Journal Information
Vol. 151. Issue 11.
Pages 464-465 (December 2018)
Vol. 151. Issue 11.
Pages 464-465 (December 2018)
Letter to the Editor
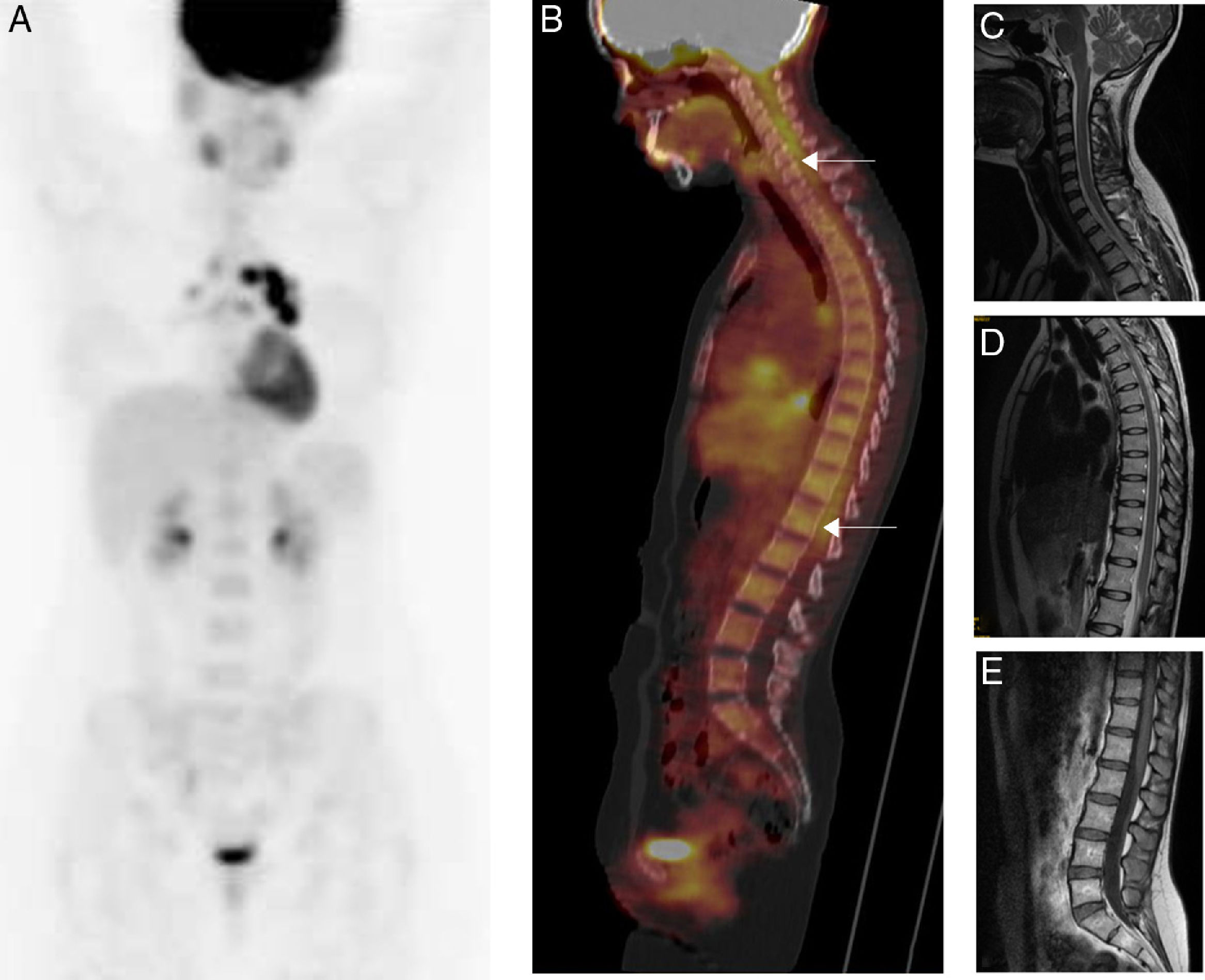
Usefulness of 18F-FDG-PET/CT imaging in a patient with neurosarcoidosis
Utilidad de la 18F-FDG-PET/CT en un paciente con neurosarcoidosis
Visits
2
a Nuclear Medicine Department, University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, University of Cantabria, Molecular Imaging Group – IDIVAL, Santander, Spain
b Department of Rheumatology, University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain
c School of Medicine, University of Cantabria, Santander, Spain
d Cardiovascular Pathophysiology and Genomics Research Unit, School of Physiology, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail