Exomic sequencing reveals genetic syndromes in up to 25% of subjects with genetic diseases which remain undiagnosed after multiple genetic studies.1,2 In 2013, Bainbridge and Ropers reported de novo variants of truncating mutations of the Additional sex combs-like 3 gene (ASXL3, locus 18q12.2, 12 exons) in 4 patients with severe psychomotor retardation, and learning and feeding difficulties.3
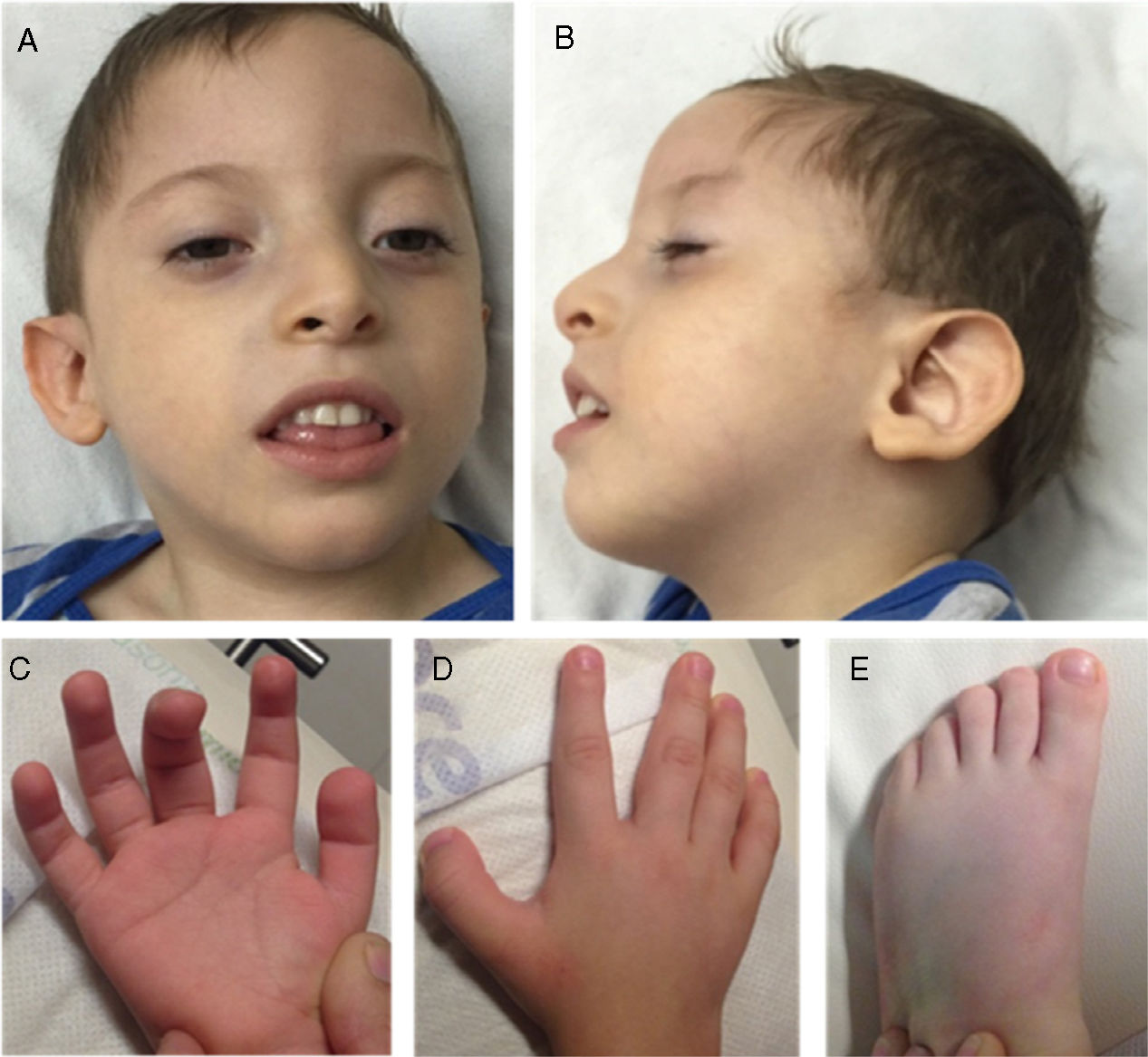
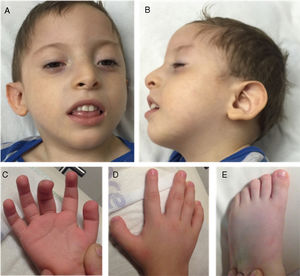
We examined a 3-year-old boy, who was the fourth child of healthy, non-consanguineous Mexican parents. The other 3 children were healthy. He was delivered vaginally after a normal, full-term pregnancy (length: p > 97; weight: p > 85; head circumference: p97; Apgar score: 7.9). He achieved head control at 6 months and could sit at one year. At 36 months of age, the patient presented severe neurodevelopmental delay and was unable to speak or walk. He also presented microcephaly (−4.35SD), short stature (−3.5SD), and poor weight gain (−4.6SD). The facial phenotype included prominent forehead, hypertelorism, high anterior hairline, thin eyebrows, mild synophrys, anteverted nostrils with hypoplastic alae nasi, high-arched palate, and low-set prominent ears. We also observed fingertip pads, broad thumb and big toe in both hands and feet, and cryptorchidism (Fig. 1). A brain MRI scan revealed cortical atrophy. Karyotyping (46, XY) and comparative genomic hybridisation (400k) yielded normal results. Baylor Miraca Genetics Laboratories performed whole exomic sequencing from purified genomic DNA extracted from the patient's peripheral blood. Sequencing consisted in DNA fragmentation by sonication and ligation with multiplex sequencing adapters on the Illumina platform.4 The process of enrichment/capture was performed by hybridisation of a microarray customised by NimbleGen (VCRome 2.1),5 as well as additional probes for 3650 Mendelian and mitochondrial genome genes.6 We used the Illumina HiSeq 2000 system for analysis (median exome coverage, 95%; median nucleotide coverage, >100×). Variant calling and annotations were performed using the Atlas-SNP/SNP-anno and Atlas-indel/HGSC-anno tools, developed in-house by Baylor College of Medicine. De novo variants and in silico predictions of nonsense changes were reported according to the American College of Medical Genetics criteria.7 The patient was heterozygous for a 4-bp deletion on chromosome 18:31320359 at NM_030632.2 (ASXL3): c.2992-2995del, p.(E998fs) in exon 11; this frameshift mutation causes an aberrant protein, predicted to be deleterious. Sanger sequencing of the ASXL3 gene in the patient's parents yielded normal results; therefore, we believe this to be a de novo variant in the proband.
