Aspiration pneumonia is becoming a common syndrome in the elderly in aging societies such as Japan. Although a number of tools have been validated for prediction of mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia, none have been established for aspiration pneumonia. The purpose of this study was to access the correlations of the A-DROP, CURB-65 and SMART-COP scores at the emergency visit with the 30-day mortality risk in patients with aspiration pneumonia.
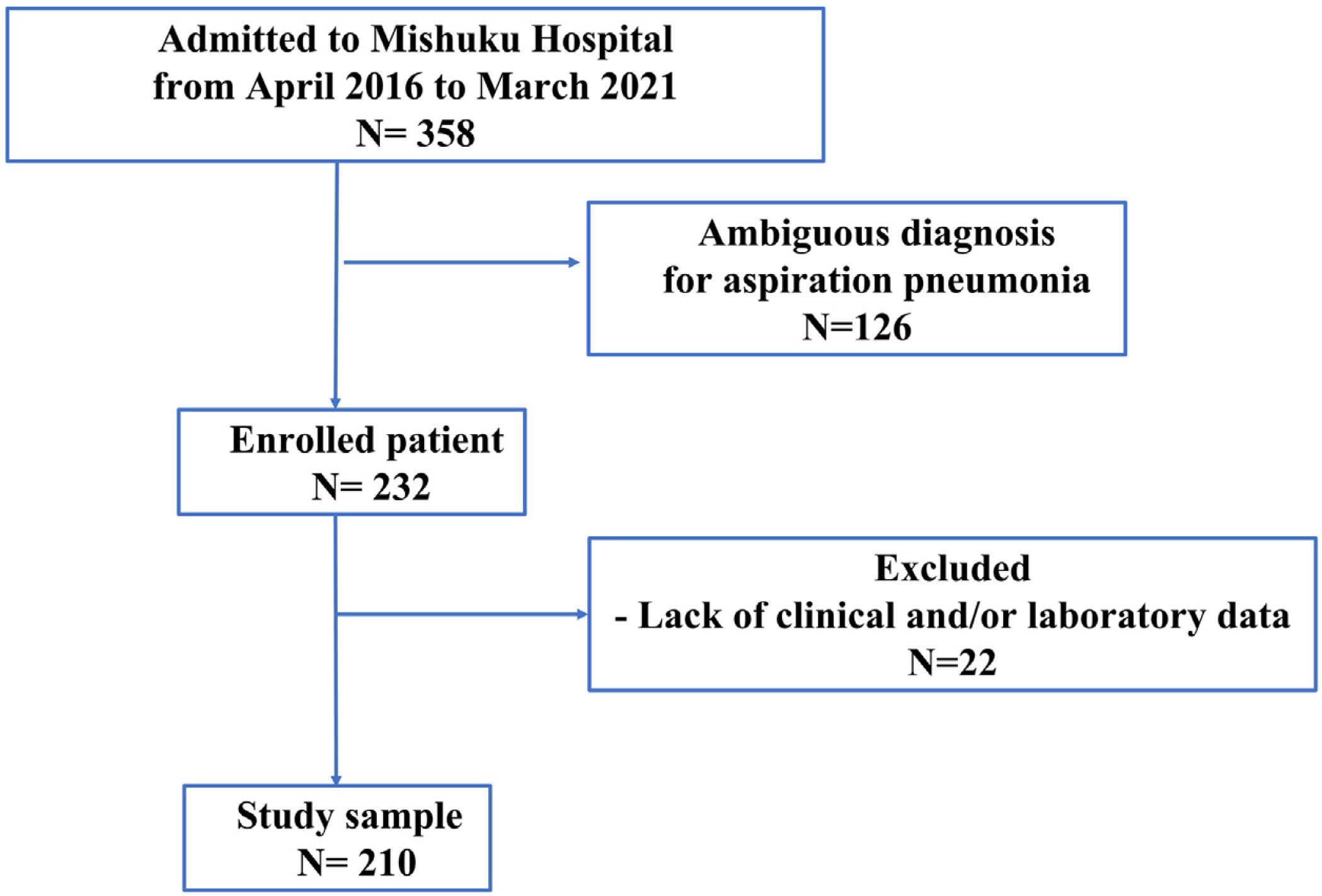
MethodsWe Titleretrospectively investigated 210 patients who presented to the emergency department at Mishuku Hospital in Tokyo, Japan.
