To assess the risk factors of CMV infection after heart transplant (HT) and its influence on long-term prognosis.
MethodsWe conducted a retrospective single-centre study of 222 H T recipients. Risk factors for CMV infection were identified by means of multivariable Cox´s regression. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox´s regression were used to assess the long-term prognostic impact of CMV infection during the first post-transplant year.
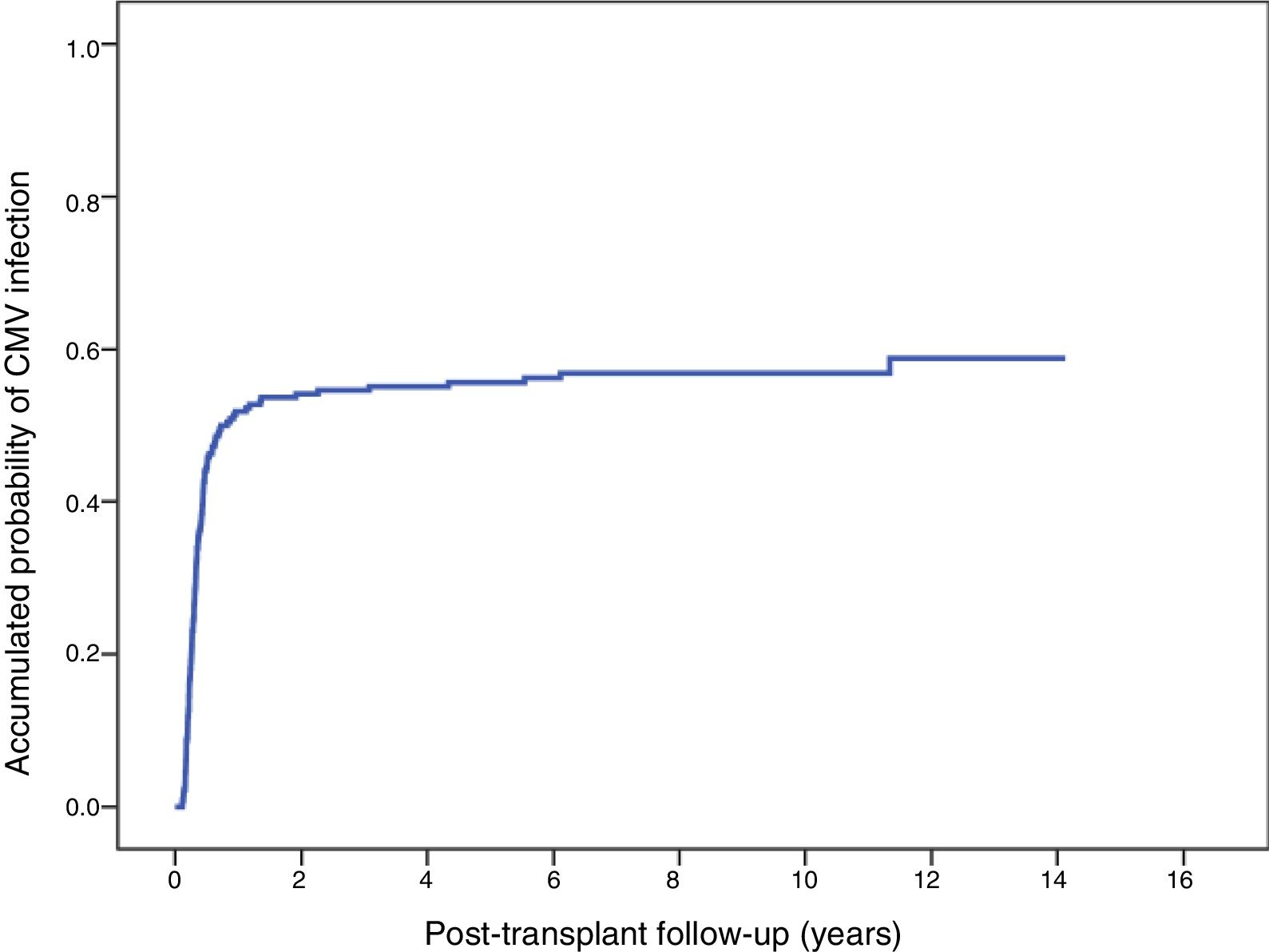
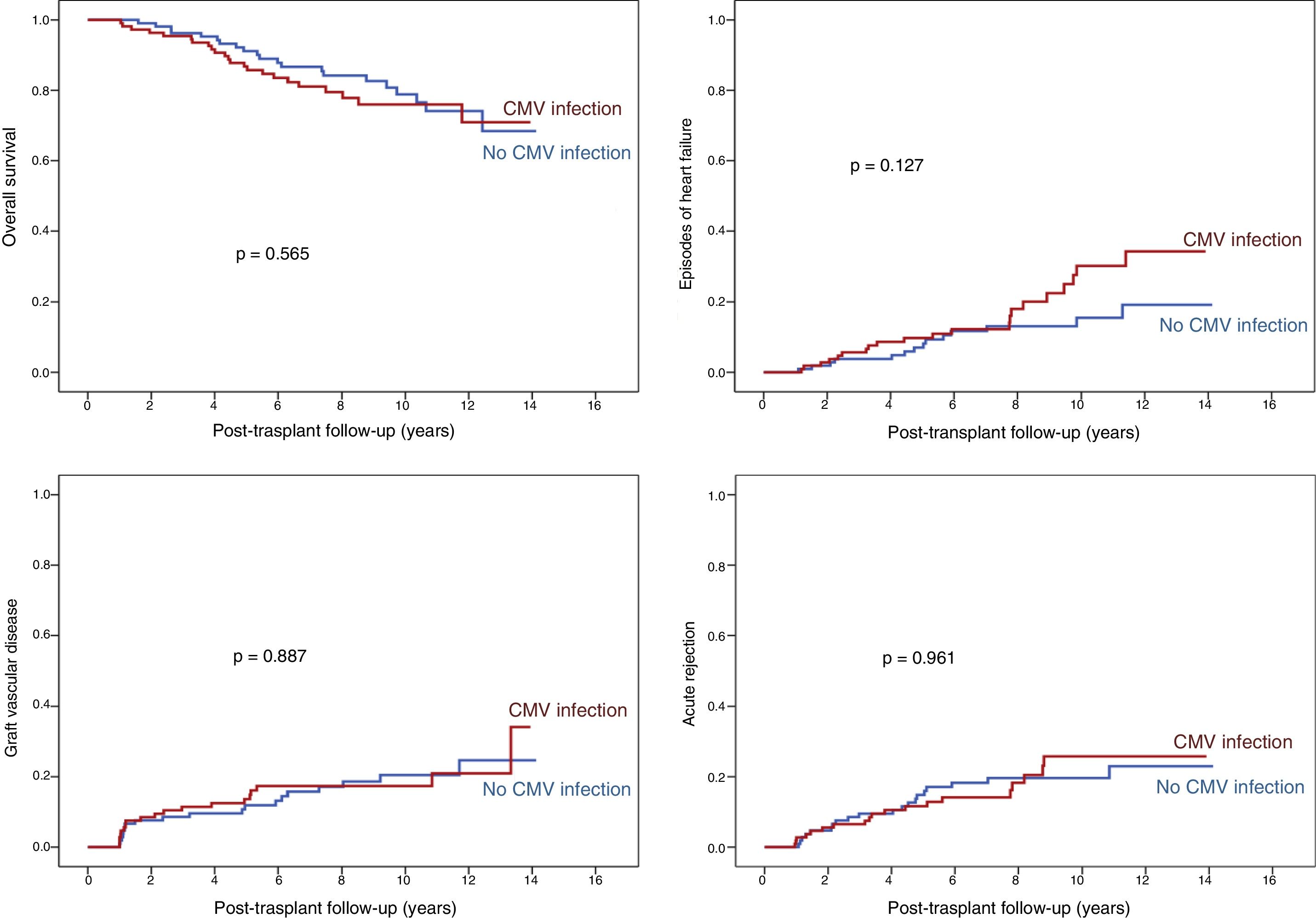
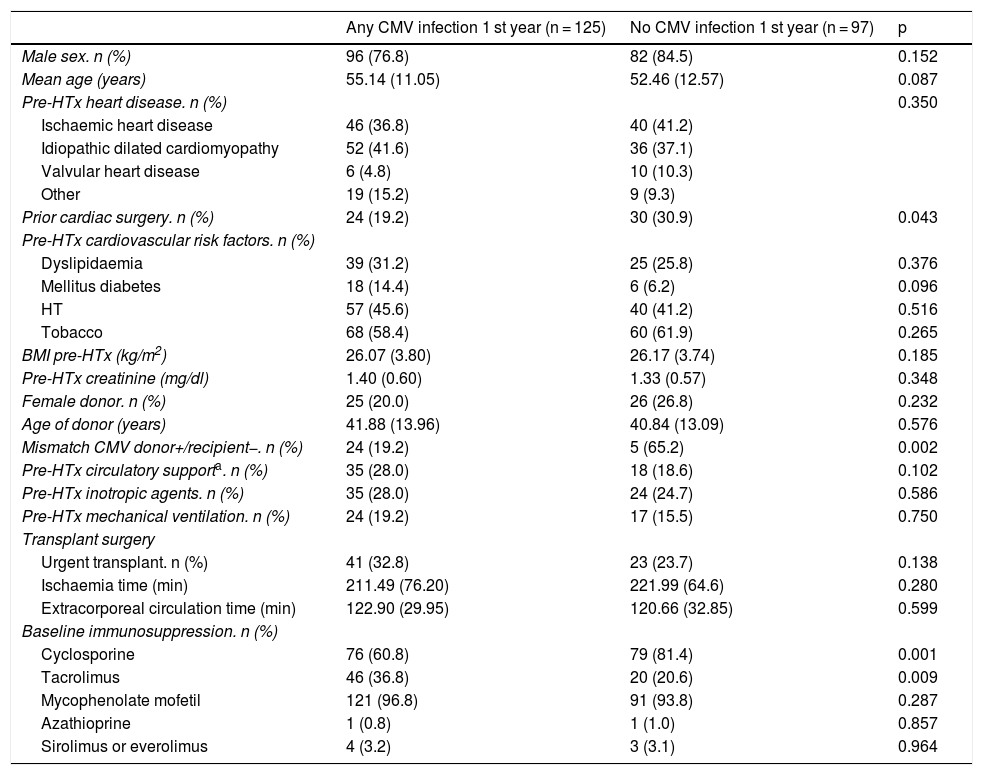
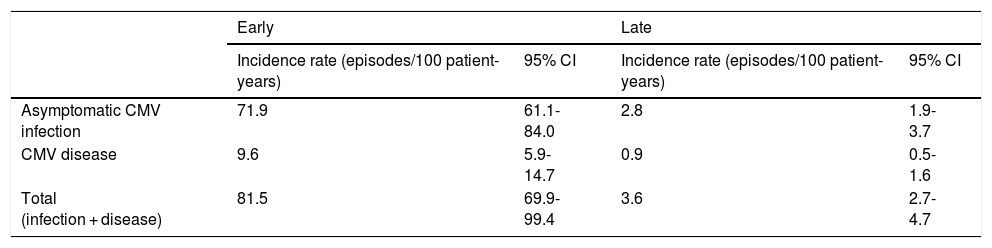
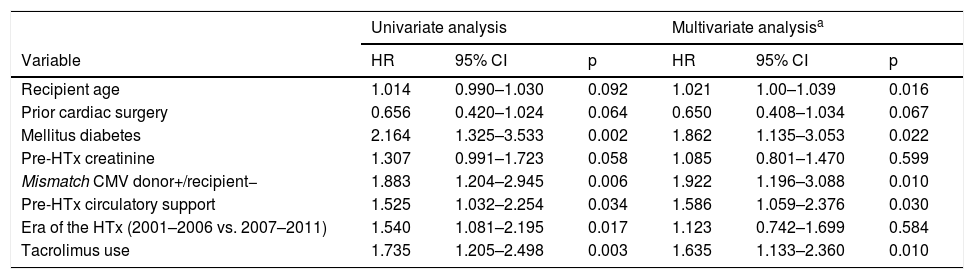
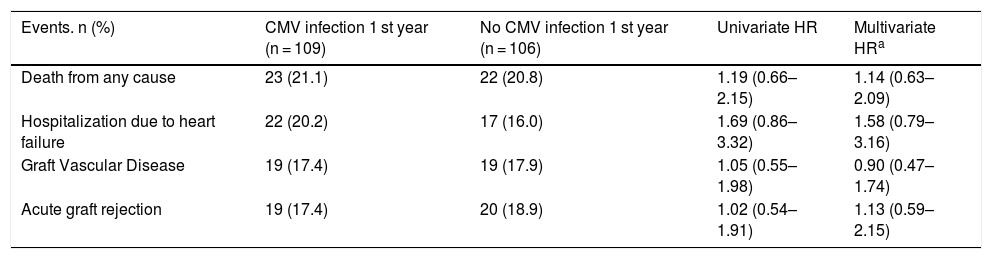
ResultsDonor-recipient CMV serologic matching (hazard ratio [HR] 1.92, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.2–3.09, p = .007), recipient age (HR 1.02, 95% CI 1.00–1.1, p = .02), diabetes mellitus (HR 1.86, 95% CI 1.4–3.05, p = .01), pre- transplant circulatory support (HR 1.59, 95% CI 1.06–2.38, p = .03) and the use of tacrolimus (HR 1.64, 95% CI 1.13–2.36, p = .009) were independently associated with increased risk of CMV infection. CMV infection during the first year post-HT was not associated with worse transplant outcomes in terms of mortality, incidence of heart failure, cardiac allograft vasculopathy or acute rejection.
ConclusionsCMV infection was not associated with impaired long-term prognosis after HT.
Analizar el impacto pronóstico de la infección por Citomegalovirus (CMV) durante el primer año tras el trasplante cardiaco (TC) y describir factores de riesgo.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo unicéntrico incluyendo 222 receptores de TC. La identificación de factores de riesgo de infección por CMV se llevó a cabo mediante regresión multivariable de Cox. Mediante los métodos de Kaplan-Meier y Cox se analizó la influencia de la infección por CMV durante el primer año sobre la supervivencia e incidencia de eventos clínicos adversos en el seguimiento a largo plazo.
ResultadosEn el análisis multivariante, el estado serológico donante/receptor frente a CMV (hazard ratio [HR] 1,92, intervalo de confianza 95% [IC 95%] 1,2–3,09; p = 0007, la edad del receptor HR 1,02, IC 95% 1,00–1,1; p = 0,02), la diabetes (HR 1,86, IC 95% 1,4-3,05; p = 0,01), el soporte circulatorio mecánico (HR 1,59, IC 95% 1,06-2,38; p = 0,03) y el uso de tacrolimus (HR 1,64, IC 95% 1,13-2,36; p = 0009, resultaron predictores independientes de infección por CMV post-trasplante. No se detectó una influencia significativa de la infección por CMV durante el primer año post-trasplante sobre la mortalidad, la incidencia de insuficiencia cardiaca, enfermedad vascular del injerto o rechazo agudo.
ConclusionesLa infección por CMV durante el primer año post-trasplante no se asoció a un peor pronóstico a largo plazo.