Journal Information
Vol. 153. Issue 2.
Pages e7-e8 (July 2019)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 153. Issue 2.
Pages e7-e8 (July 2019)
Letter to the Editor
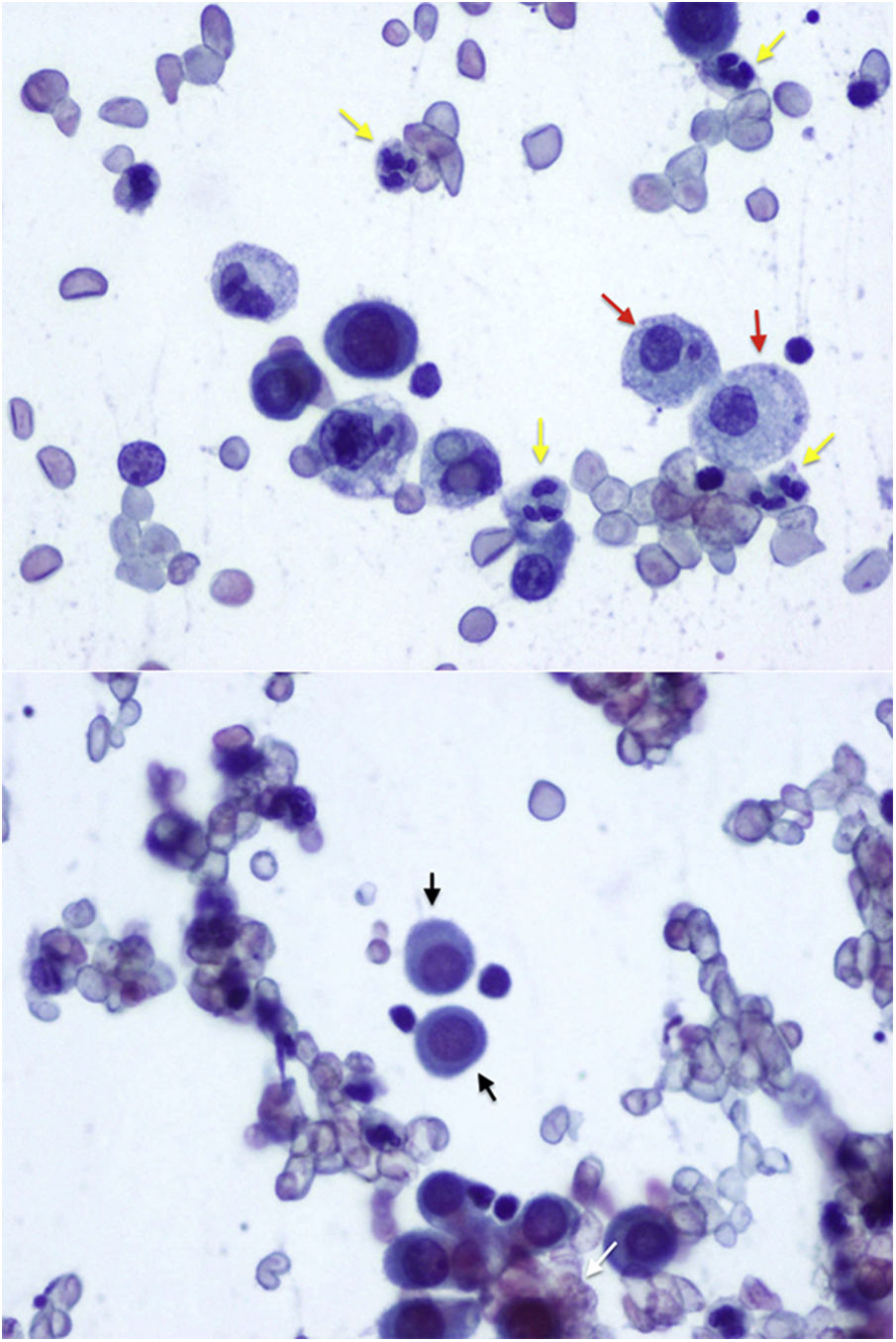
Pleural extramedullary hematopoiesis due to severe pernicious anemia
Hematopoyesis extramedular pleural secundaria a anemia perniciosa grave
Visits
3
a Servicio de Neurología, Hospital Universitario «Dr. José E. González», Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico
b Servicio de Gastroenterología, Hospital Universitario «Dr. José E. González», Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico
c Servicio de Hematología, Hospital Universitario «Dr. José E. González», Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail