La bibliometría permite medir la importancia relativa de una revista científica en su campo. El objetivo de este trabajo es analizar la producción científica de Radiología y la evolución de los parámetros bibliométricos en el periodo 2010-2019.
Materiales y métodosRevisión bibliométrica de la revista Radiología entre los años 2010 y 2019 a partir de la información obtenida de tres fuentes: base de datos Scopus, versión electrónica de la revista y editorial Elsevier. Se analizaron retrospectivamente aspectos del proceso editorial (decisión final y velocidad), los documentos publicados (tipo, subespecialidad radiológica y técnica de imagen), la tendencia de la citación y de varios índices (CiteScore, SNIP y SJR), la visibilidad, las descargas, características de las autorías (procedencia geográfica y colaboración institucional) y los artículos más citados.
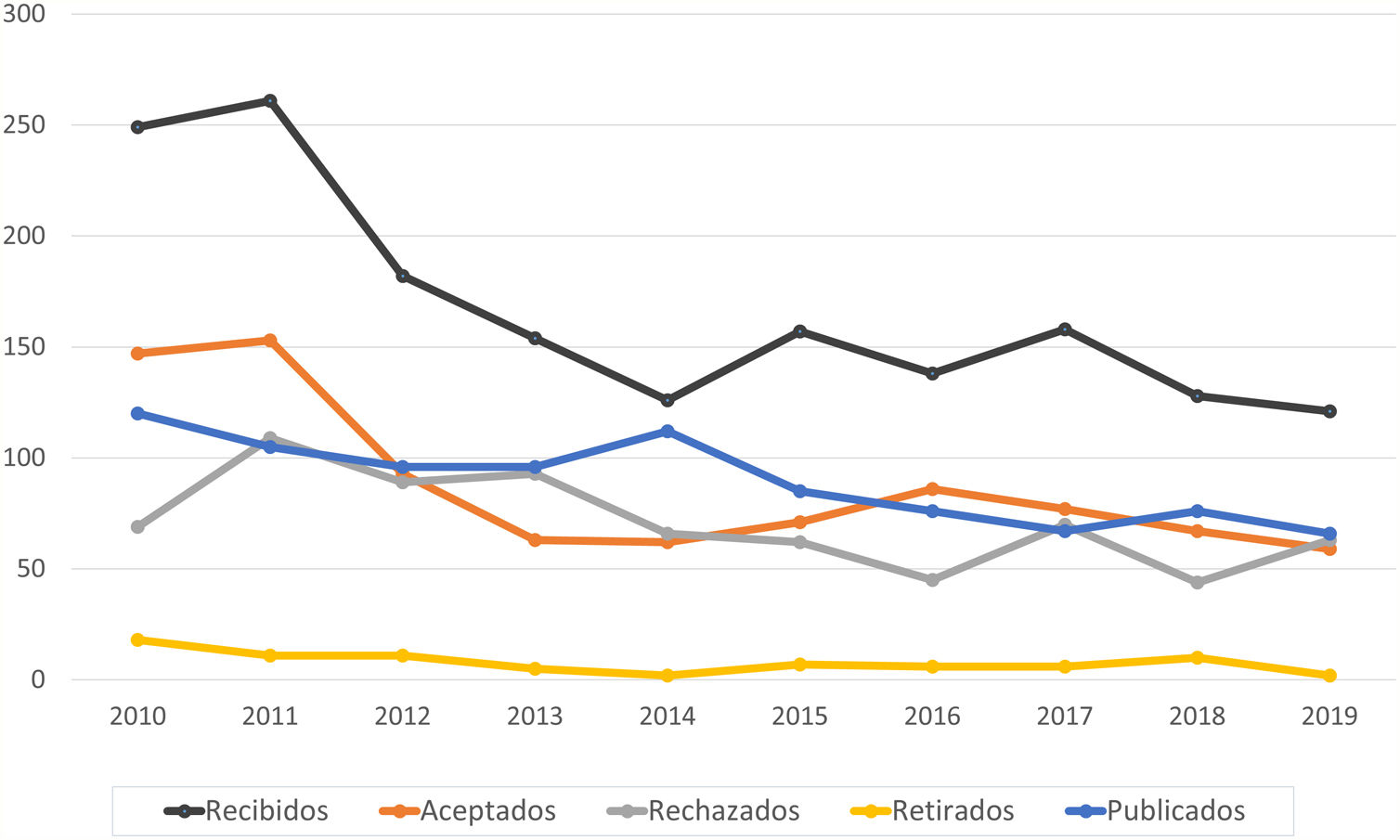
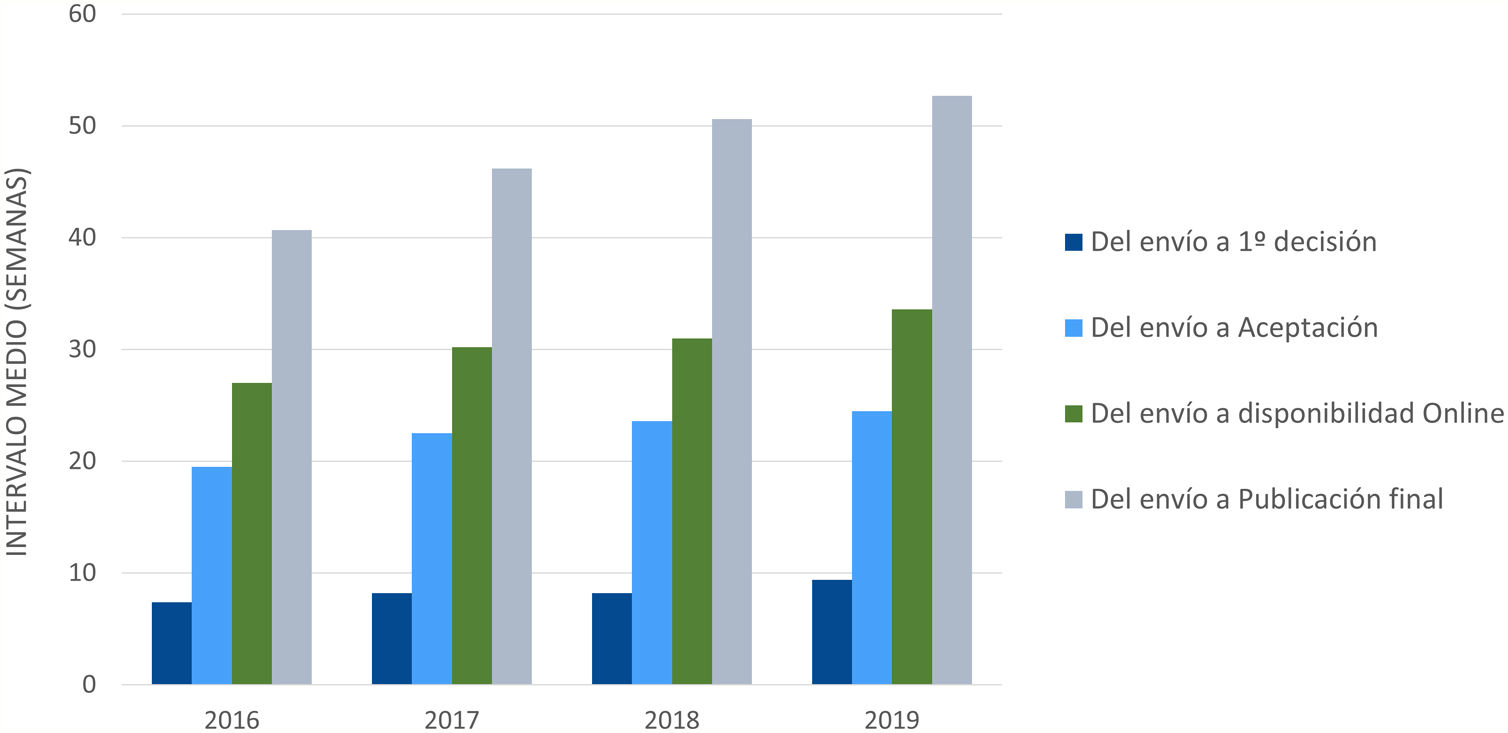
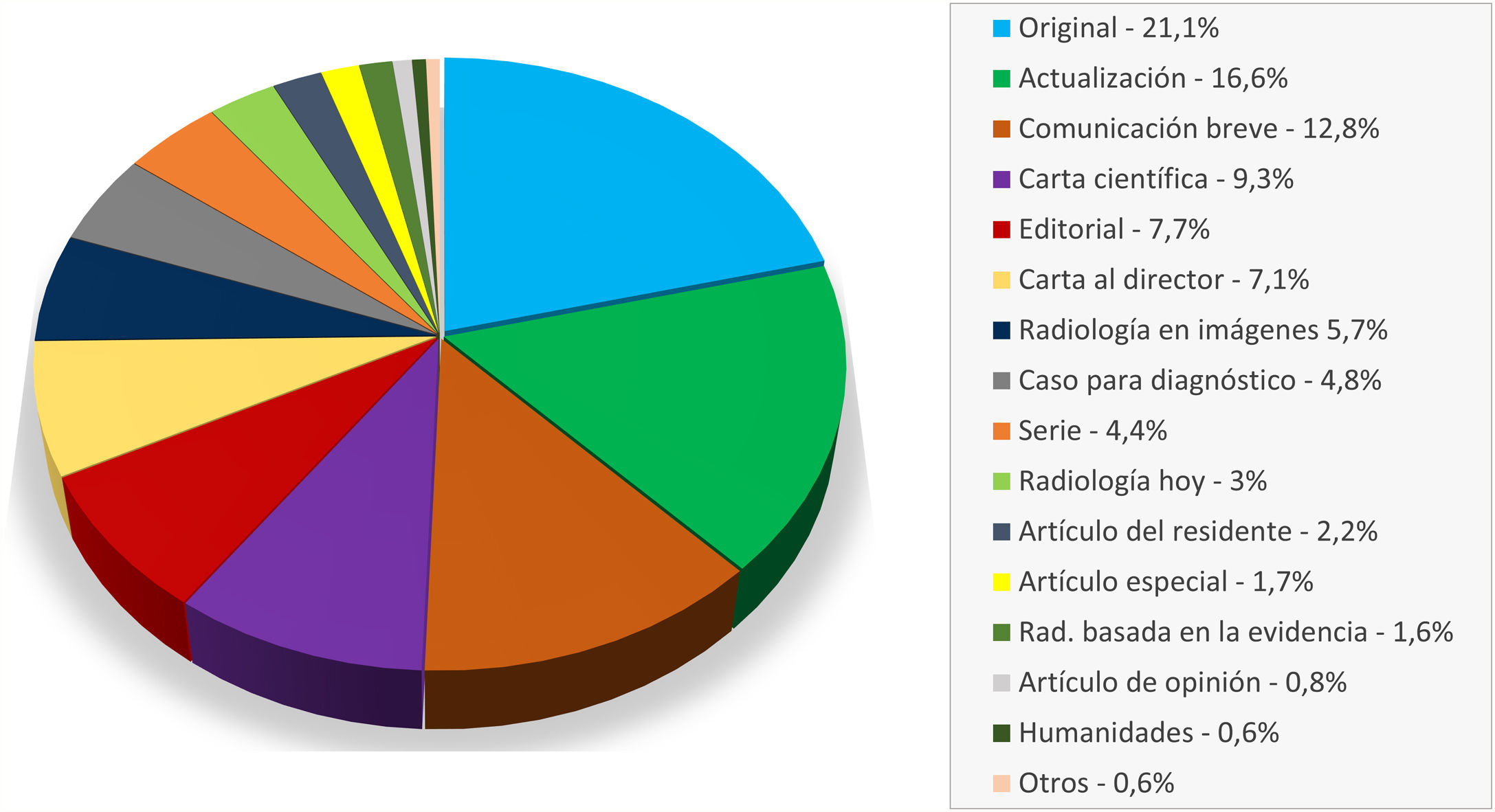
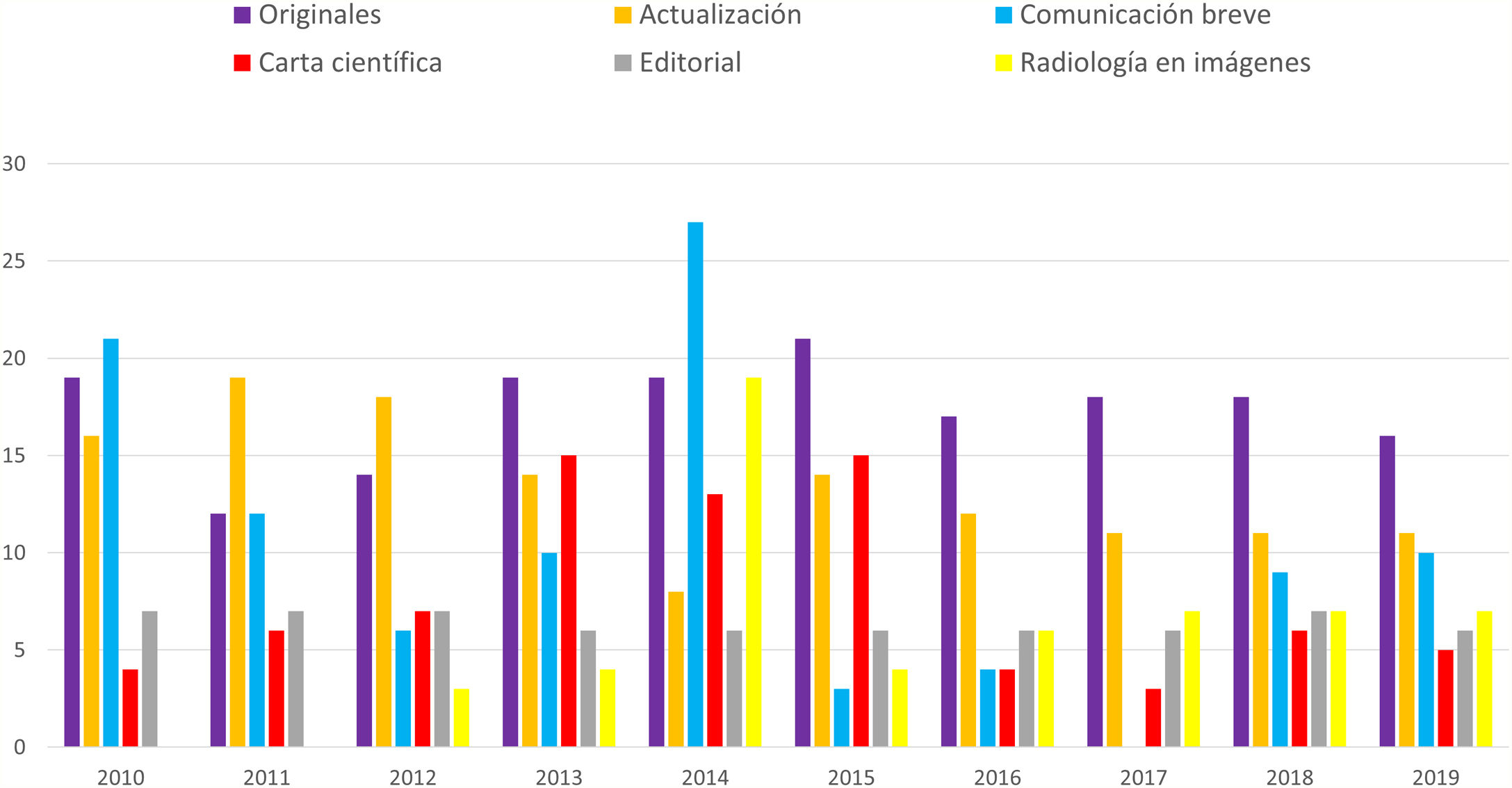
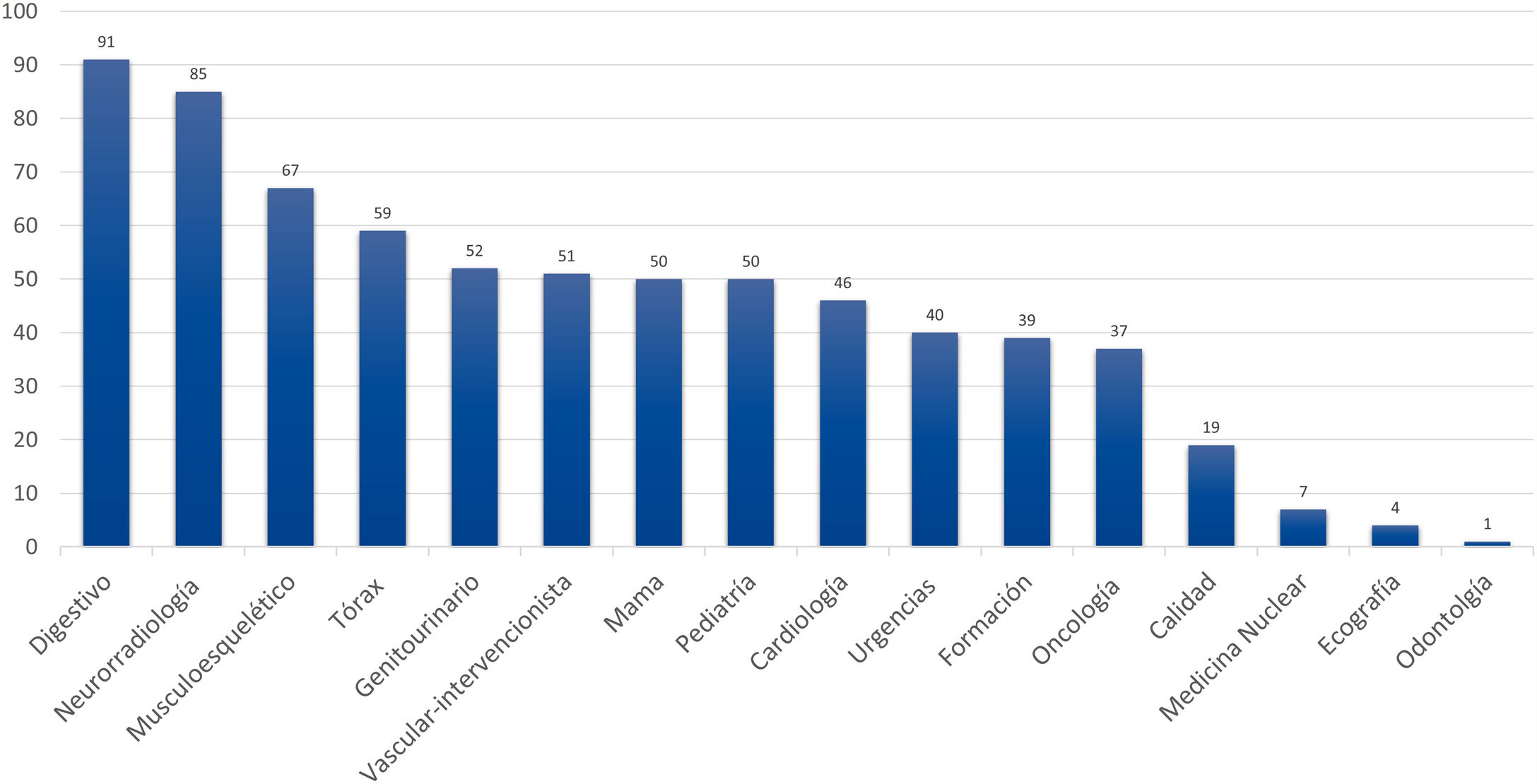
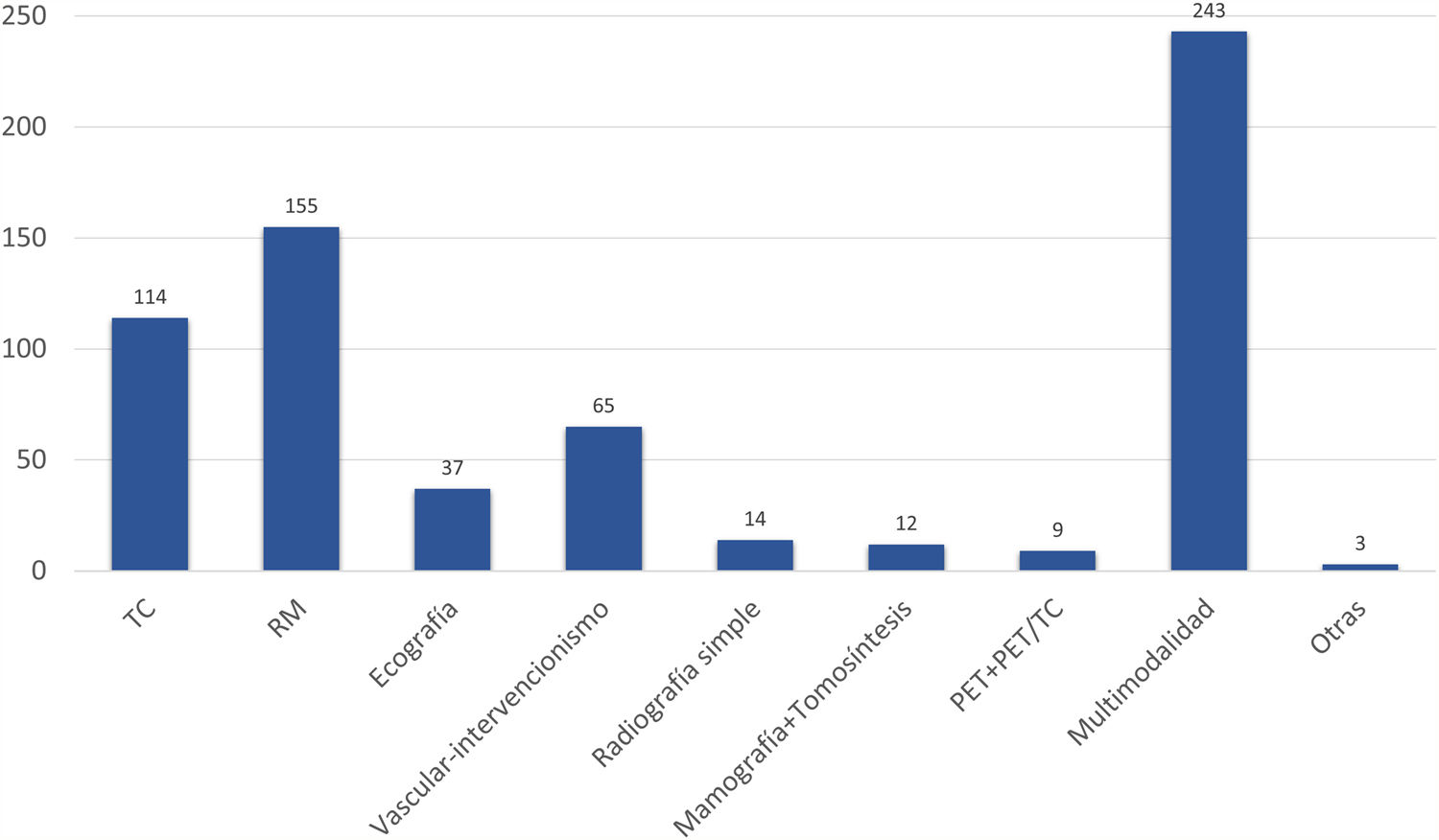
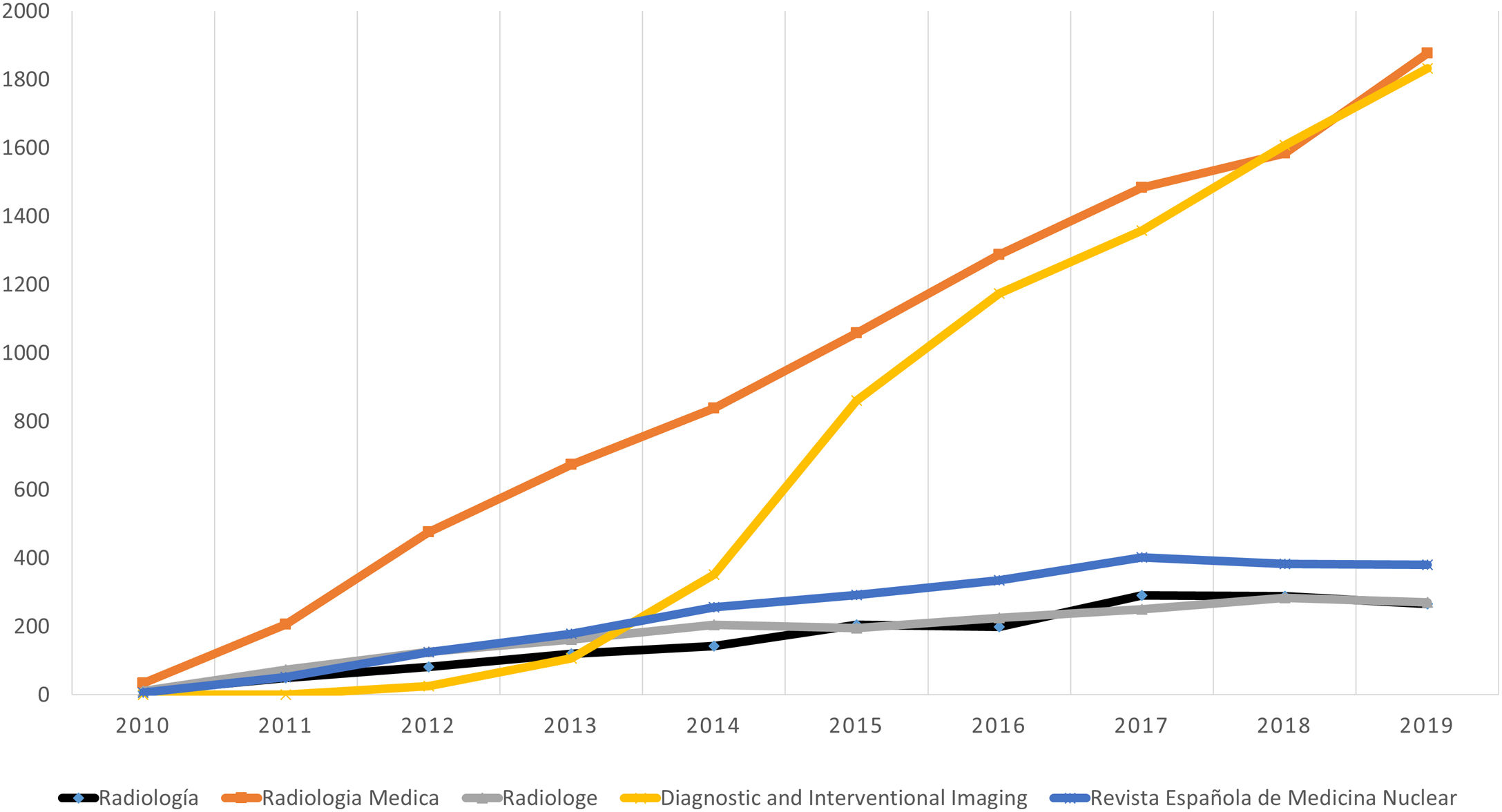
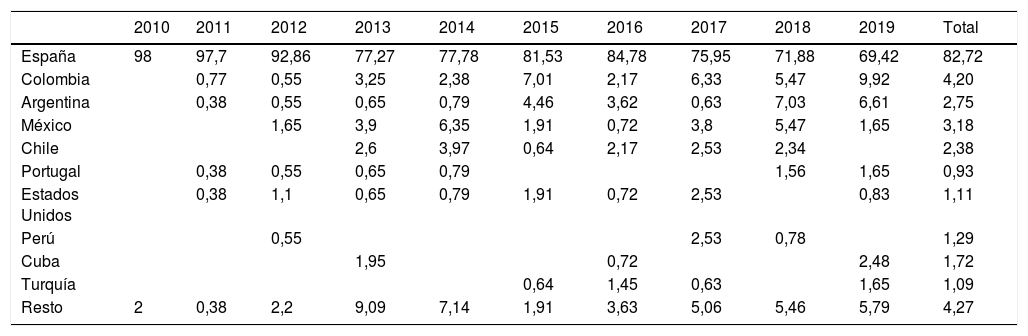
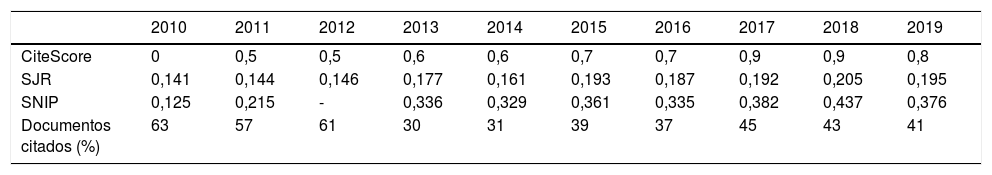
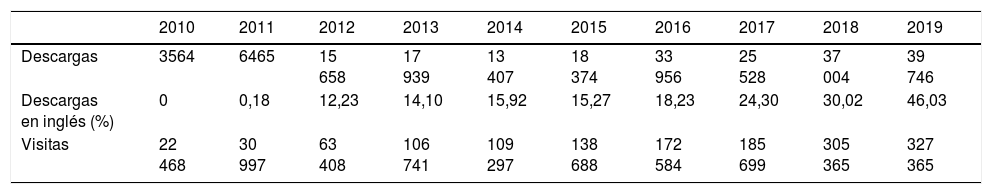
ResultadosEl número de artículos publicados por Radiología ha sufrido una lenta disminución durante la última década y los tiempos editoriales