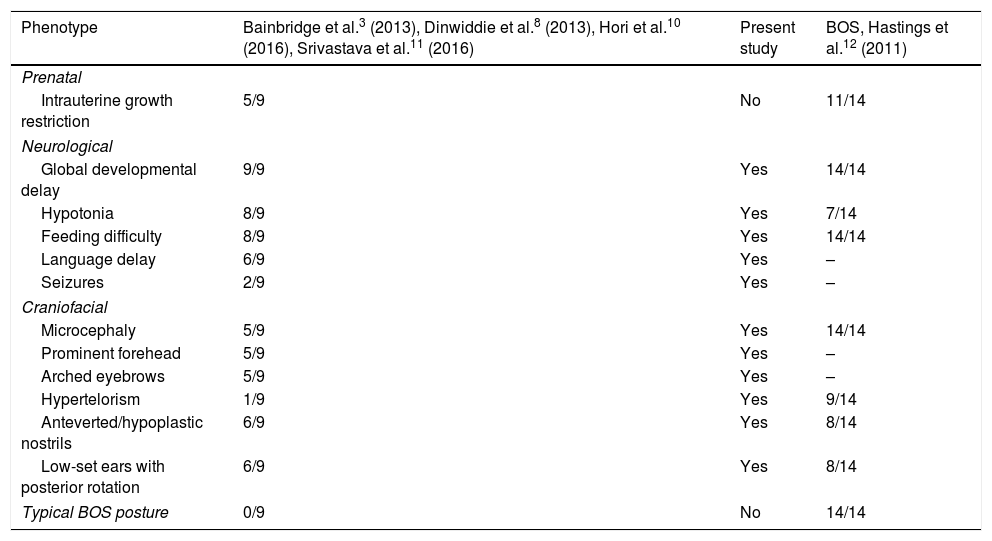
Few patients with Bainbridge-Ropers syndrome (MIM #615485) have been reported to date. Diagnosis is achieved after whole-genome and exome sequencing, since the phenotype is subtle and variable.3,8–11 The common clinical characteristics (severe psychomotor retardation, facial dysmorphism, growth failure, and feeding difficulties) can be misinterpreted as such other syndromes as Bohring-Opitz syndrome (MIM #605039) (Table 1).12,13 Bohring-Opitz syndrome is related to genetic variants of ASXL1, and no variants of ASXL3 have been detected; these syndromes are therefore considered 2 distinct entities.3,12 Most of the described variants of ASXL3 are de novo mutations producing premature stop codons or shifting the reading frame in the coding region of the ASXL3 gene, and group together in a region of exon 11.3,8,9 Bainbridge-Ropers syndrome represents a challenge for molecular diagnosis based on the analysis of a single gene or multiple-gene panel testing; therefore, the recent introduction of whole-genome or exome sequencing techniques is useful for research into the aetiology of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Comparison of the clinical characteristics of patients with Bainbridge-Ropers syndrome with variants of the ASXL3 gene and patients with Bohring-Opitz syndrome.
| Phenotype | Bainbridge et al.3 (2013), Dinwiddie et al.8 (2013), Hori et al.10 (2016), Srivastava et al.11 (2016) | Present study | BOS, Hastings et al.12 (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prenatal | |||
| Intrauterine growth restriction | 5/9 | No | 11/14 |
| Neurological | |||
| Global developmental delay | 9/9 | Yes | 14/14 |
| Hypotonia | 8/9 | Yes | 7/14 |
| Feeding difficulty | 8/9 | Yes | 14/14 |
| Language delay | 6/9 | Yes | – |
| Seizures | 2/9 | Yes | – |
| Craniofacial | |||
| Microcephaly | 5/9 | Yes | 14/14 |
| Prominent forehead | 5/9 | Yes | – |
| Arched eyebrows | 5/9 | Yes | – |
| Hypertelorism | 1/9 | Yes | 9/14 |
| Anteverted/hypoplastic nostrils | 6/9 | Yes | 8/14 |
| Low-set ears with posterior rotation | 6/9 | Yes | 8/14 |
| Typical BOS posture | 0/9 | No | 14/14 |
BOS: Bohring-Opitz syndrome.
We would like to thank our patient's family for their interest in sharing his case for scientific research purposes.
Please cite this article as: Contreras-Capetillo SN, Vilchis-Zapata ZH, Ribbón-Conde J, Pinto-Escalante D. Retraso global del desarrollo y microcefalia posnatal: síndrome de Bainbridge-Ropers con una nueva variante de novo en ASXL3. Neurología. 2018;33:484–486.
This study was presented as a free paper in poster format at the 40th National Congress of Human Genetics in Monterrey (Nuevo León, Mexico), 11–14 November 2015.