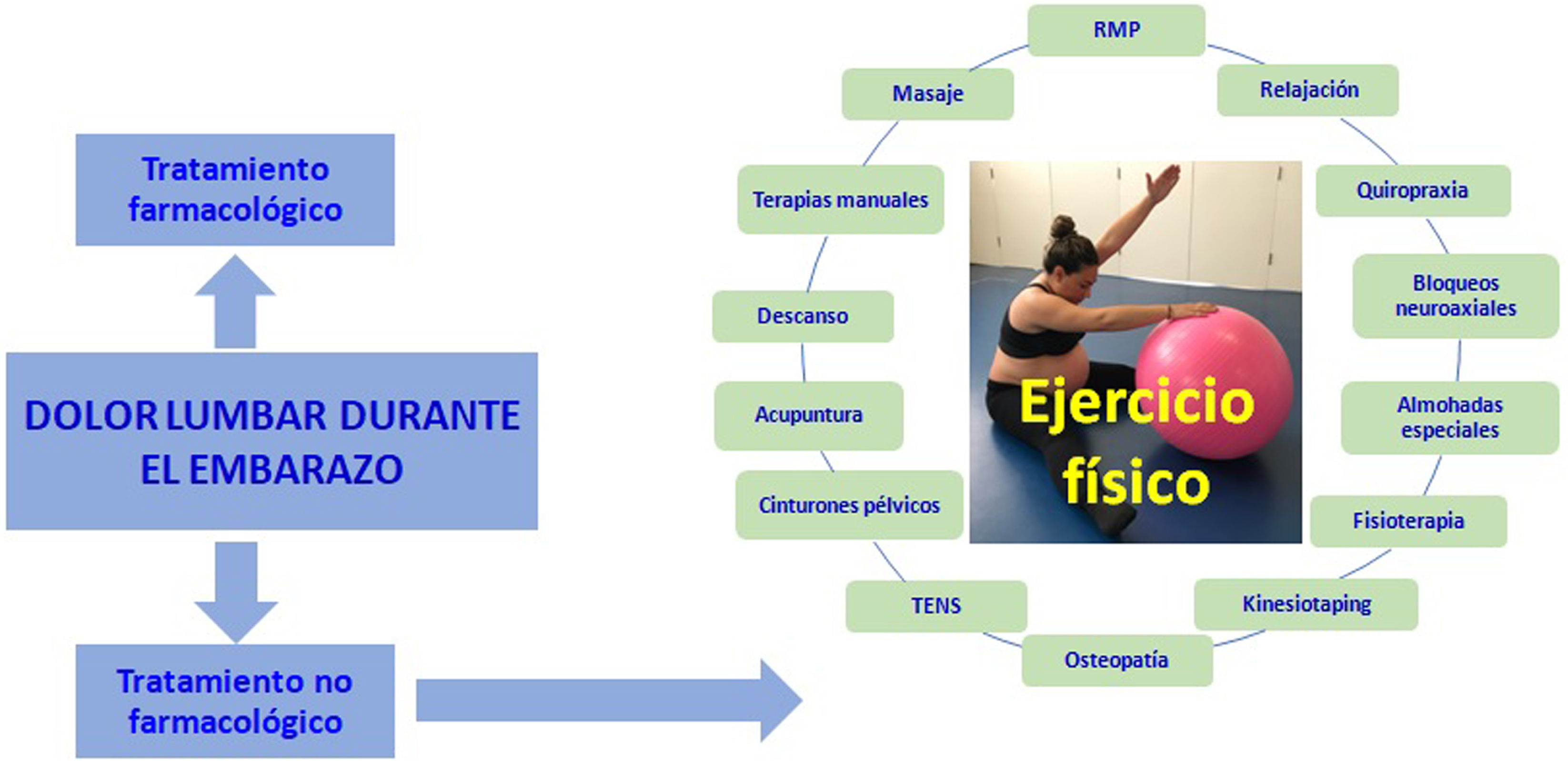
El dolor lumbar (DL) en las mujeres embarazadas puede causar un impacto negativo para realizar las actividades cotidianas, reducir la calidad de vida y aumentar el absentismo laboral. A pesar de su alta prevalencia, que varía del 13,2 al 80%, se estima que más del 50% de las mujeres embarazadas reciben poca o ninguna intervención de los profesionales sanitarios y, con frecuencia, se considera erróneamente como un fenómeno normal.
