To objectively evaluate the effects of probiotics supplement on glycemic control and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
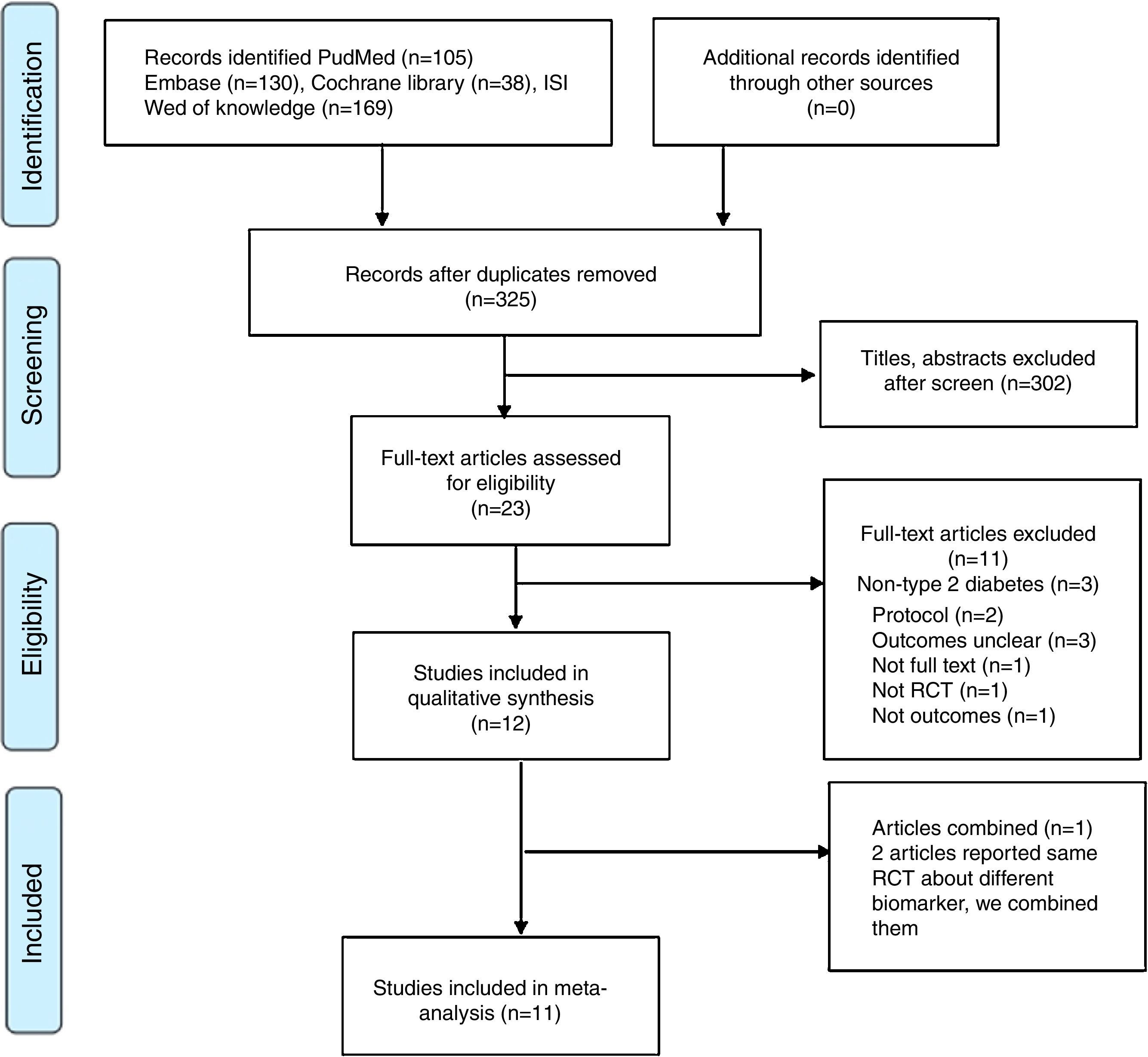
Material and methodsThe randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with regard to the probiotics or synbiotics for the treatment of T2DM were collected through retrieving 5 databases from their establishment to March 2016. After study selection, quality assessment and data extraction were performed by 2 authors independently; and STATA software was used for statistical analysis. The level of evidence was evaluated by applying the GRADE system.
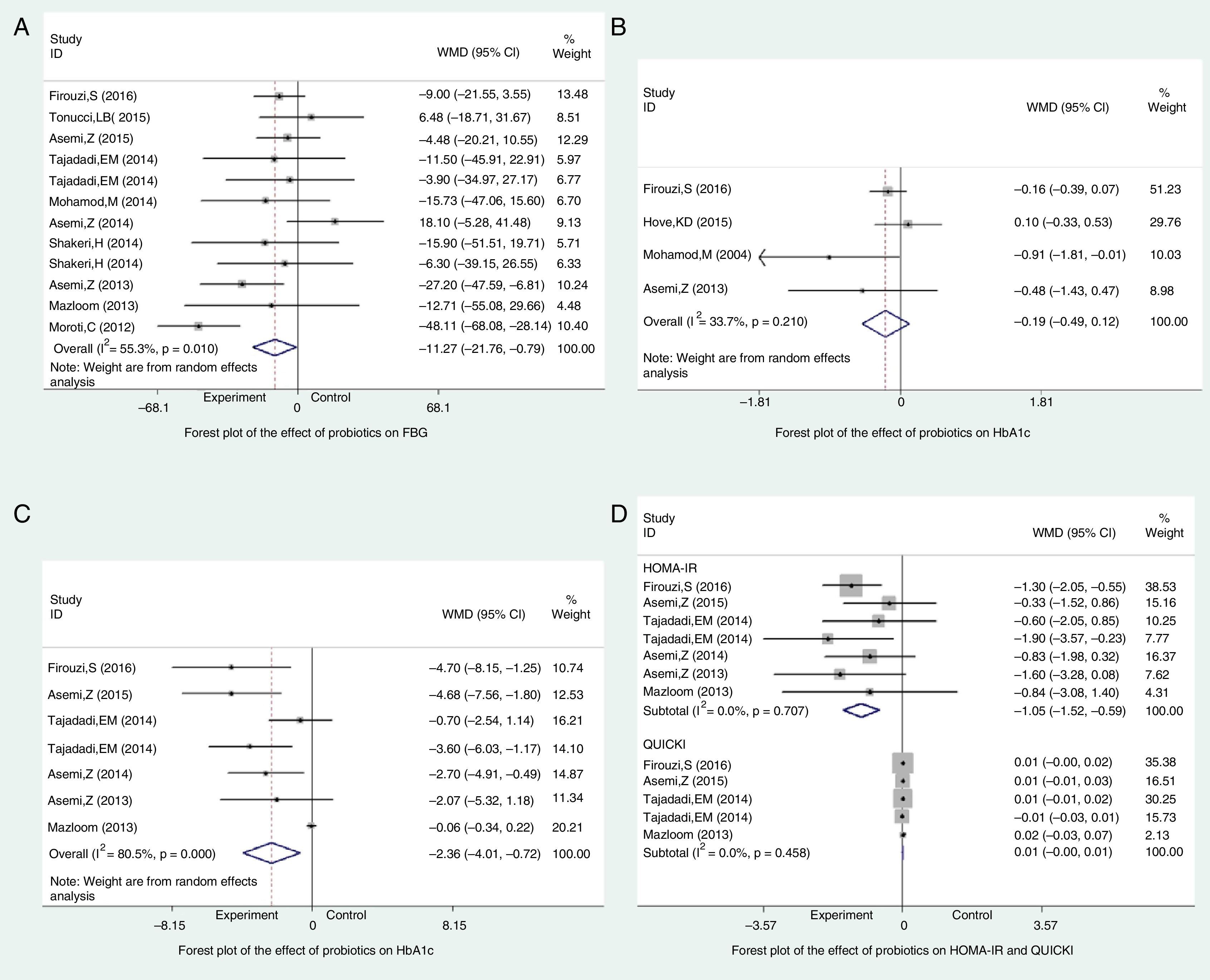
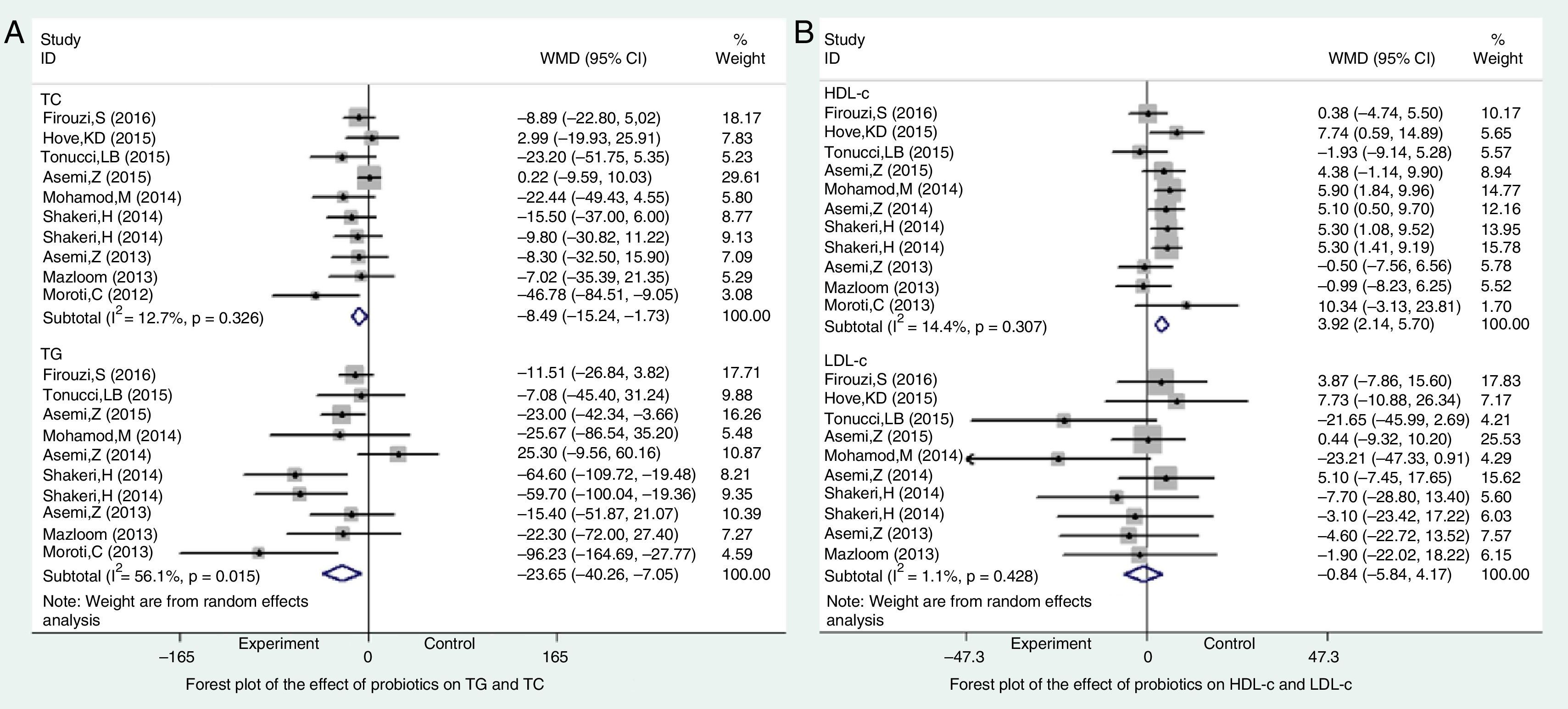
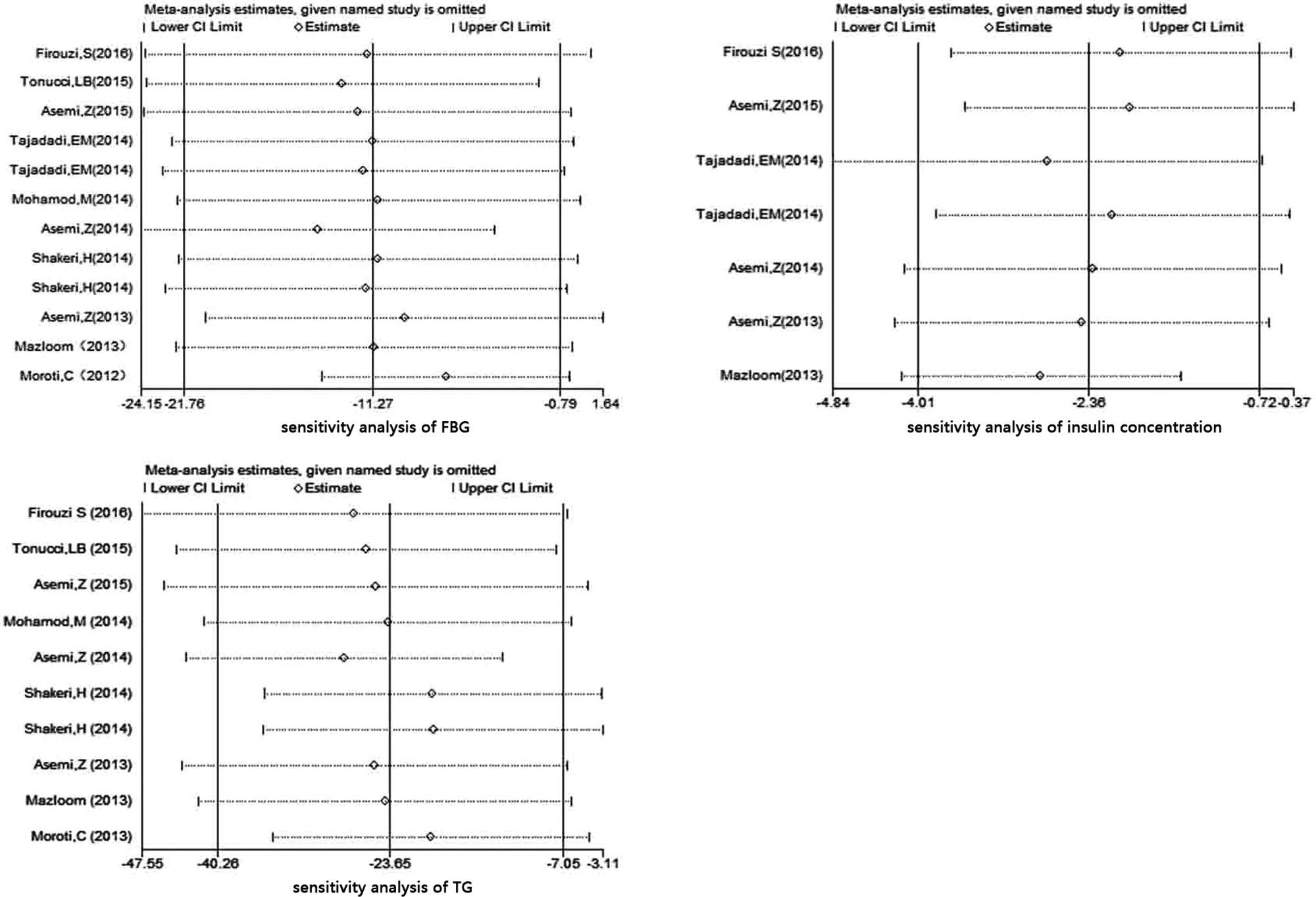
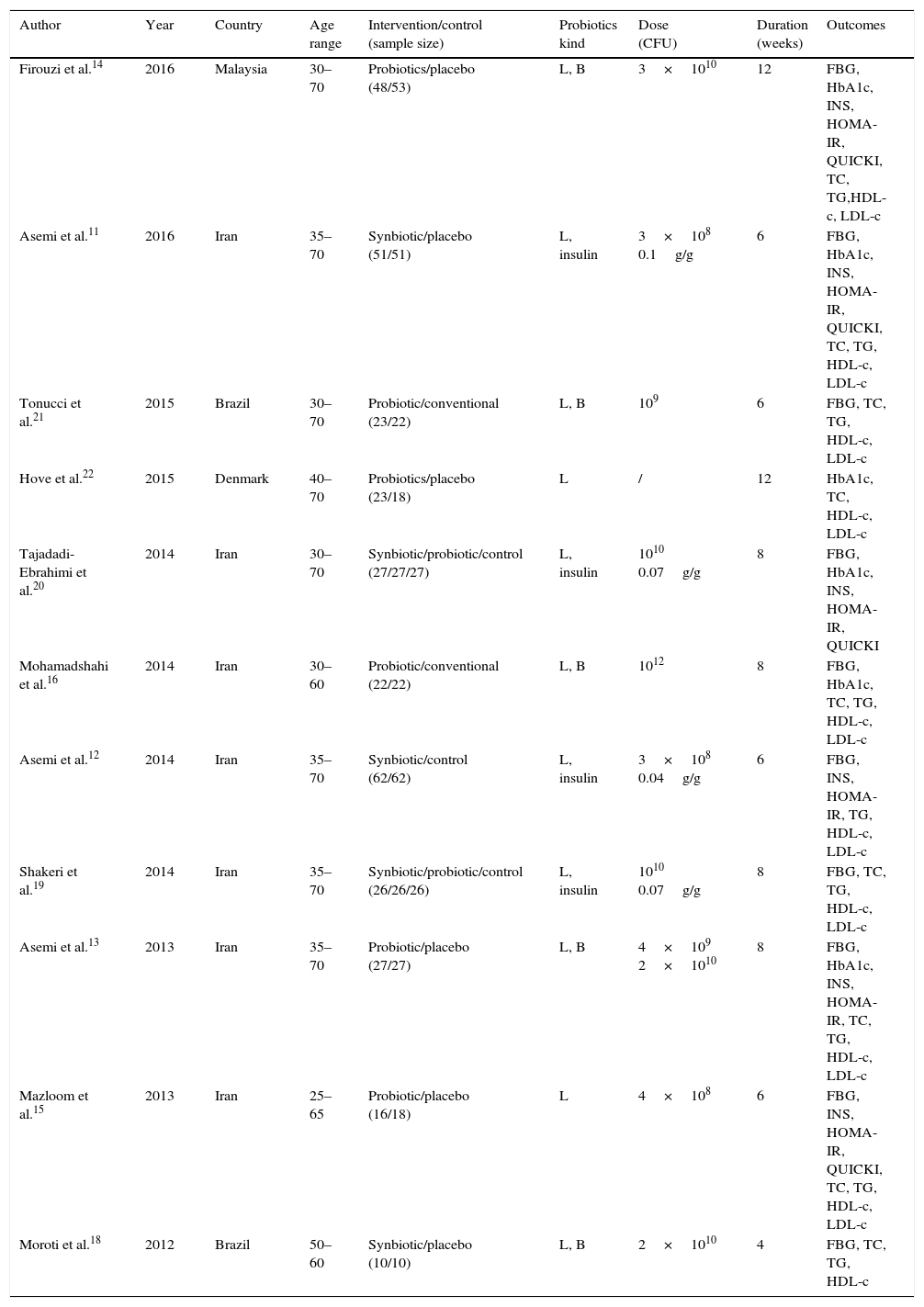
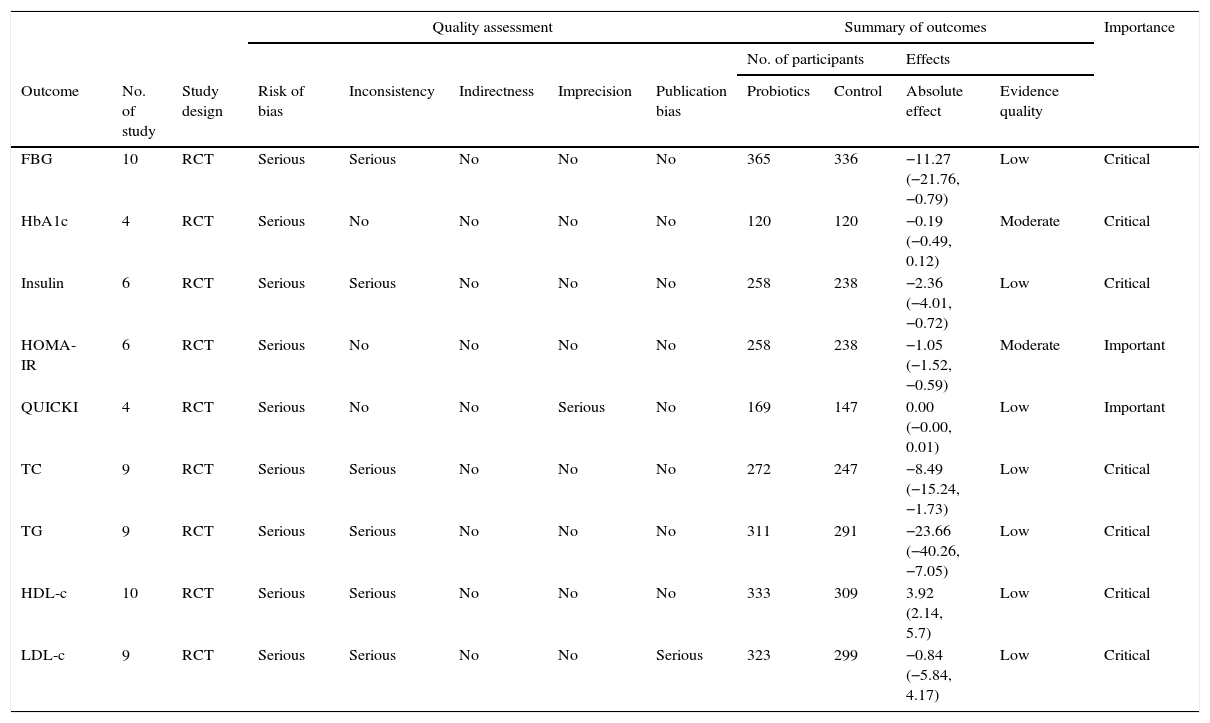
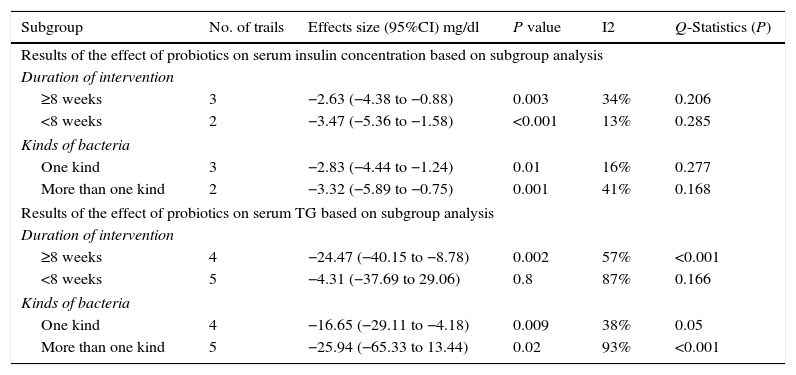
ResultsTwelve RCTs involving 770 participants were enrolled. The results of the meta-analysis showed that probiotics could significantly reduce fasting blood glucose by −11.27mg/dL (95%CI −21.76 to −0.79; P<0.001) and serum insulin concentration by −2.36μU/mL (95%CI −4.01 to −0.72; P=0.005), but with no significant reduction on HbA1c (−0.19%; 95%CI −0.49 to 0.12; P=0.23). Probiotics could significantly reduce HOMA-IR of T2DM patients (−1.05; 95%CI −1.52 to −0.59; P<0.001). Nevertheless, the effect on QUICKI was negligible (0.00; 95%CI −0.00 to 0.01; P=0.27). Results also confirmed the significant lowering effect of probiotics on total cholesterol (−8.49mg/dL; 95%CI −15.24 to −1.73; P=0.014) and triglycerides (TG; −23.66mg/dL; 95%CI −40.26 to −7.05; P<0.001), as well as the elevating effect on HDL-c (3.92mg/dL; 95%CI 2.14 to 5.7; P<0.01). However, there was no significant change on LDL-c (−0.84mg/dL; 95%CI −5.84 to 4.17; P=0.75). Subgroup analysis was conducted for 2 outcomes, that is, serum insulin concentration and TG, whose heterogeneity was too high. The results showed multiple species of probiotics had stronger reduction effect on serum insulin concentration (−3.32μU/mL; 95%CI −5.89 to −0.75; P=0.001) and TG (−25.94mg/dL; 95%CI −65.33 to 13.44; P<0.001). In addition, it also suggested that only the duration of treatment for ≥8 weeks could significantly reduce TG by −24.47mg/dL (95%CI −40.15 to −8.78; P=0.001). The duration of treatment for <8 weeks did not result in significant reduction on TG (−4.31mg/dL; 95%CI −37.69 to 29.06; P=0.8). Finally, all the evidences were at moderate and low levels according to the GRADE system.
ConclusionAs a kind of the potential biotherapeutics in the management of T2DM, probiotics can improve glucose control and lipid metabolism.
Evaluar objetivamente los efectos de los suplementos de probióticos sobre el control glucémico y el metabolismo de los lípidos en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2).
Material y métodosEnsayos controlados aleatorizados (ECA) con respecto a los probióticos o simbióticos para el tratamiento de la DM2, recogidos a través de la recuperación de 5 bases de datos, desde su creación hasta el mes de marzo de 2016. Tras el estudio y la selección, la evaluación de la calidad y la extracción de datos fueron realizadas por 2 autores independientes, utilizándose el software STATA para realizar el análisis estadístico. El nivel de evidencia se evaluó mediante la aplicación del sistema GRADE.
ResultadosFueron 12 ECA, en los que se incluyó a 770 participantes. Los resultados del metaanálisis reflejaron que los probióticos podrían reducir significativamente la glucosa en sangre en ayunas en −11,27mg/dl (IC 95% −21,76 a −0,79; p<0,001) y la concentración de insulina sérica en −2,36μU/ml (IC 95% −4,01 a −0,72; p=0,005), aunque el valor de HbA1c no mostró una reducción significativa (−0,19%; IC 95% −0,49 a 0,12; p=0,23). El probiótico podría reducir significativamente el HOMA-IR de los pacientes con DM2 (−1,05; IC 95% −1,52 a −0,59; p<0,001). Sin embargo, el efecto sobre QUICKI fue insignificante (0,00; IC 95% −0,00 a 0,01; p=0,27). Los resultados confirmaron el efecto de disminución significativa de los probióticos en el colesterol total (−8,49mg/dl; IC 95% −15,24 a −1,73; p=0,014) y en los triglicéridos (TG; −23,66mg/dl; IC 95% −40,26 a −7,05; p<0,001), así como el efecto de elevación del c-HDL (3,92mg/dl; IC 95% 2,14 a 5,7; p<0,01). Sin embargo, no se produjo ningún cambio significativo en el c-LDL (−0,84mg/dl; IC 95% −5,84 a 4,17; p=0,75). Se realizó un análisis de subgrupos para los 2 resultados (concentración de insulina en suero y TG), cuya heterogeneidad fue demasiado alta. Los resultados mostraron que multitud de probióticos tuvieron un mayor efecto de reducción de la concentración de insulina en suero (−3,32μU/ml; IC 95% −5,89 a −0,75; p=0,001) y TG (−25,94mg/dl; IC 95% −65,33 a 13,44; p<0,001). Además, también evidenciaron que solo la duración del tratamiento no inferior a 8 semanas podría reducir significativamente TG en un −24,47mg/dl (IC 95% −40,15 a −8,78; p=0,001). La duración del tratamiento inferior a 8 semanas no produjo una reducción significativa de los TG (−4,31mg/dl; IC 95% −37,69 a 29,06; p=0,8). Finalmente, según el sistema GRADE, todas las evidencias fueron de nivel moderado y bajo.
ConclusiónComo tipo de bioterapéutica potencial para el tratamiento de la DM2, los probióticos pueden mejorar el control de la glucosa y el metabolismo lipídico.