Rhupus is a very rare syndrome of overlapping rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, characterized by the presence of erosive polyarthritis associated with symptoms and signs of systemic lupus erythematosus and the presence of high specificity autoantibodies. The analysis of HLA-DR molecules would allow us to genetically characterize patients diagnosed with rhupus, being able to differentiate them from the HLA-DR profile of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Materials and methodsCross-sectional observational study of 9 patients diagnosed with Rhupus in whom the HLA-DR genotype was genetically characterized.
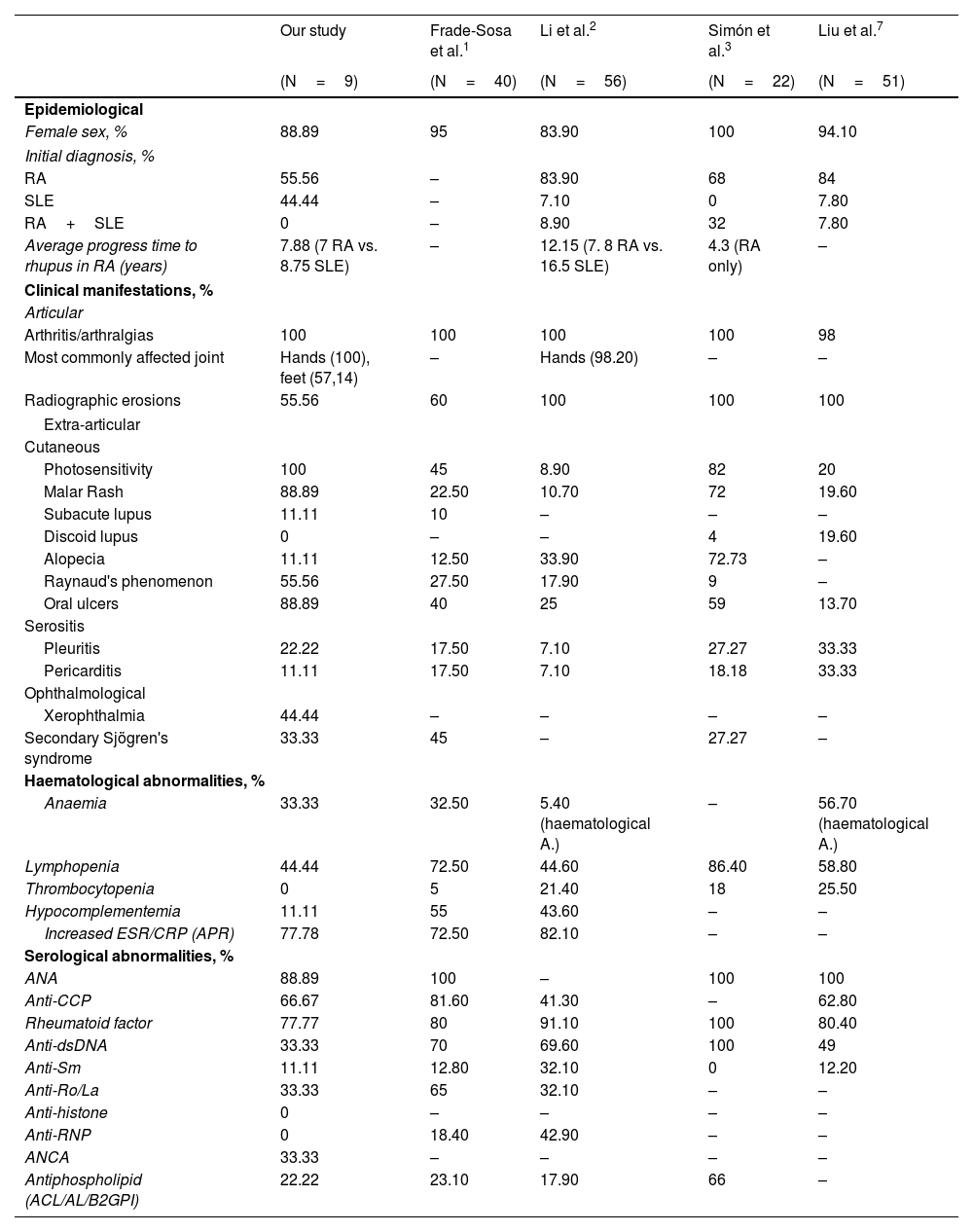
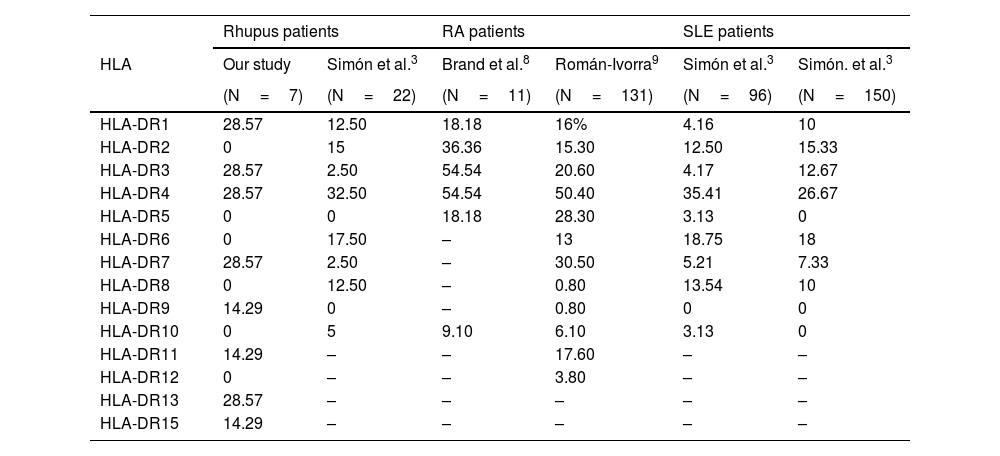
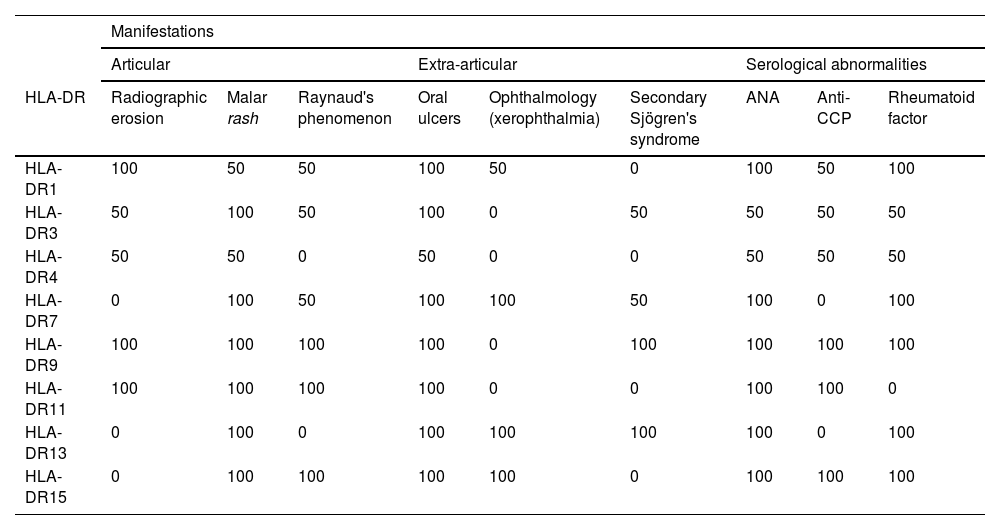
ResultsRhupus is usually more frequent in women with initial diagnosis of RA. The most frequent clinical manifestations are articular and, serologically, ANA, RF and anti-CCP positivity stand out. The most frequent HLA-DR were HLA-DR1, HLA-DR3, HLA-DR4, HLA-DR7 and HLA-DR13.
ConclusionsA higher proportion of HLA-DR1 and DR9 was observed in patients with Rhupus compared to RA and SLE, as well as a lower proportion of HLA-DR2, DR6 and DR8, which would help the early characterization of these patients prior to the overlap diagnosis.
