To describe the clinical, radiological and microbiological characteristics of vertebral osteomyelitis patients, analysing the factors that played a role on their outcome.
Patients and methodsSingle-centre retrospective observational study including patients diagnosed with vertebral osteomyelitis, based on the combination of clinical presentation with either a definitive bacteriological diagnosis and/or imaging studies.
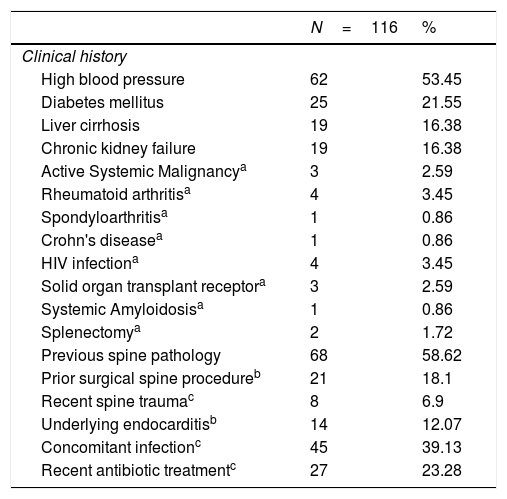
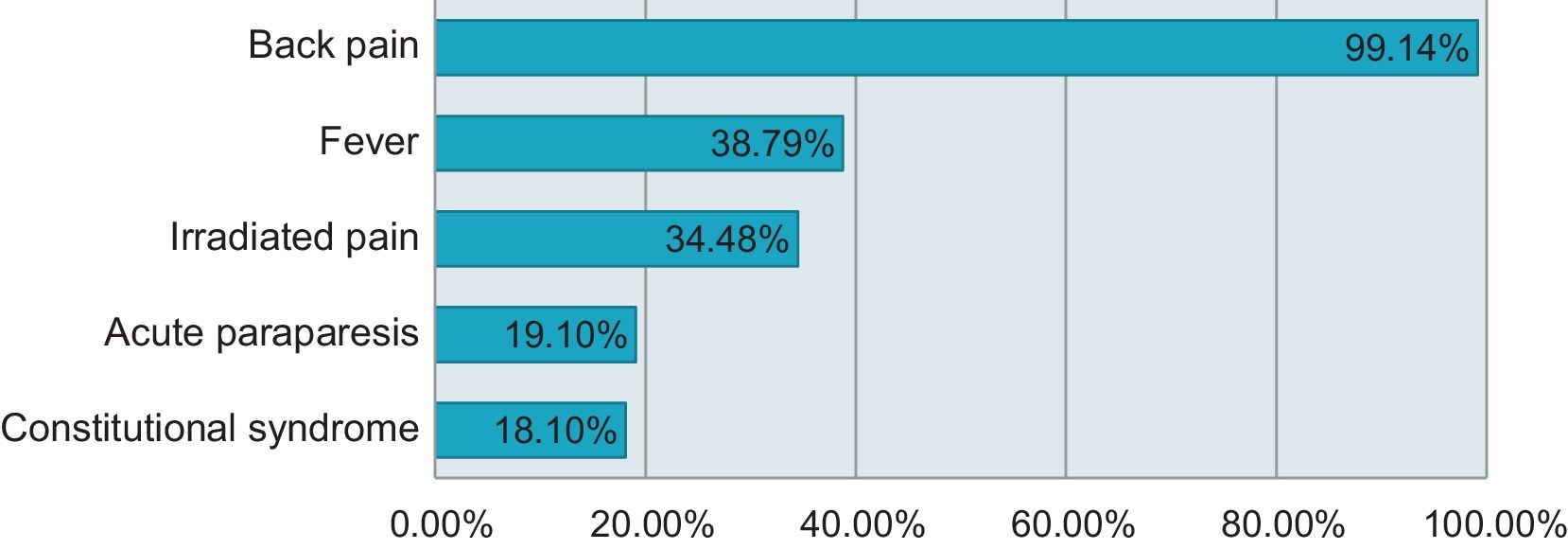
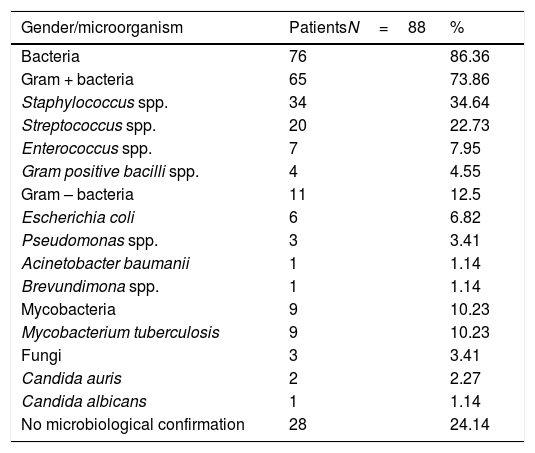
Results116 adult patients were included with a mean age of 62.75 (14.98) years. Males predominated (68.10%). Eighteen patients (15.51%) were immunosuppressed. The most frequent symptom was back pain (99.14%) followed by fever, which was detected in 45 patients (38.79%). Puncture-aspiration or biopsy was performed in 84 patients (72.10%) and its culture was positive in 48 samples (57.14%). Gram positive species predominated (73.86%) on cultures, followed by Gram negative (12.5%), mycobacteria (10.23%) and fungi (3.41%). No microorganism was identified in 28 patients (24.14%). On imaging, most of the patients (92.24%) had paravertebral or epidural abscess. 63 cases (54.31%) showed vertebral destruction and 39 (33.62%) cord compression. Twenty-two patients (18.97%) required further surgical procedures and 13 (11.21%) died.
ConclusionsThe average patient is middle aged (often male) with a history of subacute back pain, sometimes presenting fever and/or neurological damage on diagnosis. Acute phase reactants are frequently raised. Diabetes mellitus, endocarditis and immunosuppressed patients may have the worst chance of a good outcome, therefore these patients should be more carefully managed (always try to obtain an imaging-guided biopsy, correct antibiotic treatment, and a functional and clinical follow-up).
Describir las características clínicas, radiológicas y microbiológicas de pacientes con osteomielitis vertebral en nuestro centro, analizando qué variables tuvieron influencia pronóstica.
Material y métodosSe llevó a cabo un estudio observacional, unicéntrico y retrospectivo incluyendo pacientes adultos diagnosticados de osteomielitis vertebral sobre la base de la combinación de las manifestaciones clínicas con un diagnóstico microbiológico y/o radiológico compatible.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 116 pacientes con una media de edad de 62,75 (14,98) años, predominando el género masculino (68,10%). Dieciocho de ellos (15,51%) estaban inmunosuprimidos. El síntoma más frecuente fue el dolor lumbar (99,14%) seguido de la fiebre, detectada en 45 pacientes (38,79%). Se realizó punción-biopsia en 84 pacientes (72,10%) con positividad en el cultivo en 48 muestras (57,14%) donde predominó el crecimiento de Gram positivos (73,86%) seguido de Gram negativos (12,5%), micobacterias (10,23%) y hongos (3,41%). En 28 pacientes (24,14%) no se pudo identificar el agente causal. En el estudio de resonancia magnética, la mayoría de los pacientes tenían abscesificación paravertebral o epidural (92,24%); 63 pacientes (54,31%) tenían hallazgos compatibles con destrucción vertebral y 39 (33,62%), compresión medular. En 22 casos (18,97%) se requirió un abordaje quirúrgico posterior. Trece pacientes (11,21%) fallecieron a causa de la infección o de sus complicaciones.
ConclusionesEl paciente promedio es un varón de edad media, con historia de dolor lumbar de curso subagudo e insidioso, con presencia inconstante de fiebre, presente en menos de la mitad de los casos. Con relativa frecuencia se ha detectado una exploración neurológica patológica en la presentación clínica. Los reactantes de fase aguda estaban elevados en la mayoría de los pacientes. Los casos en los que exista comorbilidad (sobre todo diabetes mellitus o inmunosupresión), así como la concomitancia con endocarditis, debe de implicar un manejo más cauto.