Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are both complications linked with COVID-19. Lower limb point-of-care clinical ultrasound (POCUS) could detect occult clots, helping decide whom to treat with anticoagulation.
ObjectivesTo determine proximal DVT prevalence with POCUS screening among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Patients/MethodsLower limb POCUS was performed in all patients admitted either to the ward or intensive care unit (ICU) between April 22nd and 30th 2020. Clinical and laboratory features, prescriptions, thrombotic complications and outcomes were assessed.
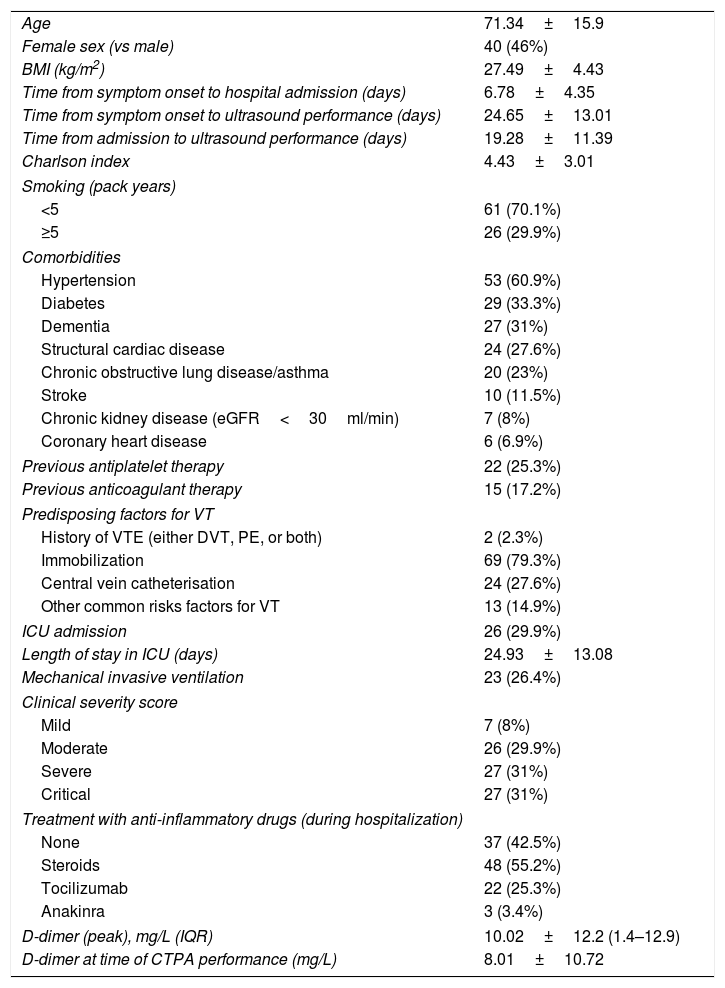
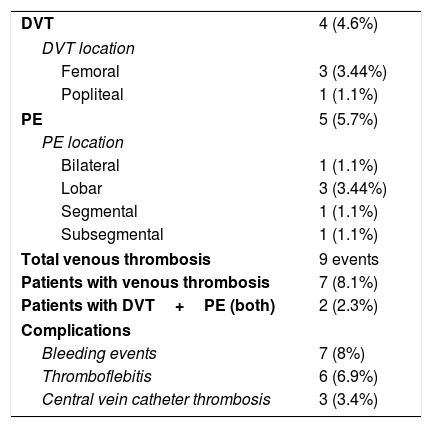
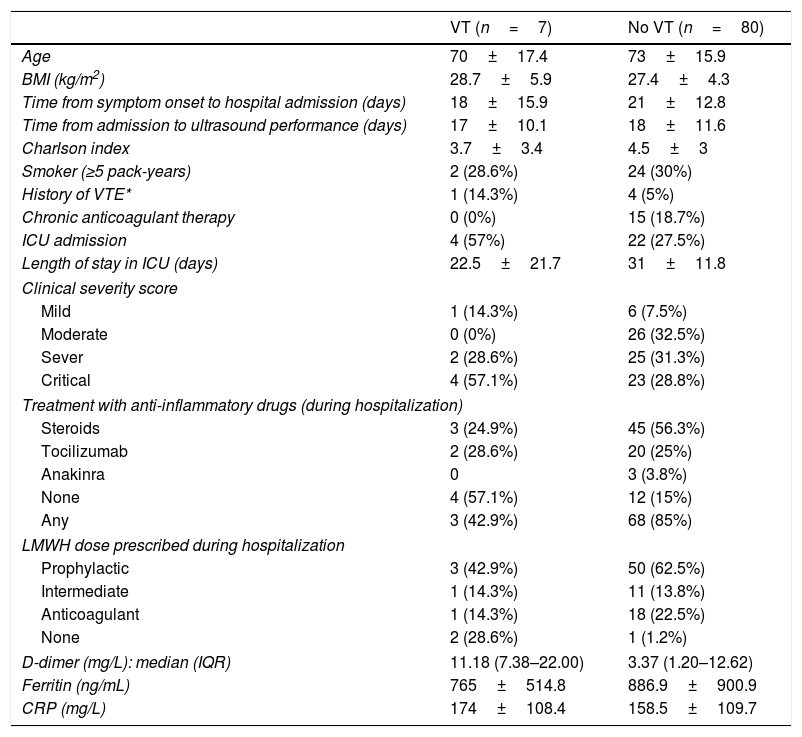
Results87 patients were screened, of which 26 (29.8%) either had been discharged from ICU (19.5%) or were still in critical condition (10.3%). DVT was found in 4 patients (3 femoral, 1 popliteal), of which 1 had not received low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) prophylaxis. 21 CT pulmonary angiograms were performed, being positive for PE in 5 cases (23.8%); only 2 of these patients suffered DVT.
ConclusionsScreening lower extremities with POCUS did not find a high rate of DVT among patients receiving LMWH-prophylaxis. However, there was a noteworthy amount of PE without DVT.
La trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) y la embolia pulmonar (EP) son complicaciones relacionadas con la COVID-19. La ecografía clínica en el punto de atención (POCUS) de las extremidades inferiores podría detectar coágulos ocultos, ayudando a decidir a quién tratar con anticoagulación.
ObjetivosDeterminar la prevalencia de la TVP proximal con el cribado mediante POCUS entre los pacientes hospitalizados por COVID-19.
Pacientes/métodosSe realizó una POCUS de miembros inferiores a todos los pacientes ingresados en planta o en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) entre el 22 y el 30 de abril de 2020. Se evaluaron las características clínicas y de laboratorio, las prescripciones, las complicaciones trombóticas y los resultados.
ResultadosSe examinaron 87 pacientes, de los cuales 26 (29,8%) habían sido dados de alta de la UCI (19,5%) o seguían en estado crítico (10,3%). Se detectó una TVP en cuatro pacientes (tres femoral, uno poplítea), de los cuales uno no había recibido profilaxis con heparina de bajo peso molecular (HBPM). Se realizaron 21 angiografías pulmonares por TC, siendo positivas para EP en cinco casos (23,8%); solo dos de estos pacientes sufrieron TVP.
ConclusionesEl cribado de las extremidades inferiores con POCUS no encontró una tasa elevada de TVP entre los pacientes que recibían profilaxis con HBPM. Sin embargo, hubo una cantidad notable de EP sin TVP.