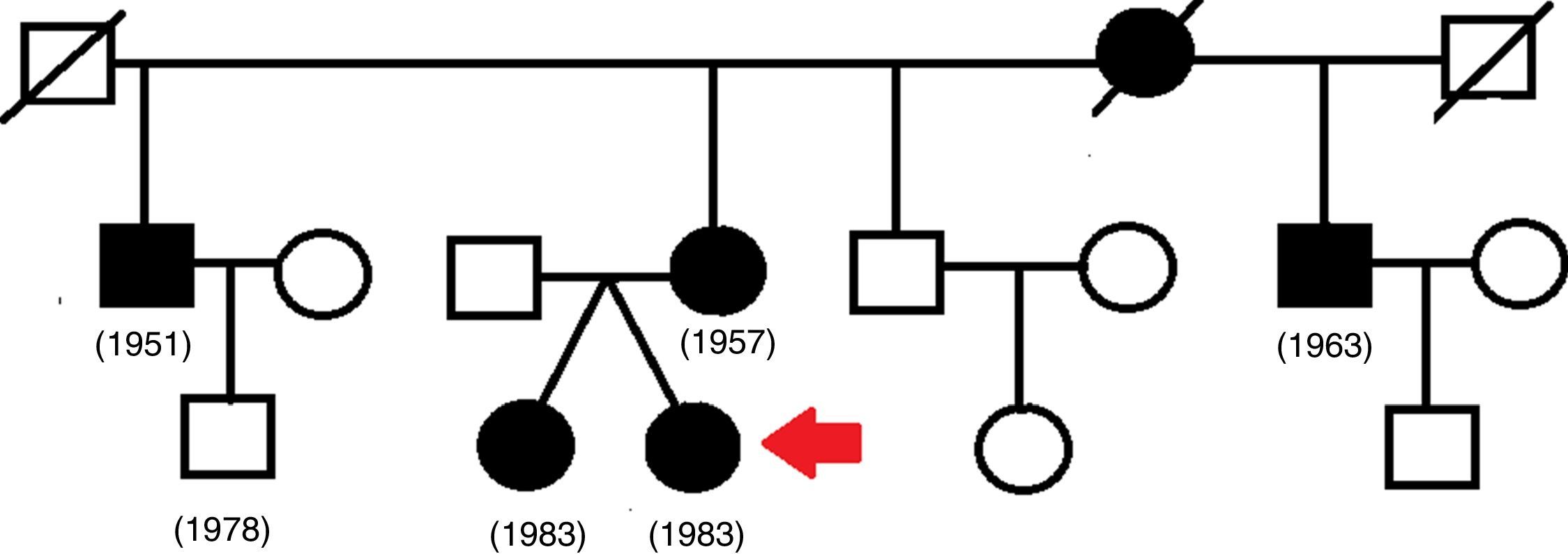
ResultsWithin the PGD cycle, we examined 4 blastomeres biopsied from cleavage-stage embryos and recommended 3 embryos for transfer. Two embryos were implanted into the uterus; however, it resulted in a singleton pregnancy with a male descendant. Three years later, the couple returned again with spontaneous gravidity. A chorionic biopsy examination of this gravidity ascertained the female sex and a pericentric inversion of chromosome 5 in 70% of the cultivated foetal cells.
ConclusionUsing indirect linkage analysis, PGD may help to identify genetic X-linked defects within embryos during screening, thereby circumventing the potential problems with abortion.
Presentar un enfoque metodológico del diagnóstico genético preimplantacional (DGP) como opción para embarazos no afectados en parejas en edad reproductiva con riesgo genético de neuropatía periférica dominante por enfermedad de Charcot-Marie-Tooth tipo 1 ligada al cromosoma X.
Pacientes y métodosLlevamos a cabo el DGP de enfermedad de Charcot-Marie-Tooth tipo 1 ligada al cromosoma X utilizando un análisis de ligamiento indirecto/haplotificación, durante el cual logramos excluir los embriones portadores de un haplotipo de alto riesgo ligado a la mutación causal p.Leu9Phe en el gen GJB1.
ResultadosDentro del ciclo de DGP, examinamos 4 blastómeros biopsiados de los embriones en fase de división, y recomendamos la transferencia de 3 embriones. Dos embriones fueron implantados en el útero; sin embargo, el resultado fue un embarazo único con un descendiente varón. Transcurridos 3 años, la pareja regresó con un embarazo espontáneo. La biopsia coriónica de este embarazo reveló el sexo femenino y una inversión pericéntrica del cromosoma 5 en el 70% de las células fetales cultivadas.
ConclusiónUtilizando el análisis de ligamiento indirecto, el DGP puede ayudar a identificar durante el cribado los defectos genéticos ligados al cromosoma X, eludiendo por tanto los problemas potenciales con el aborto.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora