The Covid-19 pandemic has put healthcare professionals around the world in an unprecedented challenge. This may cause some emotional difficulties and mental health problems. The aim of the present study was to analyze the emotional status among the health care workers form the Hospital of Igualada (Barcelona), while they were facing with Covid-19 in one of the most affected regions in all of Europe.
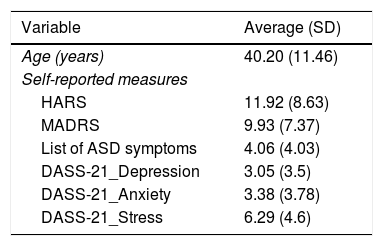
Patients and methodsA total of 395 participants were included in the study. A cross-sectional assessment was carried out between the months of March and April. Information about anxiety, depression, and stress was gathered. We also collected demographic data and concerning potentially stressful factors.
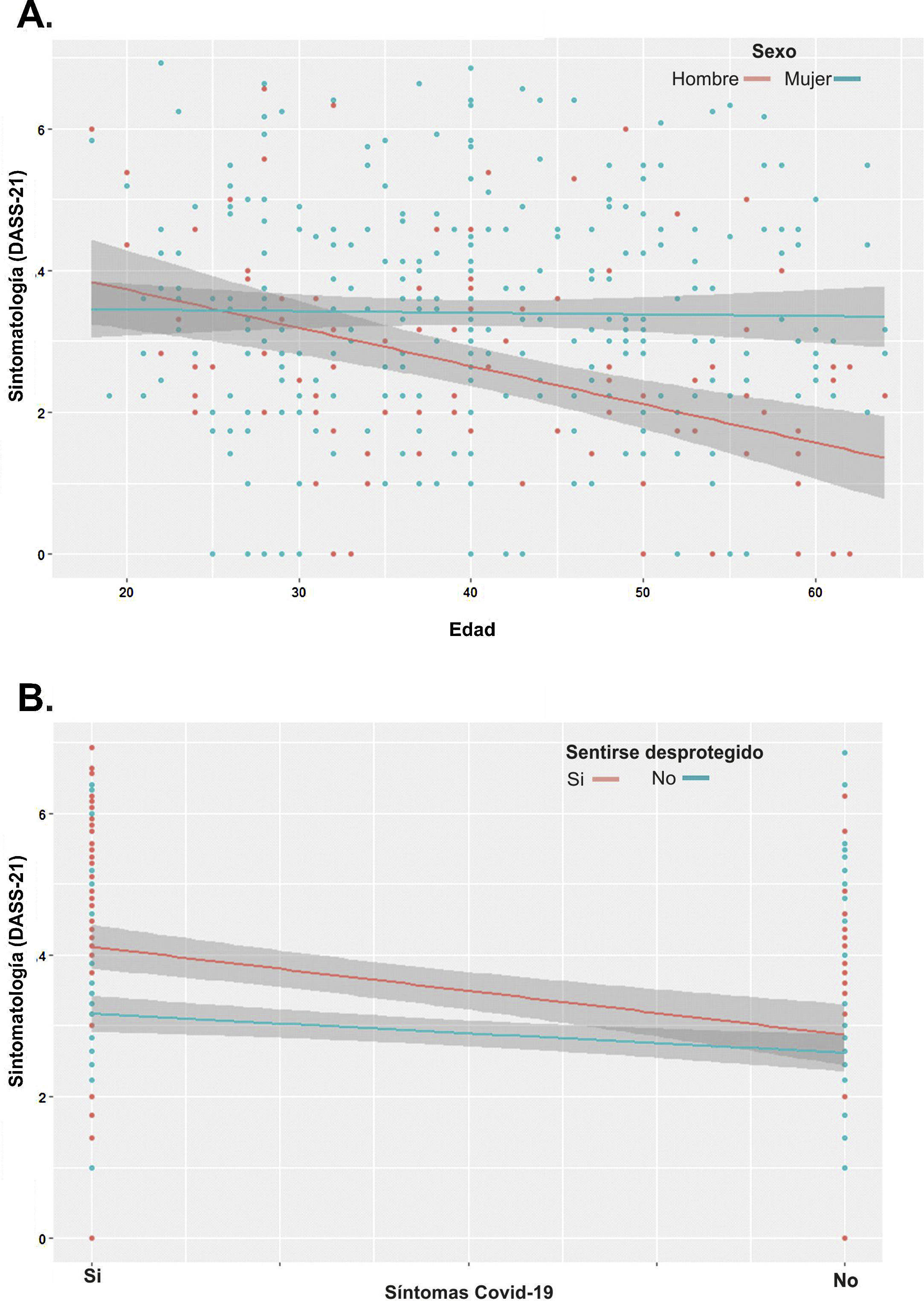
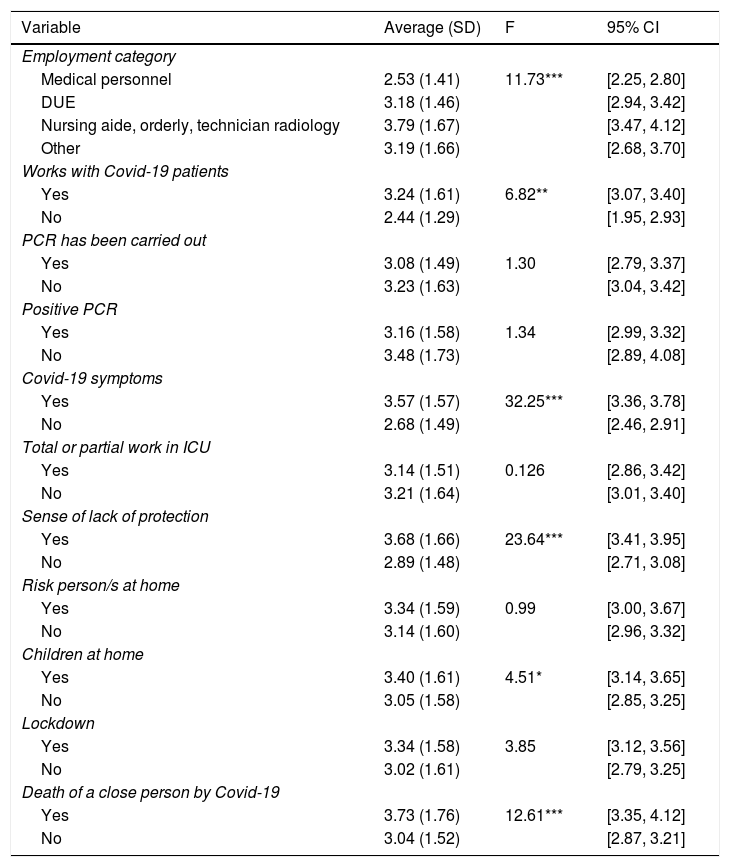
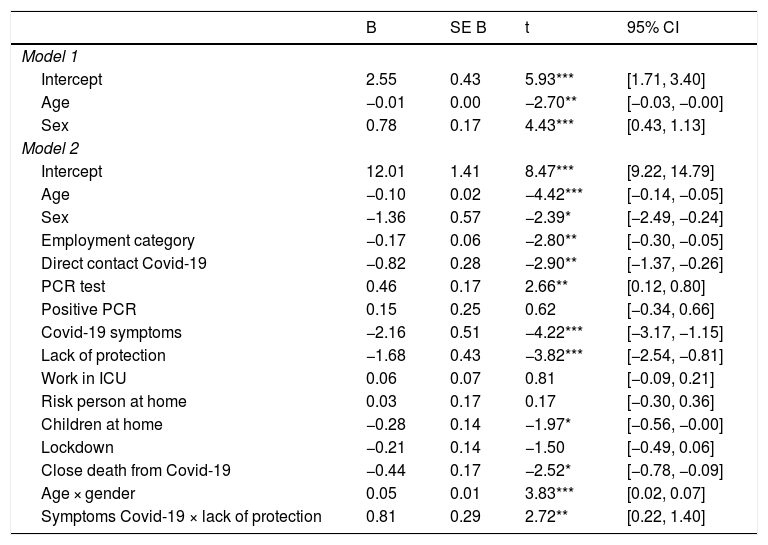
ResultsA significant proportion of professionals reported symptoms of anxiety (31.4%) and depression (12.2%) from moderate to severe intensity. Symptoms of acute stress were reported by 14.5% of participants. We performed a regression analysis, which explained the 30% of the variance associated with the degree of emotional distress (R² = 0.30). The final model reveals that females (or young males), who are working in the frontline as nursing assistants, caretakers or radiology technicians, with the uncertainty of a possible infection, the perception of inadequate protection measures and having experienced the death of a close person by Covid-19, showed a heightened risk of experiencing psychological distress.
ConclusionsCoping with the Covid-19 pandemic caused a significant impact on emotional status of healthcare workers involved in this study.
La actual pandemia de Covid-19 ha puesto a los profesionales sanitarios de todo el mundo ante un desafío sin precedentes. Esto les ha podido causarles dificultades emocionales y problemas de salud mental. El objetivo del presente estudio fue analizar el estado emocional de los trabajadores del Hospital de Igualada (Barcelona), mientras se enfrentaban a uno de los focos de contagio más importantes de Europa.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyó a un total de 395 trabajadores. Se realizó una evaluación transversal entre los meses de marzo y abril. Se recogió información sobre síntomas de ansiedad, depresión, estrés. También se recogieron datos demográficos y sobre factores potencialmente estresantes.
ResultadosUn porcentaje significativo de profesionales reportó síntomas de ansiedad (71.6%) y depresión (60.3%). El 14.5% informó de síntomas de estrés agudo. Se realizó un análisis de regresión que explicó el 30% de la variancia asociada al nivel de malestar emocional (R² = 0.30). Los factores de riesgo asociados a mayor malestar psicológico fueron el hecho de ser mujer (o hombre joven), trabajar como auxiliar de enfermería, celador o técnico de radiología, estar en contacto directo con pacientes Covid-19, no haber realizado la PCR, tener la sensación de no contar con los elementos de protección personales y haber experimentado la muerte de una persona cercana por Covid-19.
ConclusionesEl afrontamiento inicial de la situación de crisis asociada a la pandemia del Covid-19, tuvo un importante impacto emocional en los profesionales sanitarios analizados.