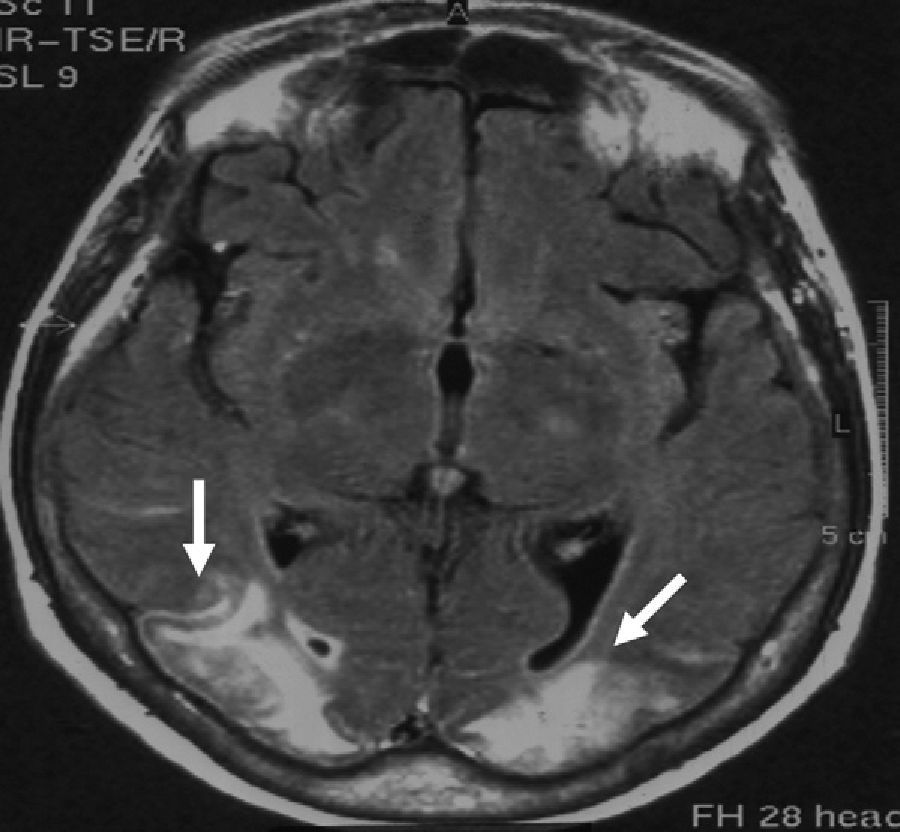
Potomania or psychogenic polydipsia is characterised by excessive drinking of liquids, such as water (polydipsia) or alcohol (dipsomania). Excessive drinking may lead to hyponatraemia (HNa) even in patients presenting no organic, metabolic, or toxic diseases.1,2 Central pontine myelinolysis (PM) and extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM) have numerous manifestations and affect different areas (generally symmetrical areas). Myelinolysis is mainly caused by hyponatraemia and the means used to correct it; to a lesser extent, it may be caused by association with hypokalaemia. We present the case of a woman aged 72 who was admitted to the hospital in a coma 3hours after its onset. Coma was preceded by disorientation and progressive stupor developing in the preceding 6hours. The patient presented decreased muscle tone in all limbs, deep tendon areflexia, lack of Babinski sign, and bilateral plantar reflex due to pain. The oculocephalic, corneal, and photomotor reflexes were present. The Glasgow coma scale score was 6/15. Studies showed no renal, cardiac, or hormonal disorders. The patient had a history of non-alcoholic potomania in the preceding 6 months (water intake of 4 to 6 litres daily). She was in psychotherapy and undergoing treatment with quetiapine (50mg/day). This treatment was beneficial for 5 months, after which potomania appeared again. Blood tests revealed hyponatraemia of 111mM/L and hypokalaemia of 2.2mM/L. The rest of the results were anodyne. The ECG showed sinus rhythm, a heart rate of 85 beats per minute, ST segment deviation, and flat T wave. The computed tomography (CT) performed in the first 12hours yielded normal results. Natraemia was corrected at a rate of 9mM/L/day; kalaemia was corrected by administering 5mM/h of potassium chloride intravenously. The patient awoke 48hours later with a confusional state, flexor withdrawal reflex in all 4 limbs, and purposeless hand movements. The Glasgow coma scale score was 12/15. At this time, natraemia was 127mM/L and kalaemia, 3.7mM/L. Doctors suspected bilateral vision loss since stimulating visual fields with rapid, nearby movements elicited no blink reflex. The brain MRI carried out on the third day of hospitalisation (Fig. 1) showed occipital lesions. There were no changes in the pons or the cerebral/cerebellar hemispheres. Blood test showed normal results on the 10th day after admission. Another brain MRI showed similar changes and the angiography of the neck vessels and intracranial arteries yielded normal results. In the fourth week of hospitalisation, the patient presented no cognitive decline, but cortical blindness had not abated. She was lucid and aware of her visual impairment. There are 2 main causes of hyponatraemia: net increase in water (total sodium remains normal), and sodium loss. Although the mechanisms often coexist, one is frequently predominant. In our case, psychogenic polydipsia triggered dilutional hyponatraemia; researchers found no primary diseases inducing potomania or hyponatraemia. PM is suspected when the patient presents severe manifestations (disorientation, stupor and coma, tetraparesis) or a history of malnutrition, alcoholism, or polydipsia. Myelinolysis is due to oligodendrocyte death, which is favoured by the predominance of proapoptotic factors.3 EPM presents similar pathological changes characterised by predominantly extrapyramidal manifestations, such as parkinsonism, dystonia, dyskinesias, and spasmodic dysphonia. According to a recent publication, EPM lesions are symmetrically arranged and located in the basal ganglia.4 We did not find any reports of osmotic myelinolysis with definitive amaurosis in the posterior half of the brain. The literature includes only one case of blindness due to optic nerve atrophy and one other case of transient vision loss due to osmotic changes resulting from an altered ammonium cycle.5,6 In cases of dipsomania, excessive beer intake may trigger hyponatraemia,7 which is sometimes accompanied by PM8; likewise, alcohol withdrawal syndrome may cause PM and EPM without associated hyponatraemia.9 In cases of asymptomatic normovolaemic hyponatraemia, guidelines suggest that correction should not exceed 10 to 12mM/L per day.10 The presence of PM and EPM associated with hyponatraemia is a formidable cause of death and disability. This letter points out a new sequela of EPM, stressing that potomania is a risk factor that can be modified to prevent the consequences described here.
Please cite this article as: Domínguez RO, Laguarde N, Pinkala E, González SE. Potomanía y desequilibrio osmótico: Ceguera cortical definitiva por mielinólisis extrapontina. Neurología. 2013;28:449–450.