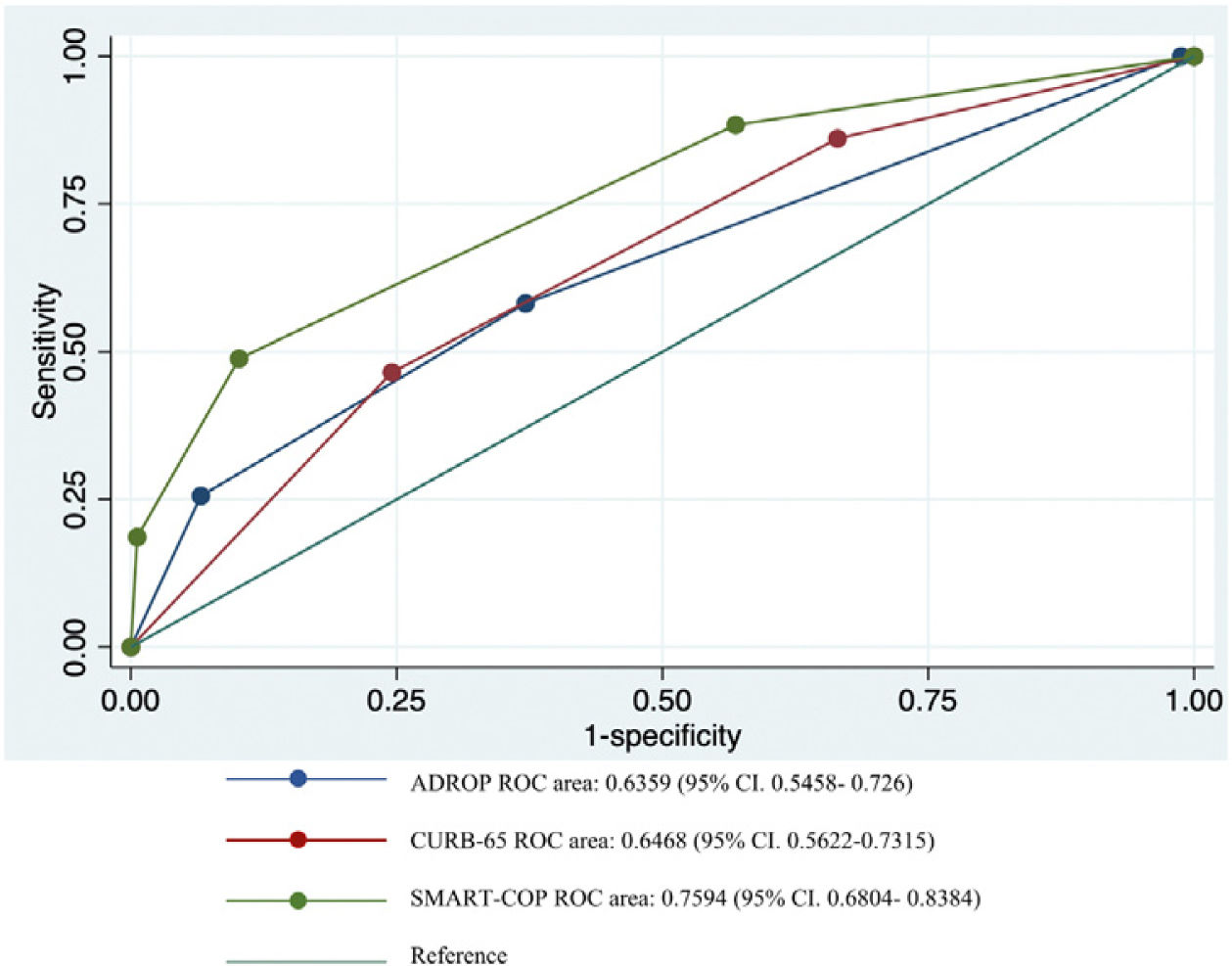
ResultsThe areas under the curve for the ability of A-DROP, Curb-65 and SMART-COP scores to predict the 30-day mortality risk were 0.6359, 0.6468 and 0.7594, respectively. Among the parameters of SMART-COP, involvement of multiple lobes on chest radiographs is the best predictor of the mortality.
ConclusionsThe SMART-COP score can be a better predictor of the 30-day mortality risk.
La neumonía por aspiración se está convirtiendo en un síndrome frecuente entre las personas de la tercera edad en sociedades envejecidas como Japón. A pesar de que se han aprobado diversas herramientas para la predicción de la mortalidad en pacientes con neumonía adquirida en la comunidad, no se ha logrado ninguna para la neumonía por aspiración. El objetivo de este estudio fue obtener correlaciones entre las puntuaciones en las escalas A-DROP, CURB-65 y SMART-COP en las visitas al servicio de urgencias y el riesgo de mortalidad a 30 días en pacientes con neumonía por aspiración.
MétodosInvestigamos de forma retroactiva 210 pacientes que acudieron al servicio de urgencias del Hospital Mishuku en Tokio, Japón, y que fueron hospitalizados con neumonía por aspiración.
ResultadosLas áreas bajo la curva de capacidad de las puntuaciones en las escalas A-DROP, CURB-65 y SMART-COP para predecir el riesgo de mortalidad a 30 días fueron 0,6359; 0,6468 y 0,7594, respectivamente. Entre los parámetros de la escala SMART-COP, la afectación de múltiples lóbulos en las radiografías de tórax es el mejor indicador de la mortalidad.
ConclusionesLa puntuación en la escala SMART-COP puede ser un mejor indicador del riesgo de mortalidad a 30 días.