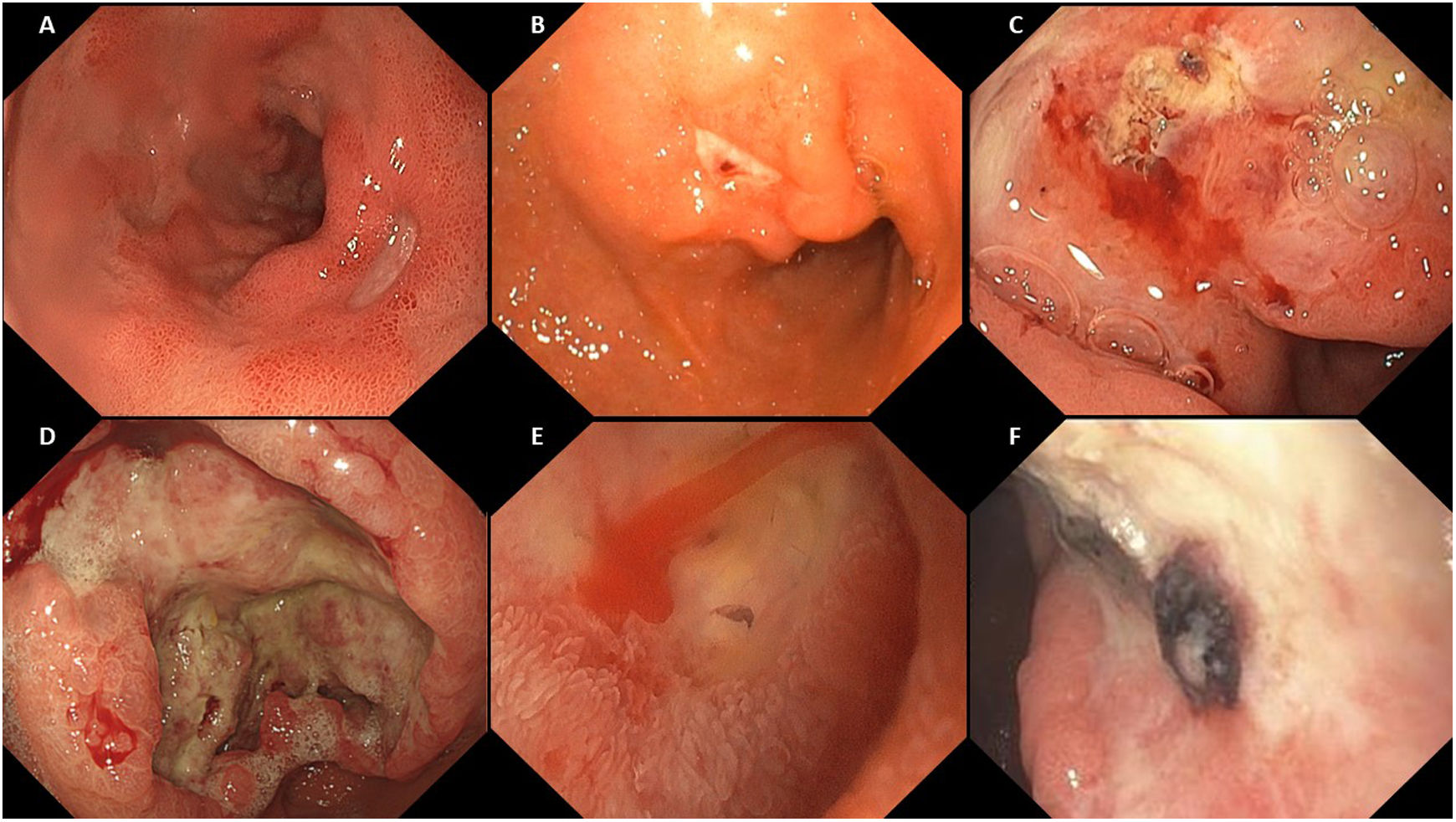
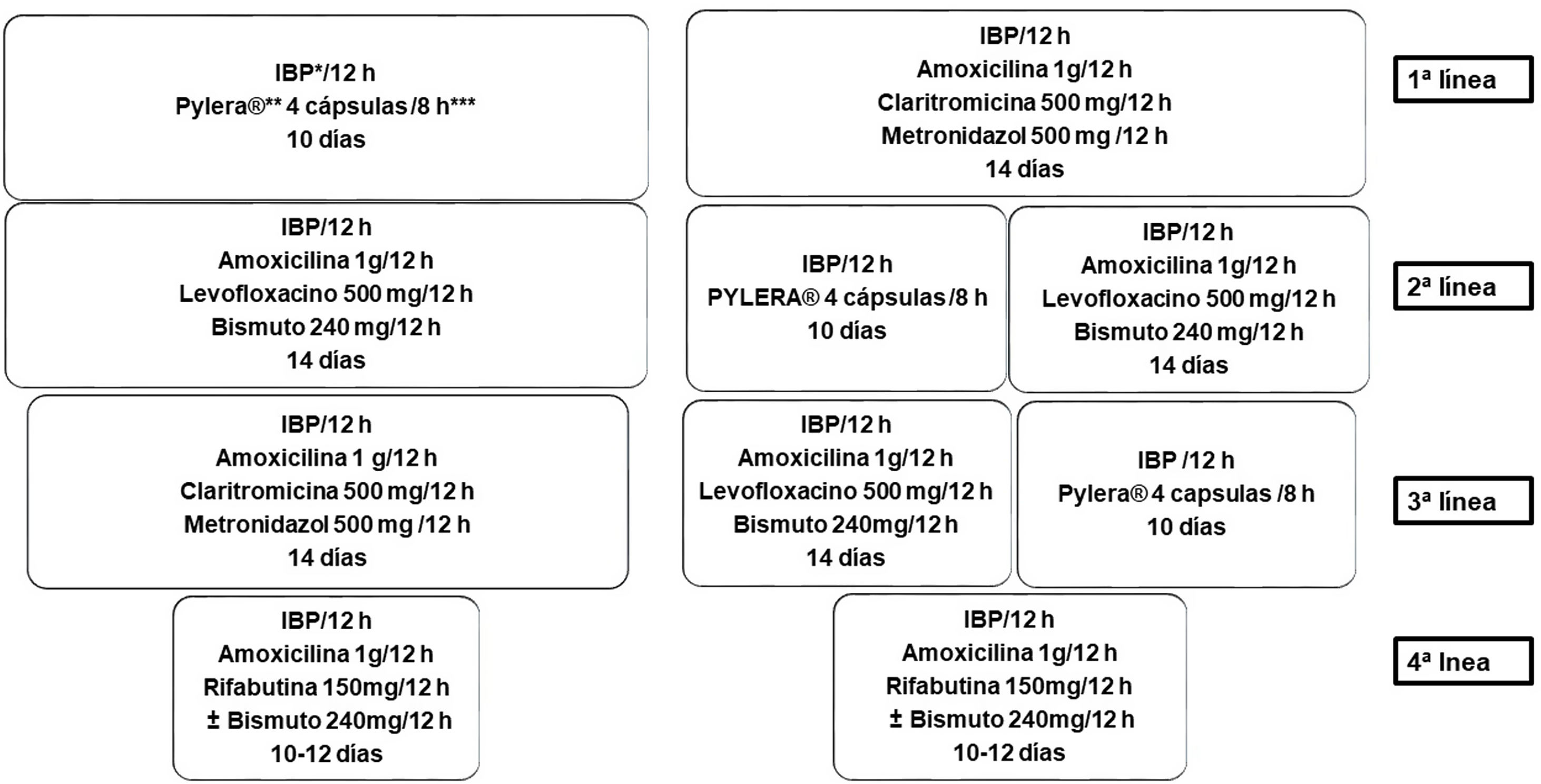
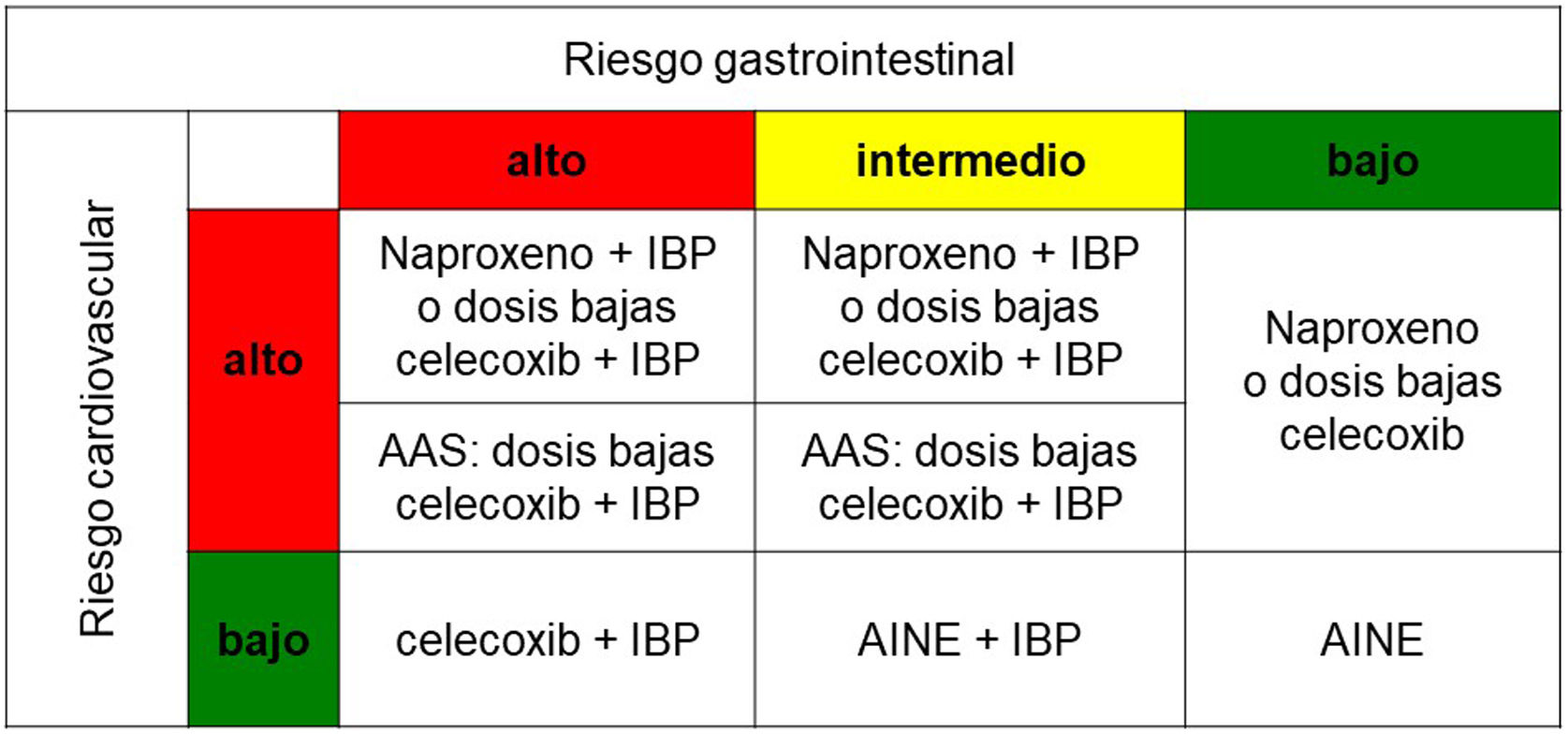
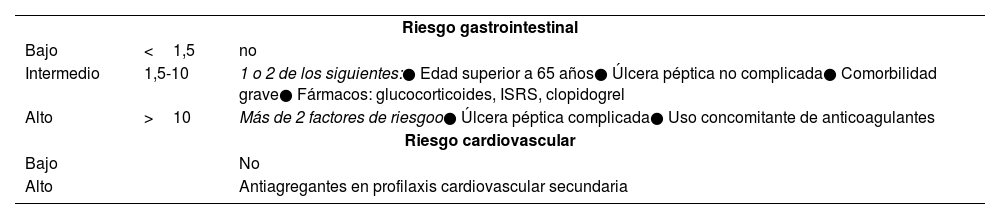
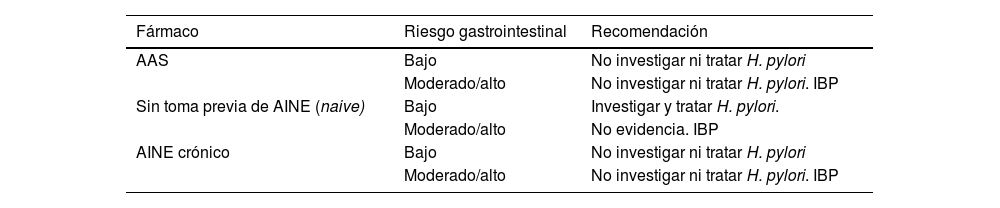
La enfermedad ulcerosa péptica es una patología frecuente; aunque su incidencia ha disminuido en los últimos años, sigue siendo una causa importante de morbimortalidad asociada a un elevado gasto sanitario. Los factores de riesgo más importantes son la infección por Helicobacter pylori(H. pylori) y el uso de antiinflamatorios no esteroideos. La mayoría de los pacientes con enfermedad ulcerosa péptica permanecen asintomáticos, siendo la clínica más frecuente la dispepsia, a menudo característica (dispepsia ulcerosa). También puede comenzar con complicaciones como hemorragia digestiva alta, perforación o estenosis. La técnica diagnóstica de elección es la endoscopia digestiva alta. El tratamiento con inhibidores de la bomba de protones, la erradicación de H. pylori y evitar el consumo de antiinflamatorios no esteroideos son la base del tratamiento. Sin embargo, la prevención es la mejor estrategia, incluye una adecuada indicación de inhibidores de la bomba de protones, la investigación y tratamiento de H. pylori, evitar los antiinflamatorios no esteroideos o utilizar aquellos menos gastrolesivos.
Peptic ulcer disease is a frequent pathology; although the incidence has decreased in recent years, it continues to be an important cause of morbidity and mortality associated with high healthcare costs. The most important risk factors are Helicobacter pylori(H. pylori) infection and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Most patients with peptic ulcer disease remain asymptomatic, with dyspepsia being the most frequent and often characteristic symptom. It can also debut with complications such as upper gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation or stenosis. The diagnostic technique of choice is upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Treatment with proton pump inhibitors, eradication of H. pylori and avoiding the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the basis of treatment.
However, prevention is the best strategy, it includes an adequate indication of proton pump inhibitors, investigation and treatment of H. pylori, avoiding non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or using those that are less gastrolesive.