We aimed to evaluate the differences in some cardiovascular risk (CVR) factors between adult patients without and with phenylketonuria (PKU) and to explore the correlation between waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI) with the previous variables.
MethodsThis was an observational case–control study that included patients older than 18 years with a diagnosis of classic PKU. The controls were age- and sex-matched individuals. We collected demographic, epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory variables, including WC, BMI, and lipid profile parameters.
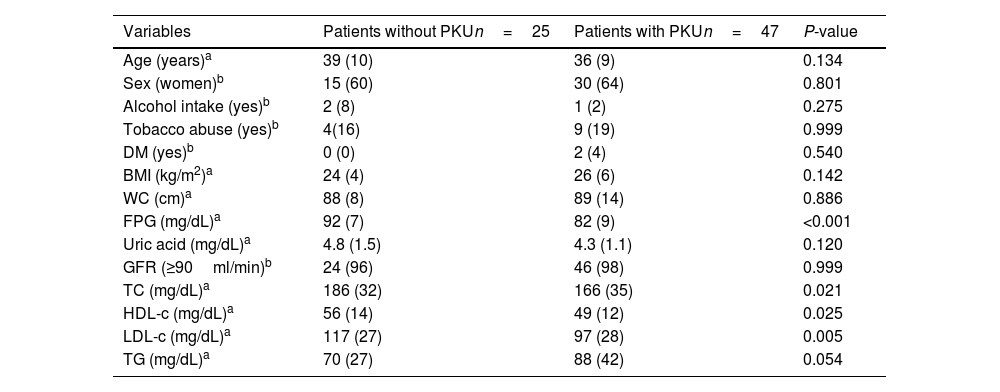
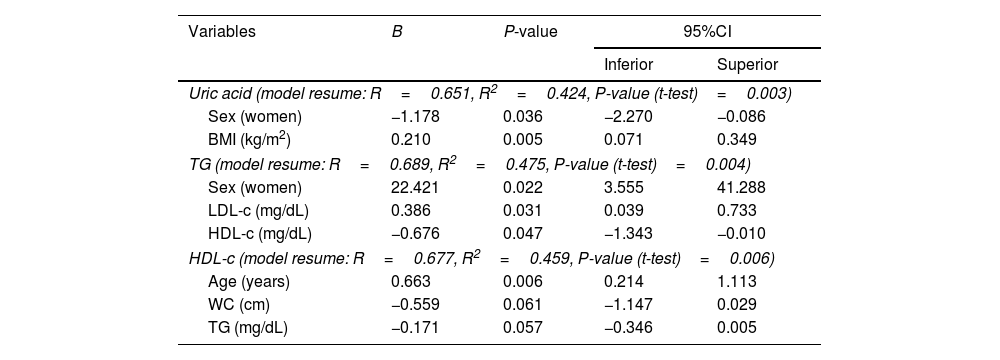
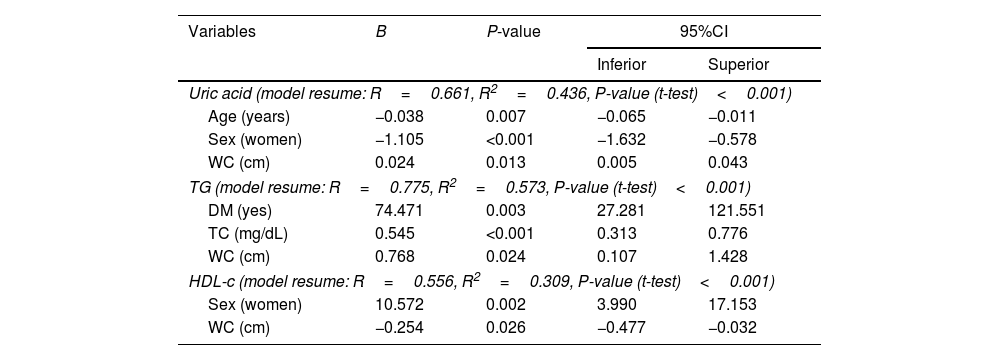
ResultsA total of 72 patients (25 controls and 47 cases) were included with a mean age of 36 years, of which 45 (62%) were women. Adult PKU patients showed lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) and higher triglyceride (TG) levels than the control group. We found an association between WC and uric acid (B=0.024, P=0.013, 95%CI: 0.005–0.043), TG (B=0.768, P=0.024, 95%CI: 0.107–1.428), and HDL-c (B=−0.254, P=0.026, 95%CI: −0.477 to (−0.032)) levels in PKU patients. However, we did not find any trend between WC and uric acid, TG and HDL-c levels that reached statistical significance (P<0.05) in patients without PKU.
ConclusionsWaist circumference rather than BMI may better represent the CVR in patients with PKU.
Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar las diferencias en algunos factores de riesgo cardiovascular entre pacientes adultos sin y con fenilcetonuria (FCU) y explorar la correlación del perímetro cintura (PC) e índice de masa corporal (IMC) con las variables previas.
MétodosFue un estudio de casos y controles que incluyó pacientes mayores de 18 años con diagnóstico de FCU clásica. Los controles fueron individuos emparejados por edad y sexo. Se recogieron variables demográficas, epidemiológicas, clínicas y de laboratorio, destacando PC, IMC y parámetros del perfil lipídico.
ResultadosSe reclutaron 72 pacientes (25 controles y 47 casos) con una edad media de 36 años (62% mujeres). Respecto al grupo control, los pacientes adultos con FCU mostraron niveles más bajos de colesterol de lipoproteínas de alta densidad (HDL-c) y más altos de triglicéridos. En los pacientes con FCU, PC se asoció con los niveles de ácido úrico (B=0,024, P=0,013, 95% CI: 0,005-0,043), triglicéridos (B=0,768, P=0,024, 95% CI: 0,107-1.428) y HDL-c (B=−0,254, P=0,026, 95% CI: −0,477–[−0,032]). Sin embargo, no encontramos ninguna tendencia entre WC y dichas variables que alcanzara significación estadística en los pacientes sin FCU. Aunque observamos una buena correlación entre el IMC y PC en pacientes sin y con FCU, el aumento de PC por unidad de aumento de IMC podría ser mayor en estos últimos.
ConclusionesPerímetro de cintura podría representar mejor que IMC el riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes con FCU.