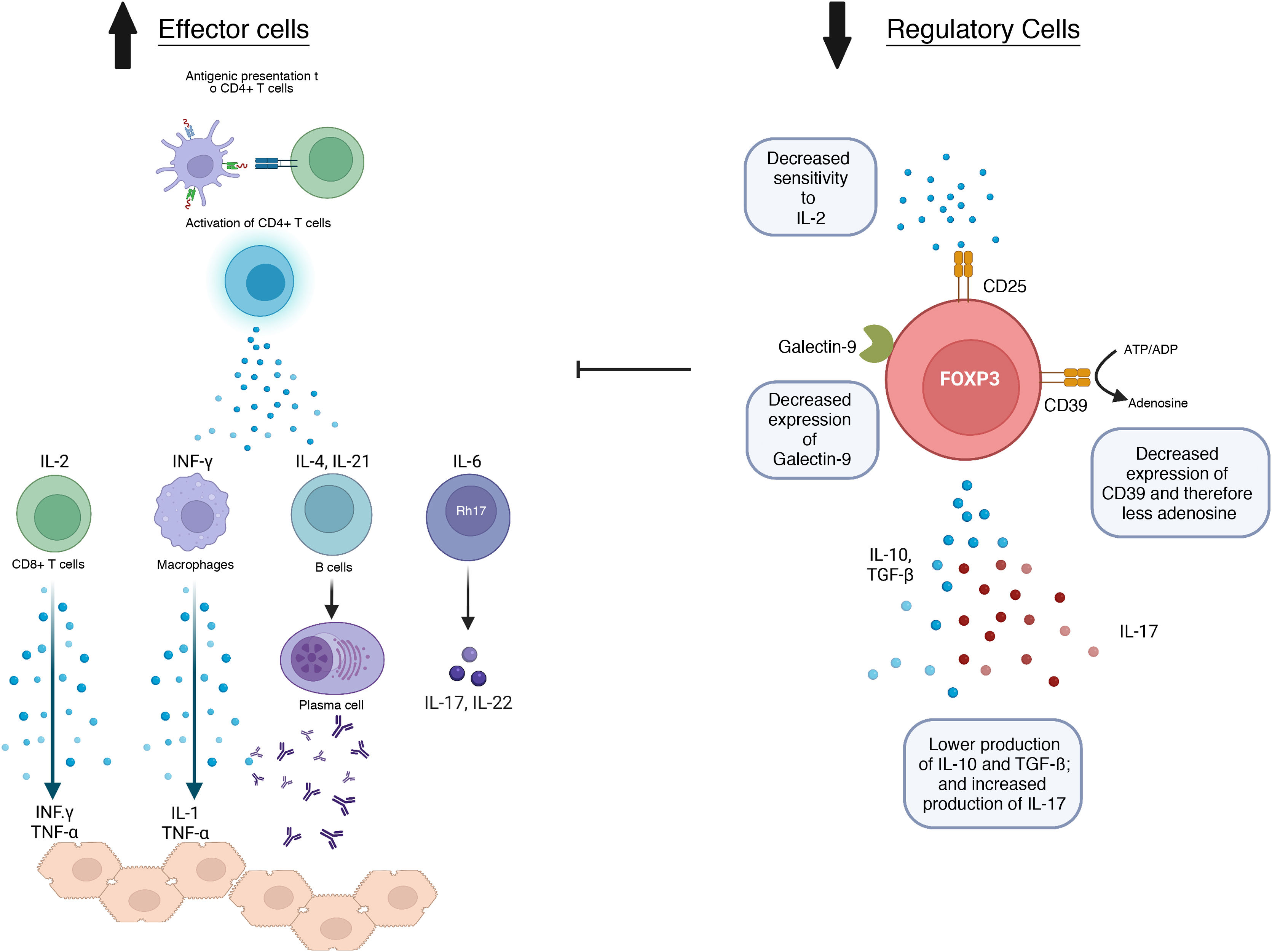
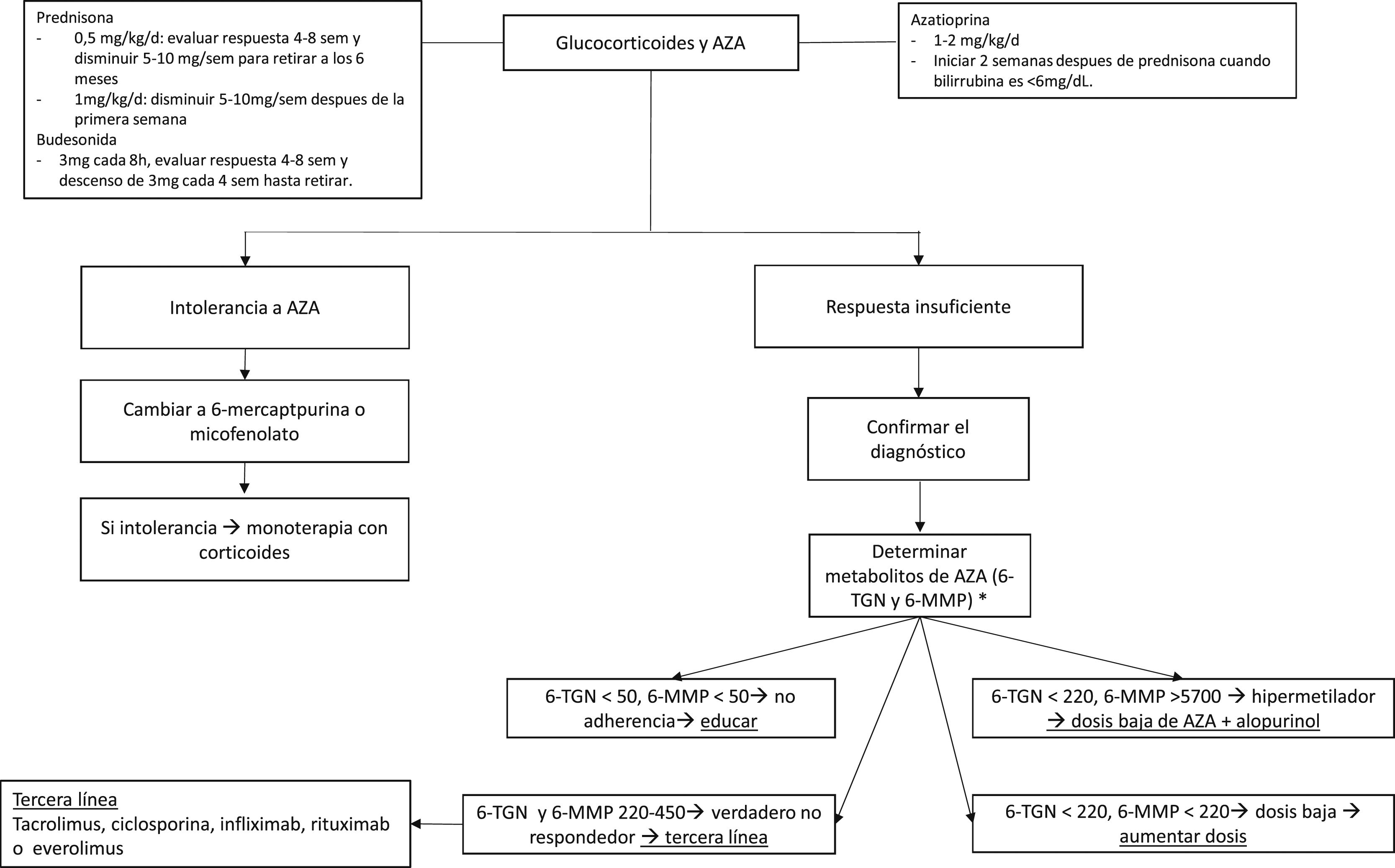
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the liver. The etiology is partly unknown and commonly affects women of all ages. It is characterised by increase in transaminase and immunoglobulin G levels, autoantibodies, and portal inflammatory infiltrate with interface hepatitis in the liver biopsy. The treatment is based on the combination of corticoids and azathioprine, but 20%–40% of patients require second- or third-line therapies due to intolerance or insufficient response. Here, we will revise the most important aspects regarding the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune hepatitis emphasizing the challenges faced in clinical practice.
La hepatitis autoinmune es una enfermedad crónica del hígado de etiología desconocida y que afecta generalmente mujeres de cualquier edad. Se caracteriza por elevación de las transaminasas e inmunoglobulina G, autoanticuerpos, e infiltrado inflamatorio portal con hepatitis de interfase en la biopsia hepática. El tratamiento generalmente se basa en la combinación de glucocorticoides y azatioprina. Sin embargo, 20%–40% de los pacientes requieren tratamientos de segunda o tercera línea por intolerancia o respuesta insuficiente. Aquí se revisarán los aspectos más importantes del diagnóstico y tratamiento de la hepatitis autoinmune con énfasis en los retos que se presentan en la práctica clínica.