Remdesivir seems to reduce the risk of hospitalization and improve clinical outcome in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
ObjectivesTo compare the clinical outcome of COVID-19 hospitalized patients treated with remdesivir plus dexamethasone versus dexamethasone alone, according to their vaccination status.
Material and methodsA retrospective observational study was carried out in 165 patients hospitalized for COVID-19 from October 2021 to January 2022. Multivariate logistic regression, Kaplan–Meier and the log-rank tests were used to evaluate the event (need for ventilation or death).
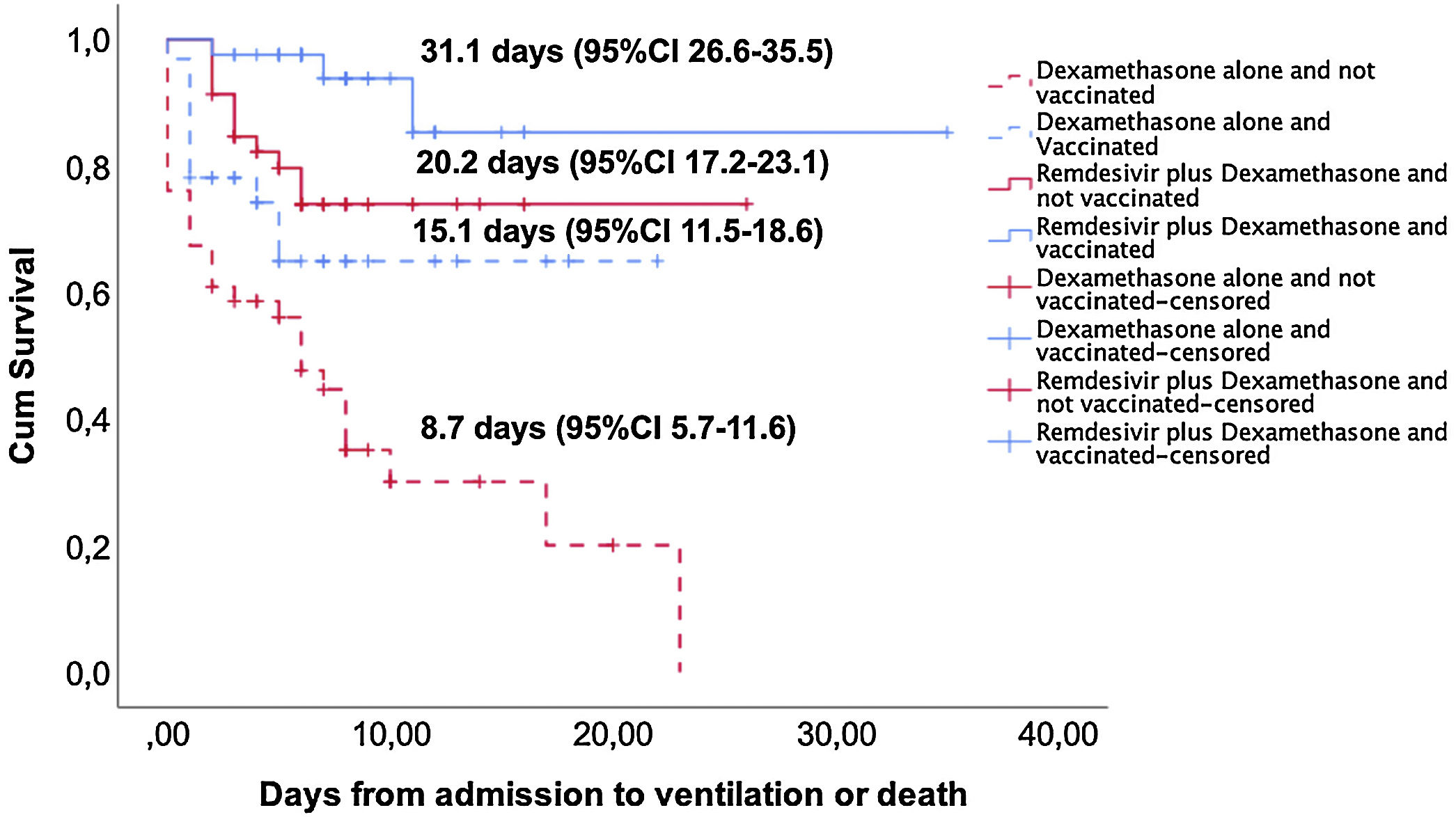
ResultsPatients treated with remdesivir plus dexamethasone (n=87) compared with dexamethasone alone (n=78) showed similar age (60±16, 47–70 vs. 62±37, 51–74 years) and number of comorbidities: 1 (0–2) versus 1.5 (1–3). Among 73 fully vaccinated patients, 42 (47.1%) were in remdesivir plus dexamethasone and 31 (41%) in dexamethasone alone. Patients treated with remdesivir plus dexamethasone needed intensive care less frequently (17.2% vs. 31%; p=0.002), high-flow oxygen (25.3% vs. 50.0%; p=0.002) and non-invasive mechanical ventilation (16.1% vs. 47.4%; p<0.001). Furthermore, they had less complications during hospitalization (31.0% vs. 52.6%; p=0.008), need of antibiotics (32.2% vs. 59%; p=0.001) and radiologic worsening (21.8% vs. 44.9%; p=0.005). Treatment with remdesivir plus dexamethasone (aHR, 0.26; 95% CI: 0.14–0.48; p<0.001) and vaccination (aHR 0.39; 95% CI: 0.21–0.74) were independent factors associated with lower progression to mechanical ventilation or death.
ConclusionsRemdesivir in combination with dexamethasone and vaccination independently and synergistically protects hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen therapy from progression to severe disease or dead.
Remdesivir parece reducir el riesgo de hospitalización y mejorar el resultado clínico en pacientes hospitalizados con COVID-19.
ObjetivosComparar el desenlace clínico de pacientes hospitalizados con COVID-19 tratados con remdesivir más dexametasona vs. dexametasona sola, según su estado de vacunación.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio observacional retrospectivo en 165 pacientes hospitalizados por COVID-19 desde octubre de 2021 hasta enero de 2022. Se consideró como evento la necesidad de ventilación o muerte.
ResultadosLos pacientes tratados con remdesivir más dexametasona (n=87) en comparación con dexametasona sola (n=78) mostraron una edad similar (60±16, 47-70 vs. 62±37, 51-74 años) y número de comorbilidades: 1 (0-2) vs. 1,5 (1-3). Entre 73 pacientes completamente vacunados, 42 (47,1%) estaban en remdesivir más dexametasona y 31 (41%) en dexametasona sola. Los pacientes tratados con remdesivir más dexametasona necesitaron cuidados intensivos con menos frecuencia (17,2 vs. 31%; p=0,002), oxígeno de alto flujo (25,3 vs. 50%; p=0,002) y ventilación mecánica no invasiva (16,1 vs. 47,4%, p<0,001). Además, tuvieron menos complicaciones durante la hospitalización (31 vs. 52,6%; p=0,008), necesidad de antibióticos (32,2 vs. 59%; p=0,001) y empeoramiento radiológico (21,8 vs. 44,9%; p=0,005). El tratamiento con remdesivir más dexametasona (aHR, 0,26; IC 95% 0,14-0,48; p<0,001) y la vacunación (aHR 0,39; IC 95% 0,21-0,74>) fueron factores independientes asociados con una menor progresión a ventilación mecánica o muerte.
ConclusionesRemdesivir en combinación con dexametasona protegieron de forma independiente y sinérgica a los pacientes hospitalizados con COVID-19 que requieren oxigenoterapia de la progresión a la enfermedad grave o la muerte.