To determine the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in the oral mucosa of blood donors (BD) and risk factors associated with HPV and oral cancer.
Materials and methodsProspective cross-sectional study, population matched to BD from the National Cancer Institute, Mexico for HPV identification in oral cytological samples using the CLART® Human Papillomavirus 2 Kit (35 genotypes) and risk factors.
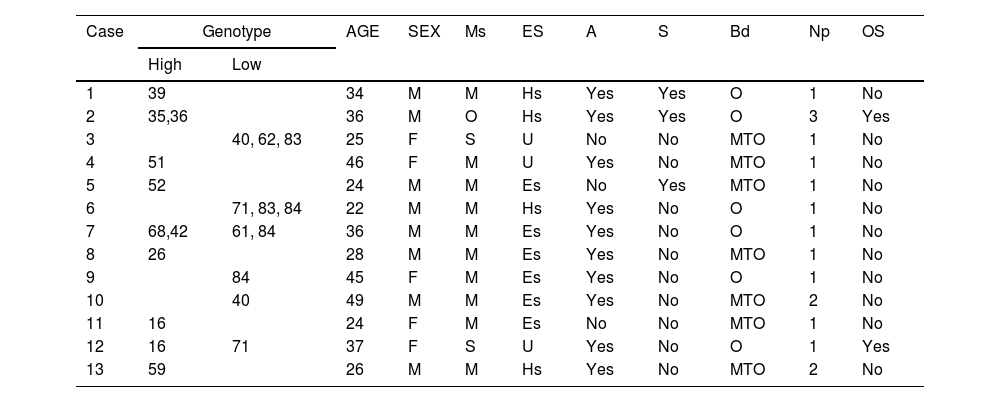
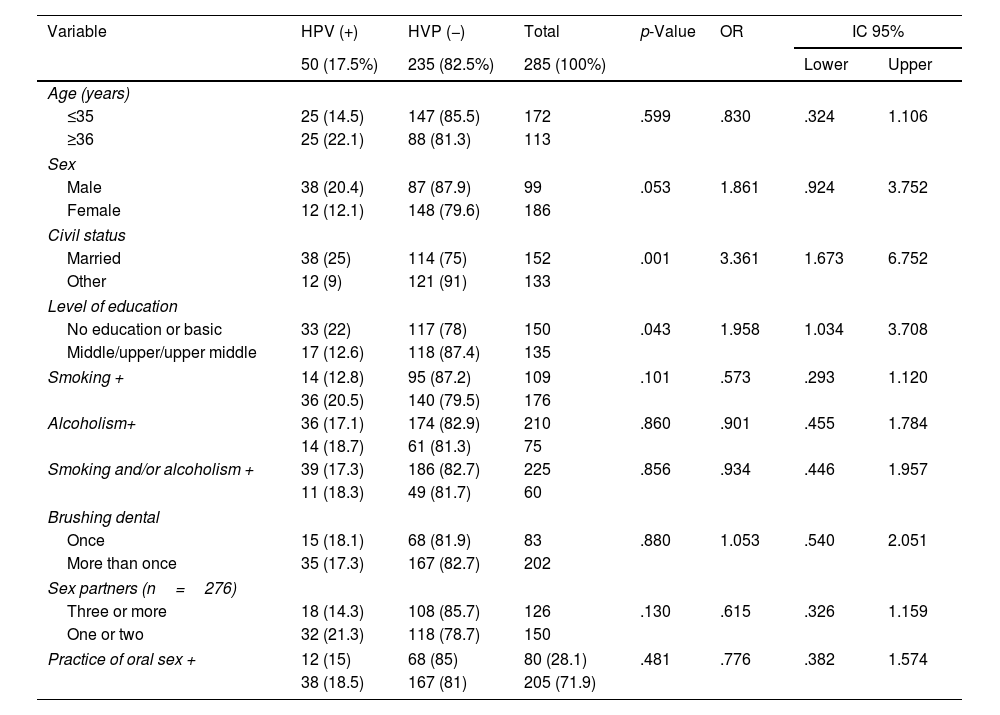
ResultsOf 352 BD with signed informed consent, 285 were selected by simple randomization. The prevalence of oral HPV was 17.5% (95% CI 13–21.9%), the genotype was identified in 13 cases, with a total of 16 genotypes (10 high-risk), the most common being 16 and 84. Five cases had multiple infections, three with at least one high-risk type. Associations were found for marital status (OR 3.3) and educational level (OR-1.9).
ConclusionsThe percentage of HPV-positive cases in blood donors with no risk practices was similar to that found in Spanish-speaking population studies in which at least one risk practice was described. The presence of other genotypes with high oncogenic risk and multitype infection, described as a marker of persistence of HPV infection, is highlighted.
Identificar la presencia del virus del papiloma humano (VPH) en la mucosa oral de donantes de sangre (DS), así como los factores de riesgo relacionados con el VPH y el cáncer oral.
Materiales y métodosEstudio transversal prospectivo. La población correspondió a los DS del Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, México, para la identificación de VPH en muestras citológicas orales con el kit CLART® Human Papillomavirus 2 (35 genotipos) y factores de riesgo.
ResultadosDe 352 DS con firma de consentimiento informado, se seleccionaron 285 por aleatorización simple. La prevalencia de VPH oral fue del 17,5% (IC 95%: 13-21,9%); en 13 casos se identificó el genotipo, con un total de 16 genotipos (10 de alto riesgo), los más frecuentes el 16 y el 84. Cinco casos presentaron infección multitipo, 3 con al menos un tipo de alto riesgo. Las asociaciones encontradas fueron para el estado civil (OR 3,3) y el nivel de estudios (OR 1,9).
ConclusionesEl porcentaje de casos positivos para VPH en DS sin prácticas de riesgo fue similar a los hallazgos en estudios de población hispanohablante en los que se ha descrito al menos una práctica de riesgo. Se destaca la presencia de otros genotipos con alto riesgo oncogénico y la infección multitipo descrita como marcador de persistencia de la infección por VPH.