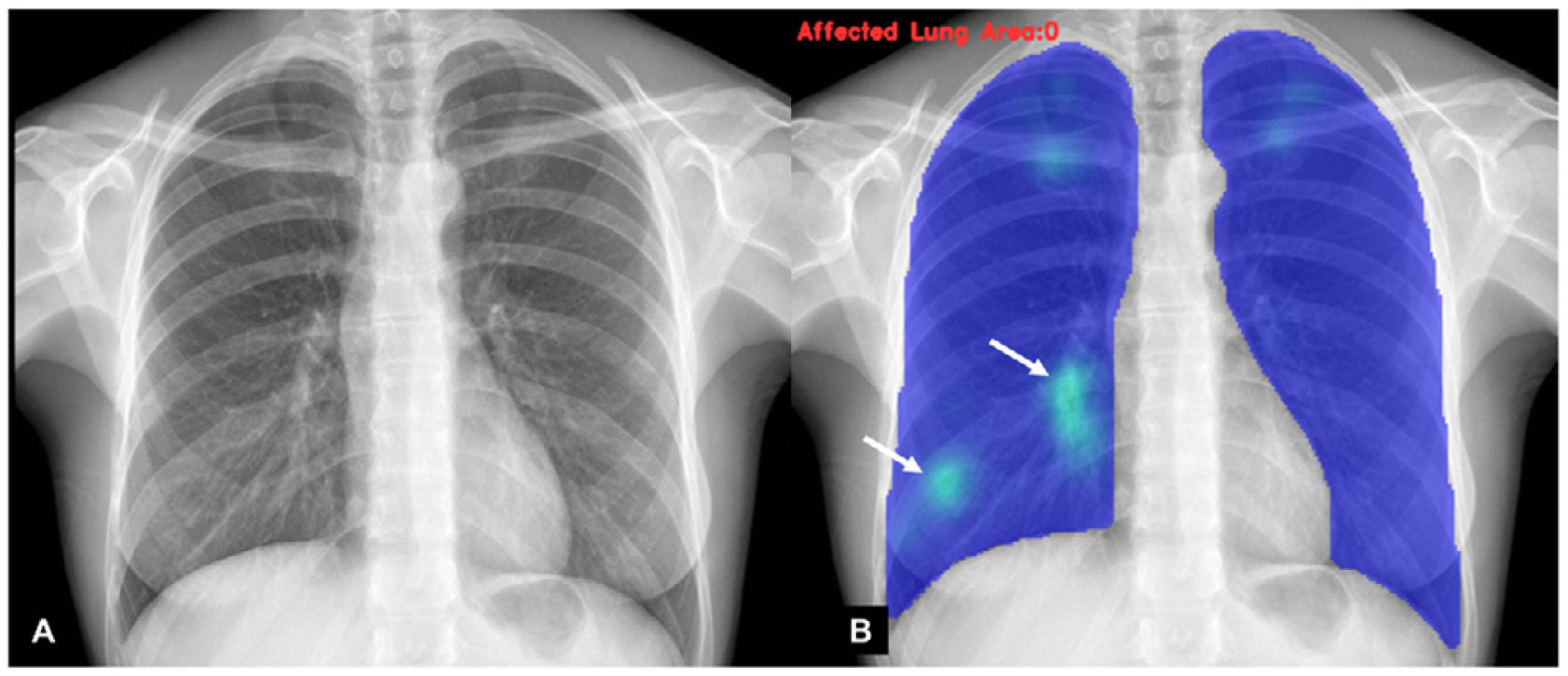
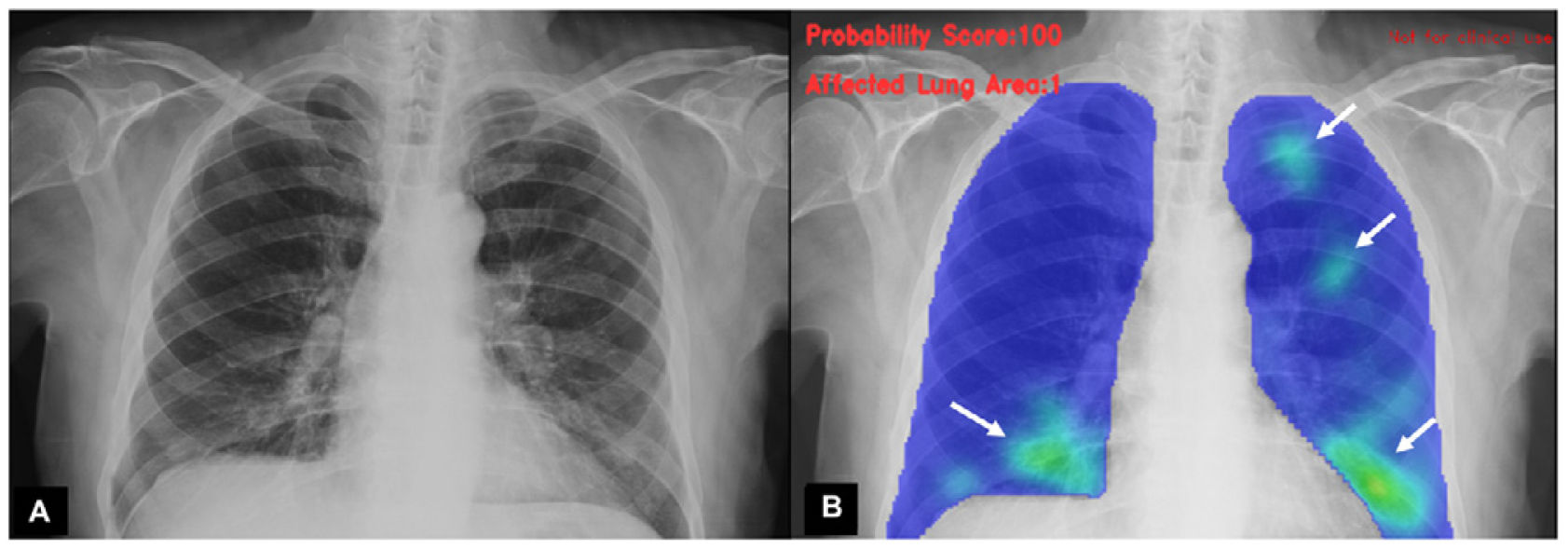
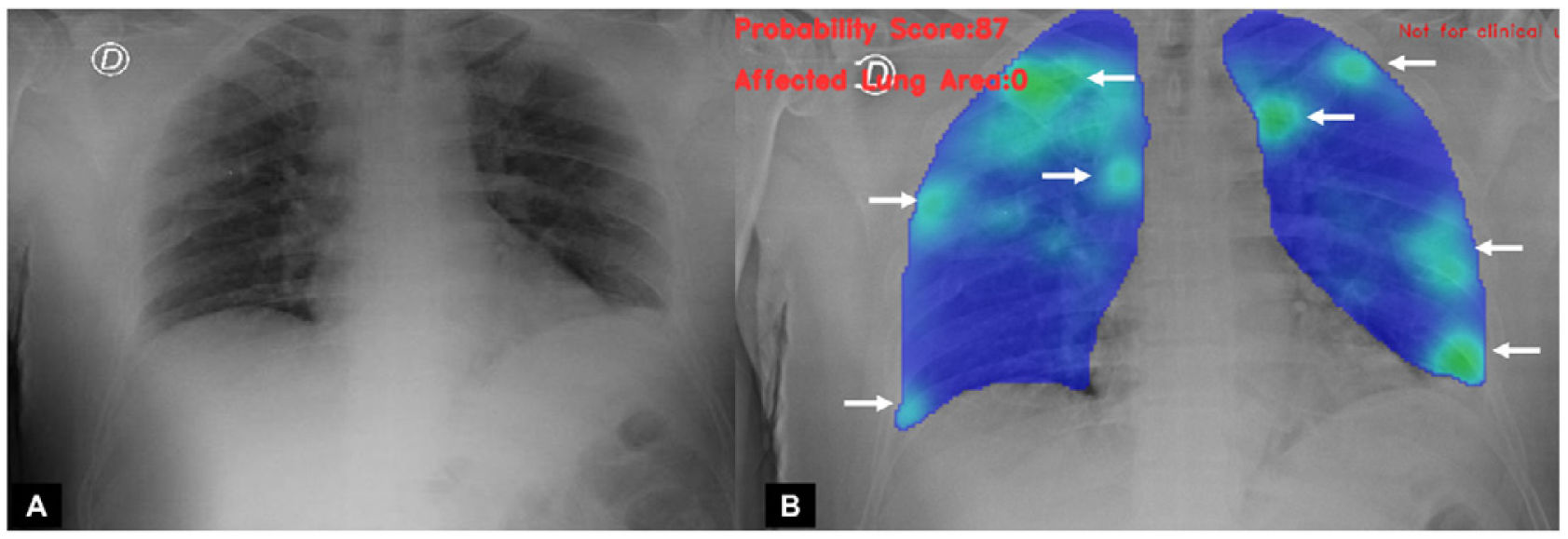
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of different artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for the identification of pulmonary involvement by SARS-CoV-2 based on portable chest radiography (RX).
Material and methodsProspective observational study that included patients admitted for suspected COVID-19 infection in a university hospital between July and November 2020. The reference standard of pulmonary involvement by SARS-CoV-2 comprised a positive PCR test and low-tract respiratory symptoms.
Results493 patients were included, 140 (28%) with positive PCR and 32 (7%) with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. The AI-B algorithm had the best diagnostic performance (areas under the ROC curve AI-B 0.73, vs. AI-A 0.51, vs. AI-C 0.57). Using a detection threshold greater than 55%, AI-B had greater diagnostic performance than the specialist [(area under the curve of 0.68 (95% CI 0.64–0.72), vs. 0.54 (95% CI 0.49–0.59)].
ConclusionAI algorithms based on portable RX enabled a diagnostic performance comparable to human assessment for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 lung involvement.
Evaluar el rendimiento diagnóstico de diferentes algoritmos de inteligencia artificial (IA) para la identificación de compromiso pulmonar por SARS-CoV-2 basados en radiografía (Rx) de tórax portátil.
Material y métodoEstudio observacional prospectivo que incluyó pacientes ingresados por sospecha de infección por COVID-19 en un hospital universitario entre julio y noviembre de 2020. El patrón de referencia de compromiso pulmonar por SARS-CoV-2 comprendió una PCR positiva y síntomas respiratorios bajos.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 493 pacientes, 140 (28%) con PCR positiva y 32 (7%) con neumonía por SARS-CoV-2. El algoritmo AI-B tuvo el mejor rendimiento diagnóstico (áreas bajo la curva ROC AI-B 0,73 vs. AI-A 0,51 vs. AI-C 0,57). Utilizando un umbral de detección superior al 55%. AI-B presentó mayor precisión que el especialista (área bajo la curva de 0,68 [IC 95%: 0,64–0,72] vs. 0,54 [IC 95%: 0,49–0,59]).
ConclusiónLos algoritmos de IA basados en Rx portátiles permiten una precisión diagnóstica comparable a la humana para la detección de compromiso pulmonar por SARS-CoV-2.