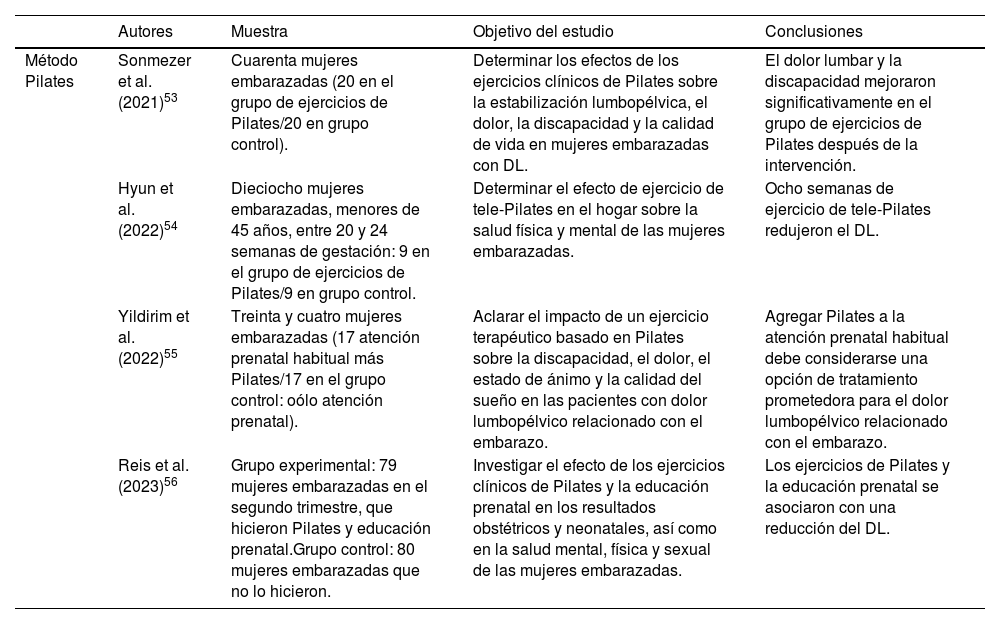
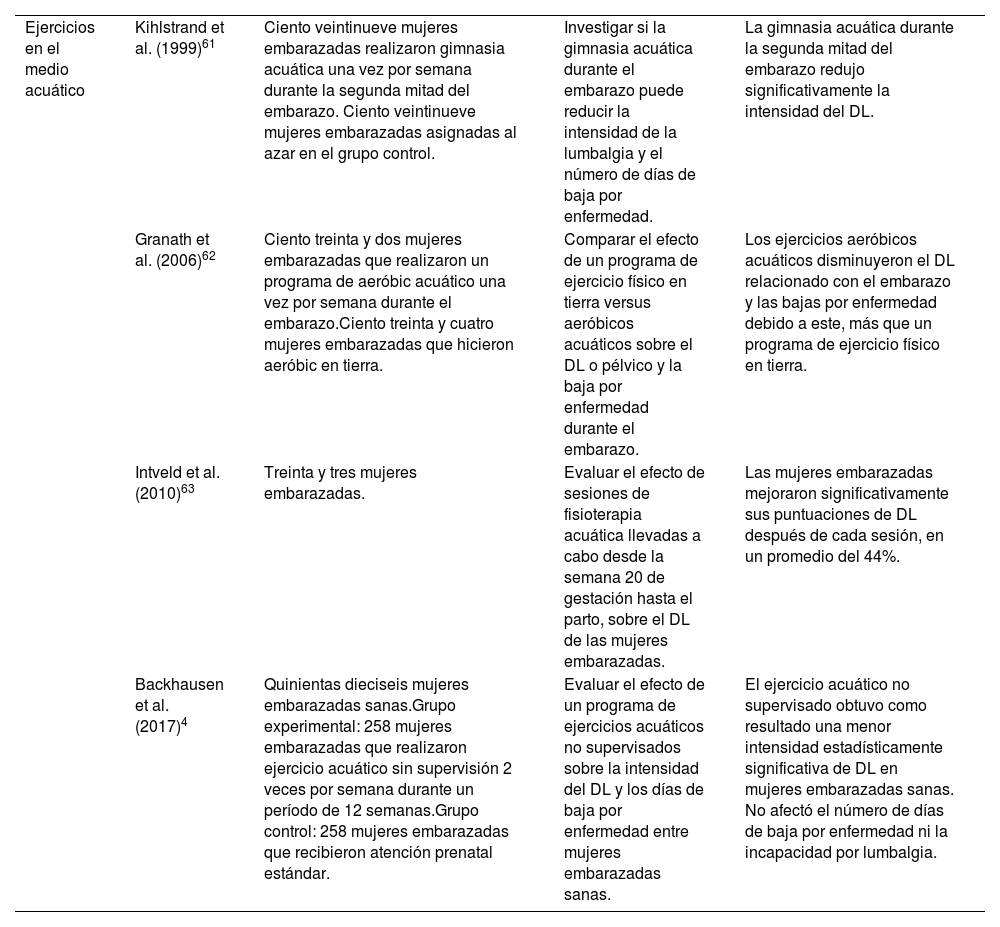
Dados los efectos secundarios que tiene el tratamiento farmacológico del DL de la mujer embarazada, y que el ejercicio físico realizado durante la gestación ha mostrado su eficacia para disminuir la intensidad de este, el objetivo de este artículo es concienciar al médico de atención primaria para que prescriba ejercicio físico a la mujer embarazada con DL y evite la inactividad física como consecuencia del DL, ya que esta puede provocar una mayor incidencia de complicaciones obstétricas y de cesáreas.
Low back pain (LBP) in pregnant women can have a negative impact on daily activities, reduce quality of life and increase absenteeism from work. Despite its high prevalence, ranging from 13.2 to 80%, it is estimated that more than 50% of pregnant women receive little or no intervention from healthcare professionals, and it is often mistakenly considered as a normal phenomenon.
Given the side effects of pharmacological treatment of LBP in pregnant women, and the fact that physical exercise during pregnancy has been shown to be effective in reducing the intensity of LBP, the aim of this article is to raise awareness among primary care physicians so that they prescribe physical exercise to pregnant women with LBP and avoid physical inactivity as a consequence of LBP, as this can lead to a higher incidence of obstetric complications and caesarean section.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.