El Rhupus es un síndrome muy raro de superposición de artritis reumatoide y lupus eritematoso sistémico, caracterizado por la presencia de poliartritis erosiva asociada a síntomas y signos de lupus eritematoso sistémico y la presencia de autoanticuerpos con alta especificidad. El análisis de las moléculas de HLA-DR permitiría caracterizar genéticamente a pacientes diagnosticados de rhupus, pudiendo diferenciarse del perfil HLA-DR de pacientes con artritis reumatoide y con lupus eritematoso sistémico.
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional transversal de 9 pacientes con diagnóstico de Rhupus en los que se caracterizó genéticamente el genotipo HLA-DR.
ResultadosEl Rhupus suele ser más frecuente en mujeres con diagnóstico inicial de AR. La clínica más frecuente es articular y serológicamente destaca la positividad ANA, FR y anti-CCP. Los HLA-DR con mayor frecuencia fueron el HLA-DR1, HLA-DR3, HLA-DR4, HLA-DR7 y HLA-DR13.
ConclusionesSe ha observado en pacientes con Rhupus mayor proporción HLA-DR1 y DR9 en comparación con AR y LES, así como una menor proporción de HLA-DR2, DR6 y DR8, lo que ayudaría la caracterización precoz de estos pacientes previamente al diagnóstico de solapamiento.