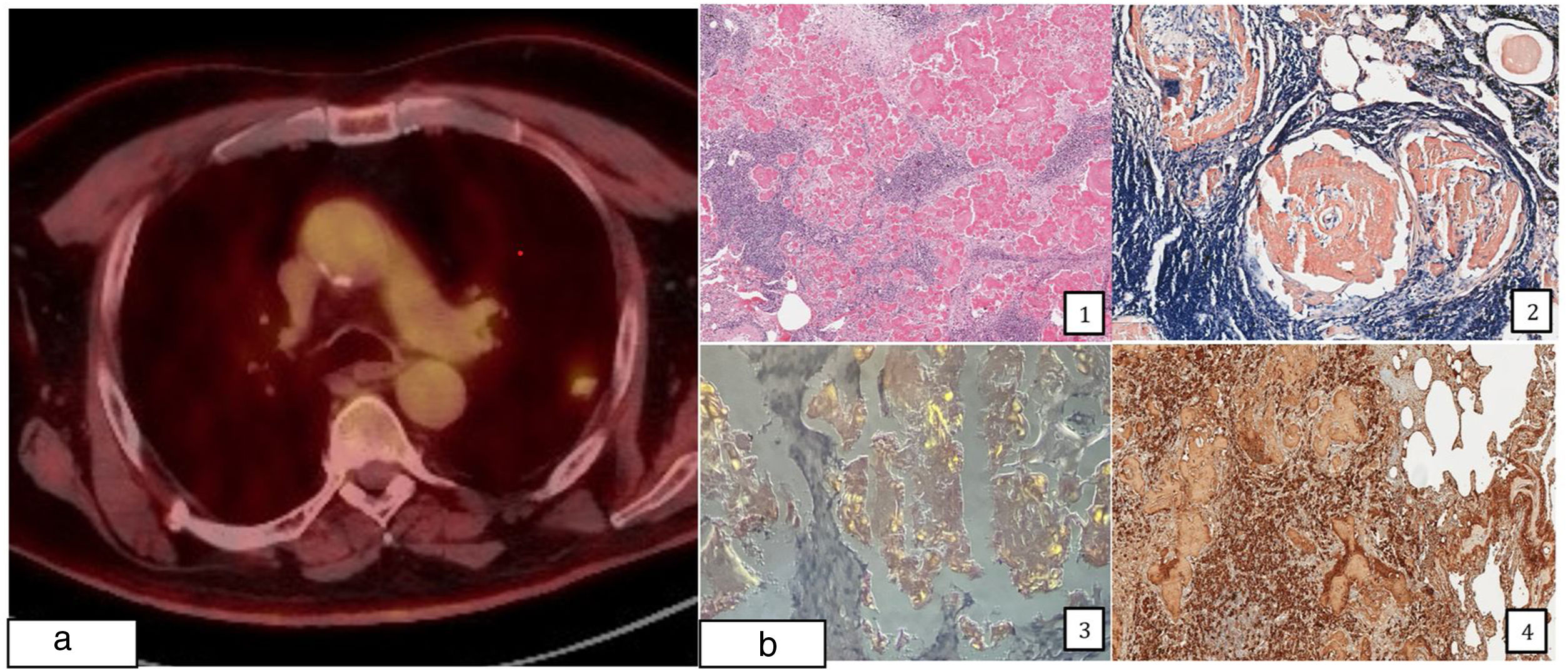
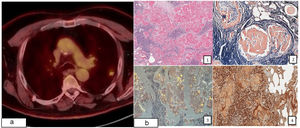
A 74-year-old man, ex-smoker with recent diagnosis of prostate cancer, underwent a 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET) for the extension study. It showed a 19mm (SUVmax 2.98) polylobulated lesion with spiculated edges in the left upper lobe (LUL) and right lower paratracheal (SUVmax 3.15) and subcarinal (SUVmax 3.05) lymph nodes (Fig. 1a). Bronchoscopy and echobronchoscopy were performed with inconlusive results. Pulmonary function testing was normal, but the nodule was suspected to represent malignancy, so the patient was referred to thoracic surgery. Histopathologic result of segmentectomy confirmed nodular amyloidosis diagnosis (Fig. 1b). Nodular pulmonary amyloidosis is an unusual pathology, usually presented as an incidental finding on chest radiography. Most patients, as the one reported here are asymptomatic, but wheeze, cough, and recurrent pneumonia are present depending on the localization.1,2 Differential diagnosis include neoplasia, tubercuosis, and histoplasmosis. The gold standard diagnosis is histopathologic confirmation, marked by green birefringence of Congo restained tissue under cross-polarization.1,2 Histologically, amyloidoma nodules are composed of homogenous eosinophilic material.2 In conclusion, nodular amyloidosis, although rare, should be included in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary nodule. Histological confirmation is important due to imaging similarities between nodular amyloidosis and malignant lung tumors.
(a) Left upper lobe nodule (SUVmax 2.98) in 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET). (b) 1, Deposits of acellular eosinophilic amorphous material associated with an extensive inflammatory infiltrate (hematoxylin–eosin) 2, Congo red stain 3, green birefringence of Congo restained tissue under cross-polarization 4, immunohistochemistry, Kappa light chains.
Publication after obtaining informed consent.
FundingNo funding has been received to produce this document.
Authors’ contributionsSelene Cuenca Peris and Ana Flor Pérez have prepared the manuscript. They have collected the relevant information on the case and have done the bibliographical review to write it up.
Cecilia López Valdivia made the pathological diagnosis and has given us the pathological anatomy images with their description.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest directly or indirectly related to the contents of the manuscript. This is an original publication.
This is an observational study, it has not required any additional intervention to write this clinical image. For this reason, an evaluation by the ethics committee has not been required.