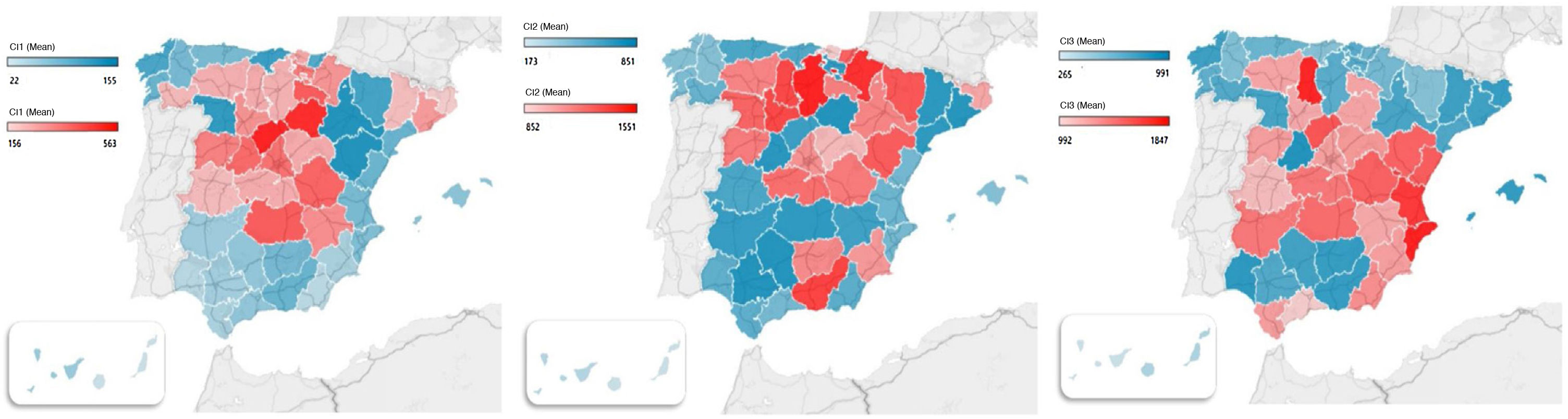
Several studies have analyzed the influence of meteorological and geographical factors on the incidence of COVID-19. Seasonality could be important in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2. This study aims to evaluate the geographical pattern of COVID-19 in Spain and its relationship with different meteorological variables.
MethodsA provincial ecological study analyzing the influence of meteorological and geographical factors on the cumulative incidence of COVID-19 in the 52 (24 coastal and 28 inland) Spanish provinces during the first three waves was carried out. The cumulative incidence was calculated with data from the National Statistical Institute (INE) and the National Epidemiological Surveillance Network (RENAVE), while the meteorological variables were obtained from the Spanish Meteorological Agency (AEMET).
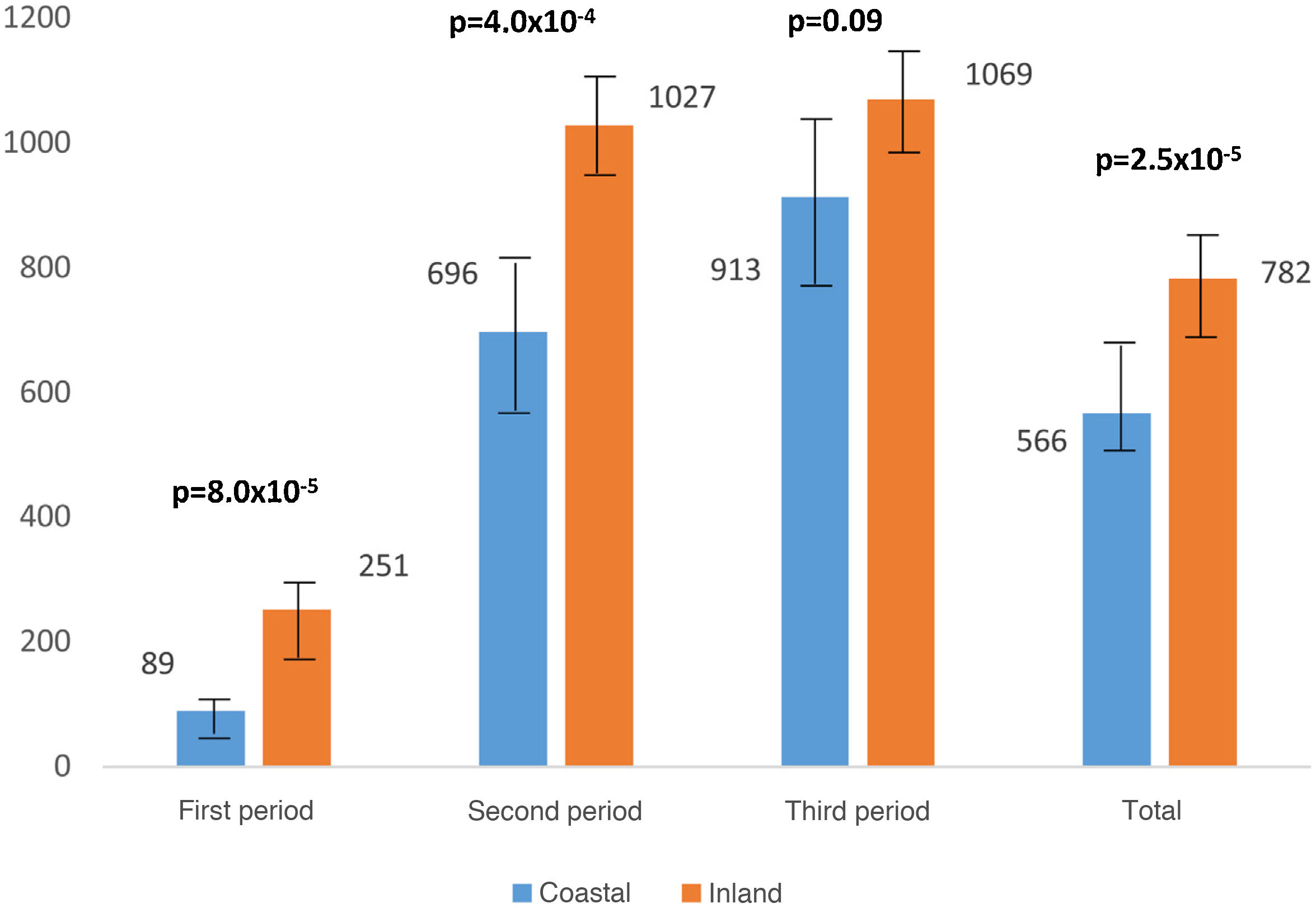
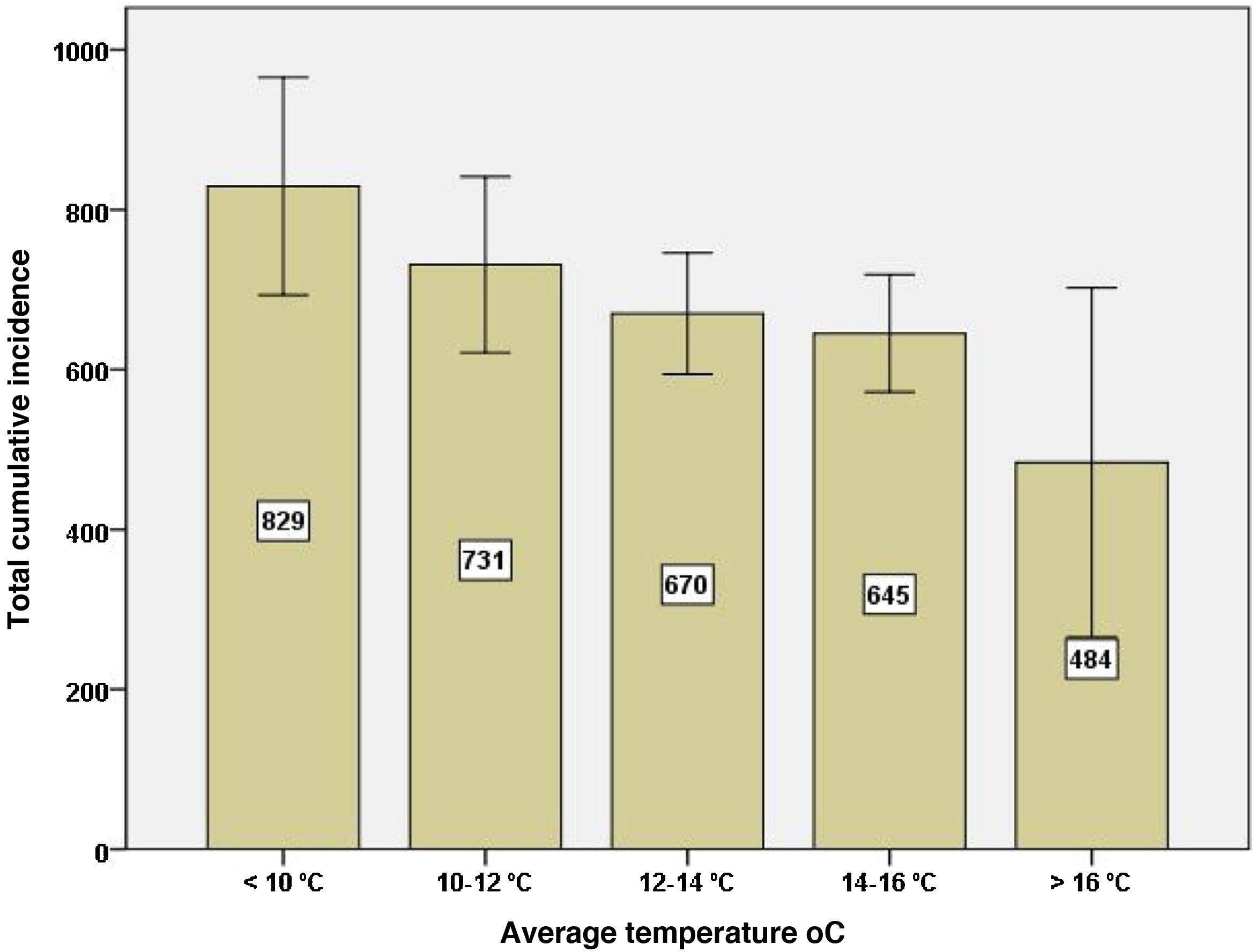
ResultsThe total cumulative incidence, in all three waves, was lower in the coastal provinces than in the inland ones (566 ± 181 vs. 782 ± 154; P = 2.5 × 10−5). The cumulative incidence correlated negatively with mean air temperature (r = −0.49; P = 2.2 × 10−4) and rainfall (r = −0.33; P = .01), and positively with altitude (r = 0.56; P = 1.4 × 10−5). The Spanish provinces with an average temperature <10 °C had almost twice the cumulative incidence than the provinces with temperatures >16 °C. The mean air temperature and rainfall were associated with the cumulative incidence of COVID-19, regardless of other factors (Beta Coefficient of −0.62; P = 3.7 × 10−7 and −0.47; P = 4.2 × 10−5 respectively)
ConclusionsMeteorological and geographical factors could influence the evolution of the pandemic in Spain. Knowledge regarding the seasonality of the virus would help to predict new waves of COVID-19 infections
Varios estudios han analizado la influencia de factores meteorológicos y geográficos en la incidencia de COVID-19. La estacionalidad podría tener importancia en la transmisión de SARS-CoV-2. Nuestro estudio evalúa el patrón geográfico de la COVID-19 en España y su relación con las distintas variables meteorológicas.
MétodosEstudio ecológico a escala provincial que analiza la influencia de factores meteorológicos y geográficos en la incidencia acumulada de COVID-19 en las 52 provincias españolas (24 costeras y 28 del interior) durante las tres primeras olas. La incidencia acumulada se calculó con los datos del Instituto Nacional Estadística (INE) y la Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica (RENAVE), las variables meteorológicas se obtuvieron de la Agencia estatal de meteorología (AEMET).
ResultadosLa incidencia acumulada total, en los tres periodos, fue menor en las provincias costeras que en las del interior (566 ± 181 vs. 782 ± 154; P = 2,5 × 10−5). La incidencia acumulada correlacionó negativamente con la temperatura media (r = −0,49; P = 2,2 × 10−4) y las precipitaciones (r = −0,33; P = ,01), y positivamente con la altitud (r = 0,56; P = 1,4 × 10−5). Las provincias españolas con una temperatura media <10 °C tuvieron casi el doble de incidencia acumulada que las provincias con temperaturas >16 °C. La temperatura media y las precipitaciones fueron las variables asociadas con la incidencia acumulada provincial de COVID-19, con independencia de otros factores (Coeficiente Beta de −0,62; P = 3,7 × 10−7 y −0,47; P = 4,2 × 10−5 respectivamente).
ConclusionesLos factores meteorológicos y geográficos podrían influir en la evolución de la pandemia en España. El reconocimiento de la estacionalidad del COVID-19 ayudaría a predecir nuevas olas.