To review the radio-pathologic features of symptomatic breast cancers not detected at digital mammography (DM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT).
Material and methodsRetrospective analysis of 169 lesions from symptomatic patients with breast cancer that were studied with DM, DBT, ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance (MR). We identified occult lesions (true false negatives) in DM and DBT. Clinical data, density, US and MR findings were analyzed as well as histopathological results.
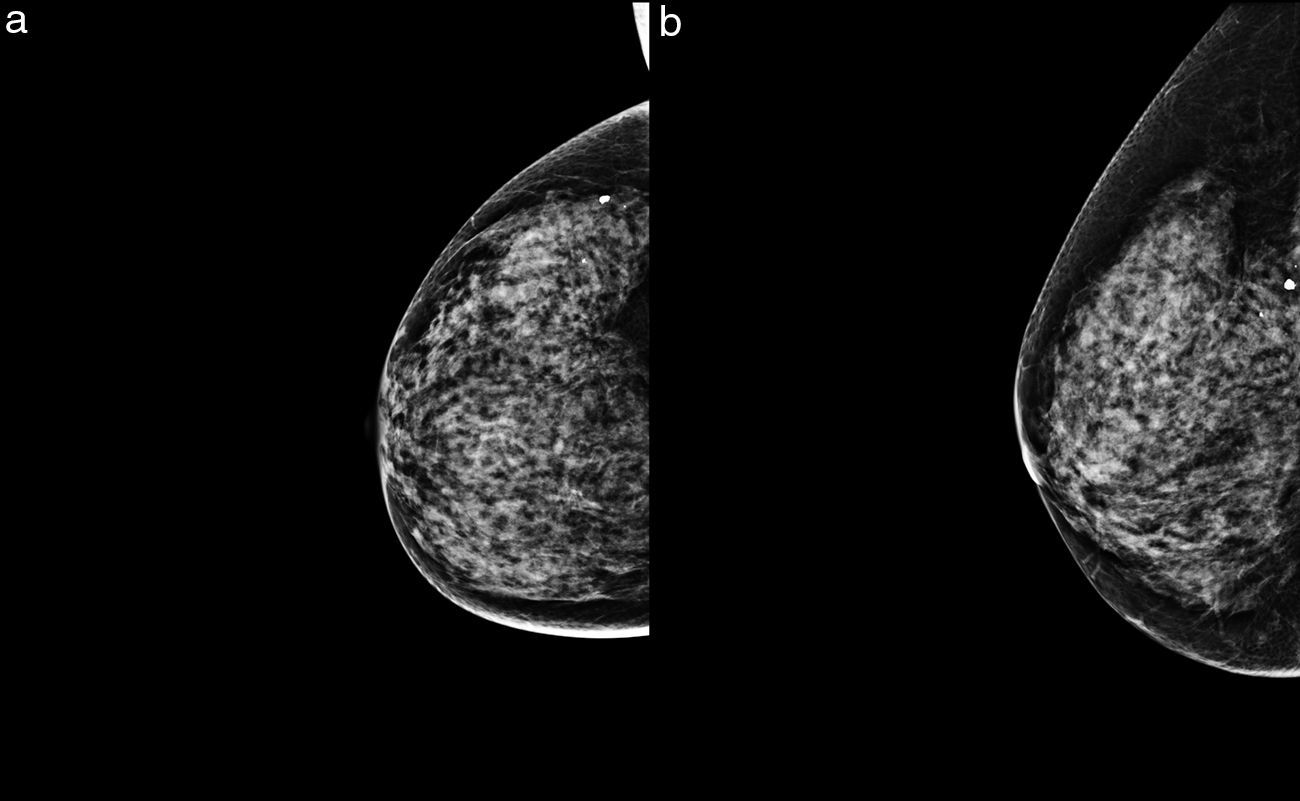
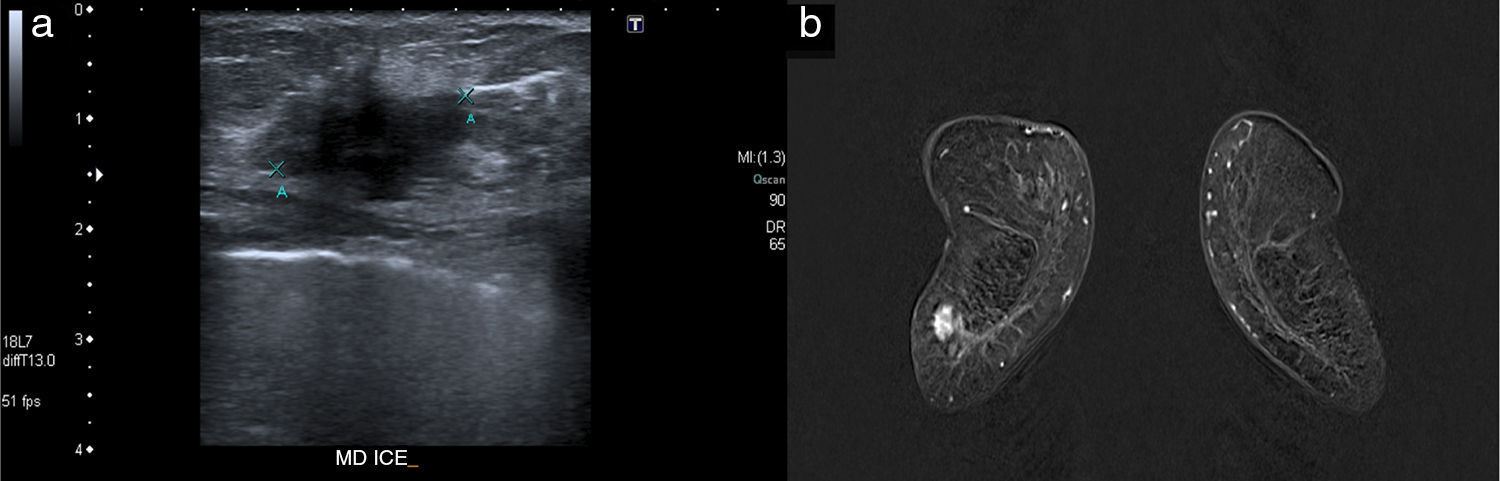
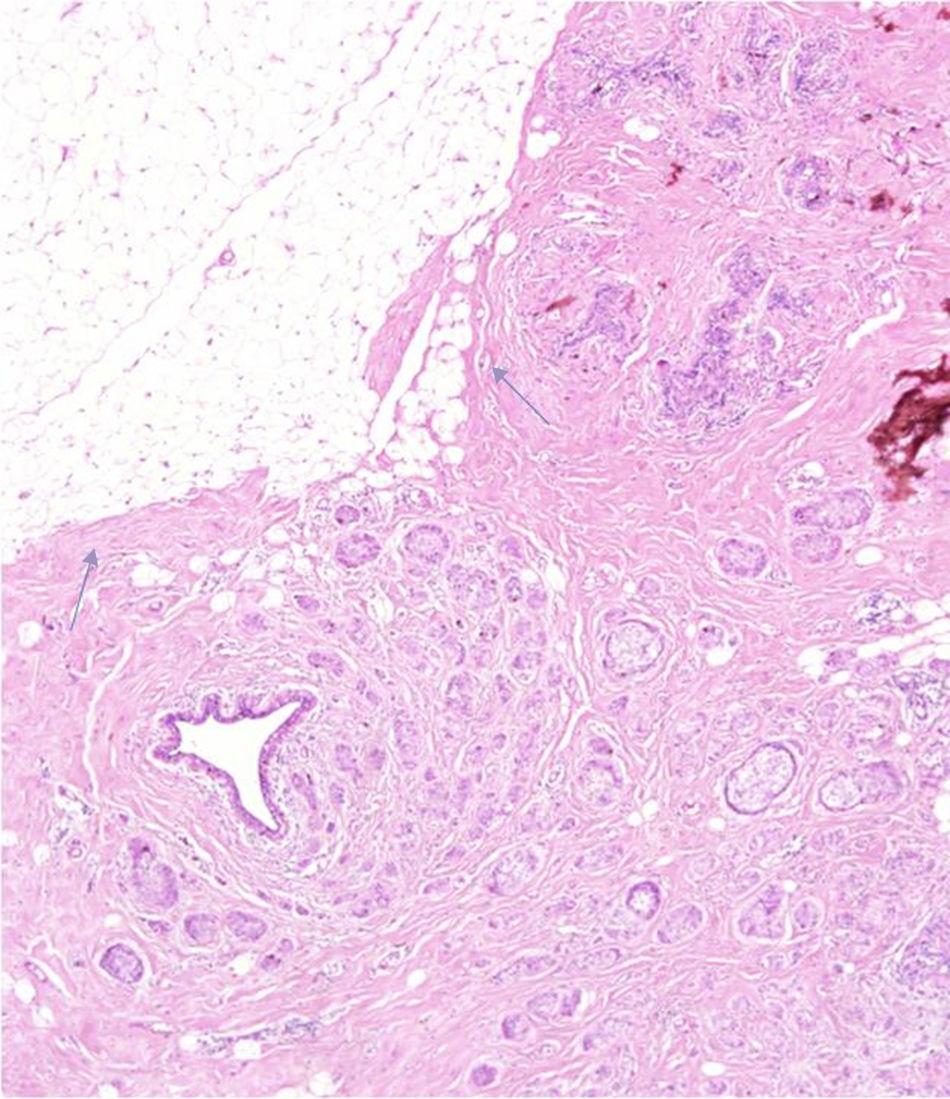
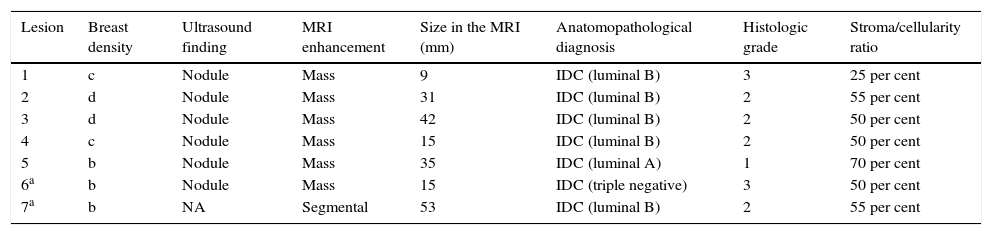
ResultsWe identified seven occult lesions in DM and DBT. 57 per cent (4/7) of the lesions were identified in high-density breasts (type c and d), and the rest of them in breasts of density type b. Six carcinomas were identified at US and MR (BI-RADS 4 masses); the remaining lesion was only identified at MR. The tumor size was larger than 3cm at MRI in 57 per cent of the lesions. All tumors were ductal infiltrating carcinomas, six of them with high stromal