se han prolongado. Los artículos originales suponen el mayor número de publicaciones, y los temas más frecuentes son la radiología del aparato digestivo y la neurorradiología. Sin embargo, los índices bibliométricos disponibles y las visitas y descargas de los artículos aumentan cada año. En cuanto a la autoría, aunque predomina un origen español, la participación de autores internacionales es cada vez más frecuente, al igual que la colaboración entre diferentes instituciones.
ConclusionesEsta revisión pone de manifiesto la progresión del trabajo científico de la revista Radiología. Del mismo modo, ha revelado los aspectos que se deben corregir para contribuir al crecimiento de Radiología.
Bibliometrics makes it possible to measure the relative importance of a scientific journal in its field. The current study analyzed the scientific publications in Radiología and the bibliometric parameters of the journal in the period comprising 2010 through 2019.
Materials and methodsWe reviewed the bibliometrics for Radiología through information obtained from three sources: Scopus, the online version of the journal, and the publisher (Elsevier). We retrospectively analyzed aspects related to the editorial process (final decision and speed), the articles published (type, subspecialty of radiology, and imaging technique), the trends in citation and various indices
(CiteScore, SNIP, and SJR), visibility, downloads, author characteristics (geographical origin and institutional collaboration), and the most cited articles.
ResultsThe number of articles published in Radiología gradually decreased during the decade, and the time to publication increased. Original research articles account for the largest share of the articles published. The most common subject areas were radiology of the digestive tract and neuroradiology. Nevertheless, the bibliometric indicators and the number of downloads of articles increased every year. Regarding the authorship of the articles published, although authors from Spain predominate, the participation of authors from other countries became increasingly common. Collaboration among different institutions also became increasingly common in the period analyzed.
ConclusionsThis review shows the progression of the journal's scientific work and some aspects that must be addressed to favor the growth of Radiología.