proportion. According to molecular classification, we found only one triple-negative breast cancer, the other lesions were luminal-type. We analyzed the tumor margins of two resected carcinomas that were not treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, both lesions presented margins that displaced the adjacent parenchyma without infiltrating it.
ConclusionOccult breast carcinomas in DM and DBT accounted for 4 per cent of lesions detected in patients with symptoms. They were mostly masses, all of them presented the diagnosis of infiltrating ductal carcinoma (with predominance of the luminal immunophenotype) and were detected in breasts of density type b, c and d.
Revisar las características radiopatológicas de carcinomas mamarios sintomáticos ocultos en mamografía digital (MD) y tomosíntesis (TS).
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de 169 lesiones provenientes de pacientes sintomáticas con diagnóstico histológico de cáncer de mama y que fueron estudiadas con MD, TS, ecografía y resonancia magnética (RM). Se identificaron las lesiones ocultas (falsos negativos verdaderos) en MD y TS. Se analizaron datos clínicos, de densidad, los hallazgos con ecografía y RM, y la histopatología de las lesiones.
ResultadosSe detectaron siete lesiones neoplásicas ocultas en MD y TS. El 57% (4/7) se presentó en mamas densas (tipo c y d), y las restantes en mamas de densidad b. Se identificaron seis de los carcinomas por ecografía y RM (masas BI-RADS 4); la lesión restante solo se visualizó en RM. En el 57% de las neoplasias, el tamaño medido con RM fue mayor de 3cm. Todas fueron carcinomas ductales infiltrantes, seis de ellos con alta proporción estromal. En cuanto a los subtipos moleculares, solo una fue triple negativo y las demás fueron de tipo luminal. Se analizaron los márgenes tumorales de dos carcinomas intervenidos sin quimioterapia previa, y ambos presentaban márgenes que desplazaban sin infiltrar el parénquima adyacente.
ConclusiónLos carcinomas ocultos en MD y TS representaron el 4% de las lesiones detectadas en pacientes sintomáticas, fueron mayoritariamente masas, todas tuvieron diagnóstico de carcinoma ductal infiltrante (con predominio del inmunofenotipo luminal) y se detectaron en mamas de densidad tipo b, c y d.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora