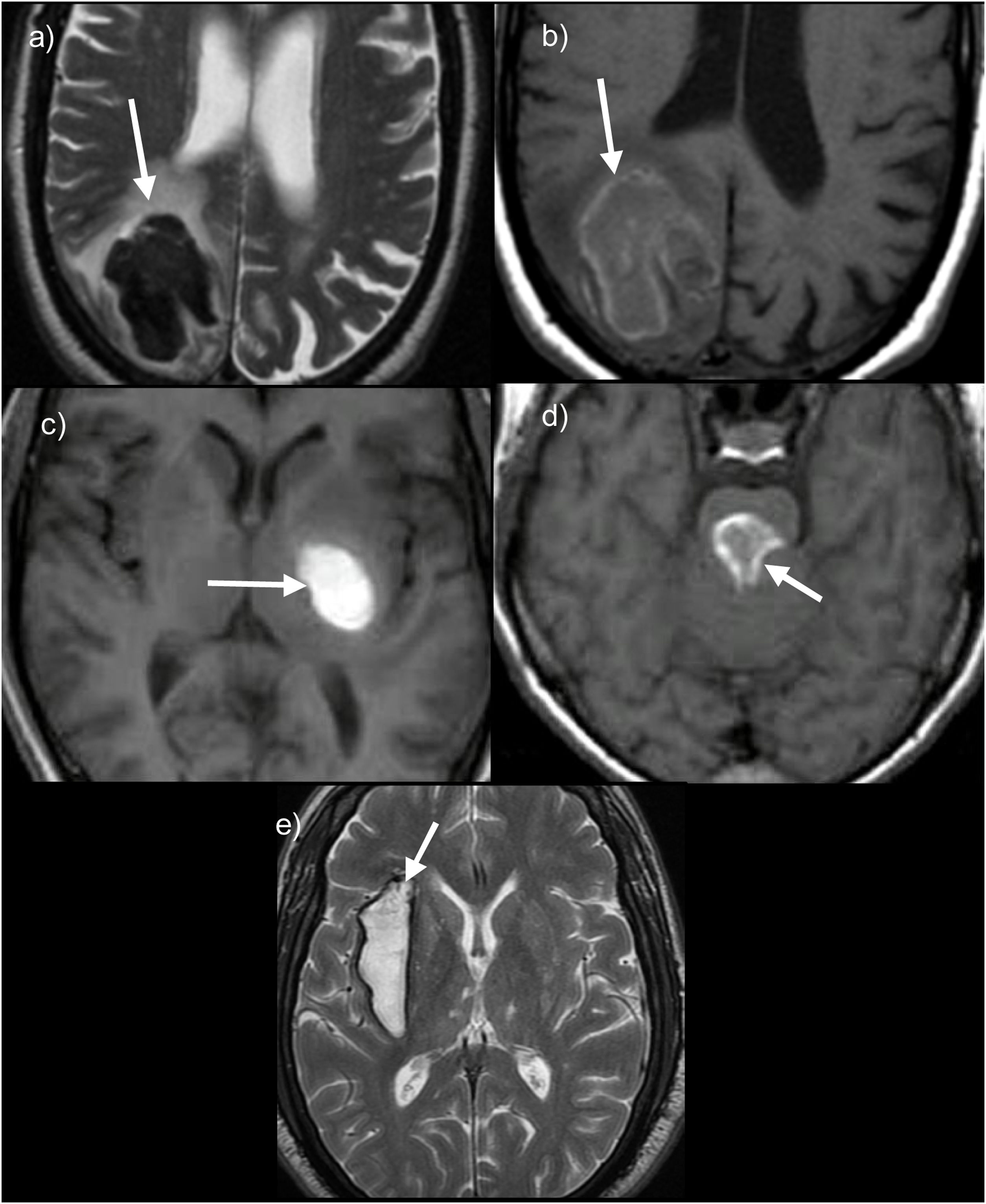
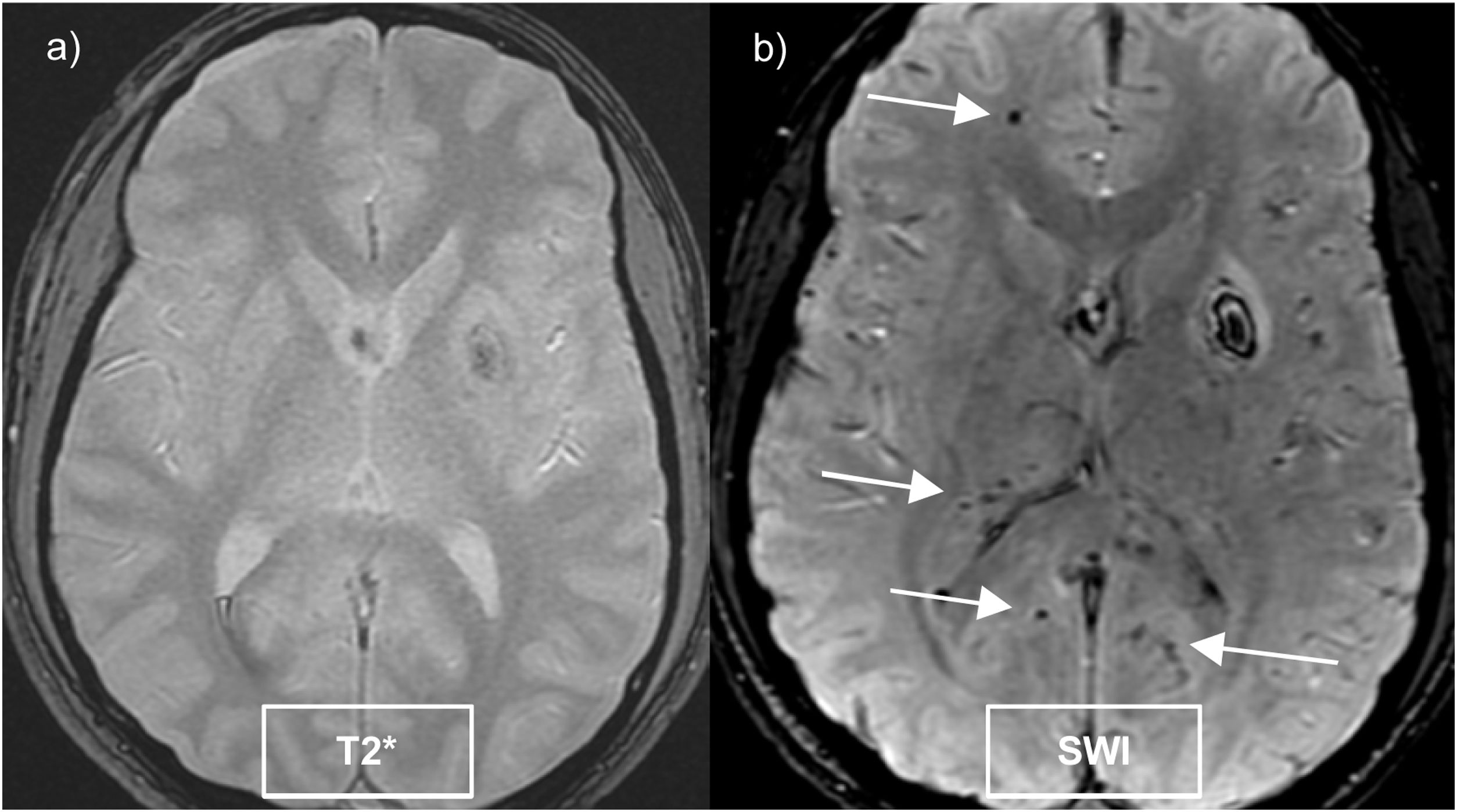
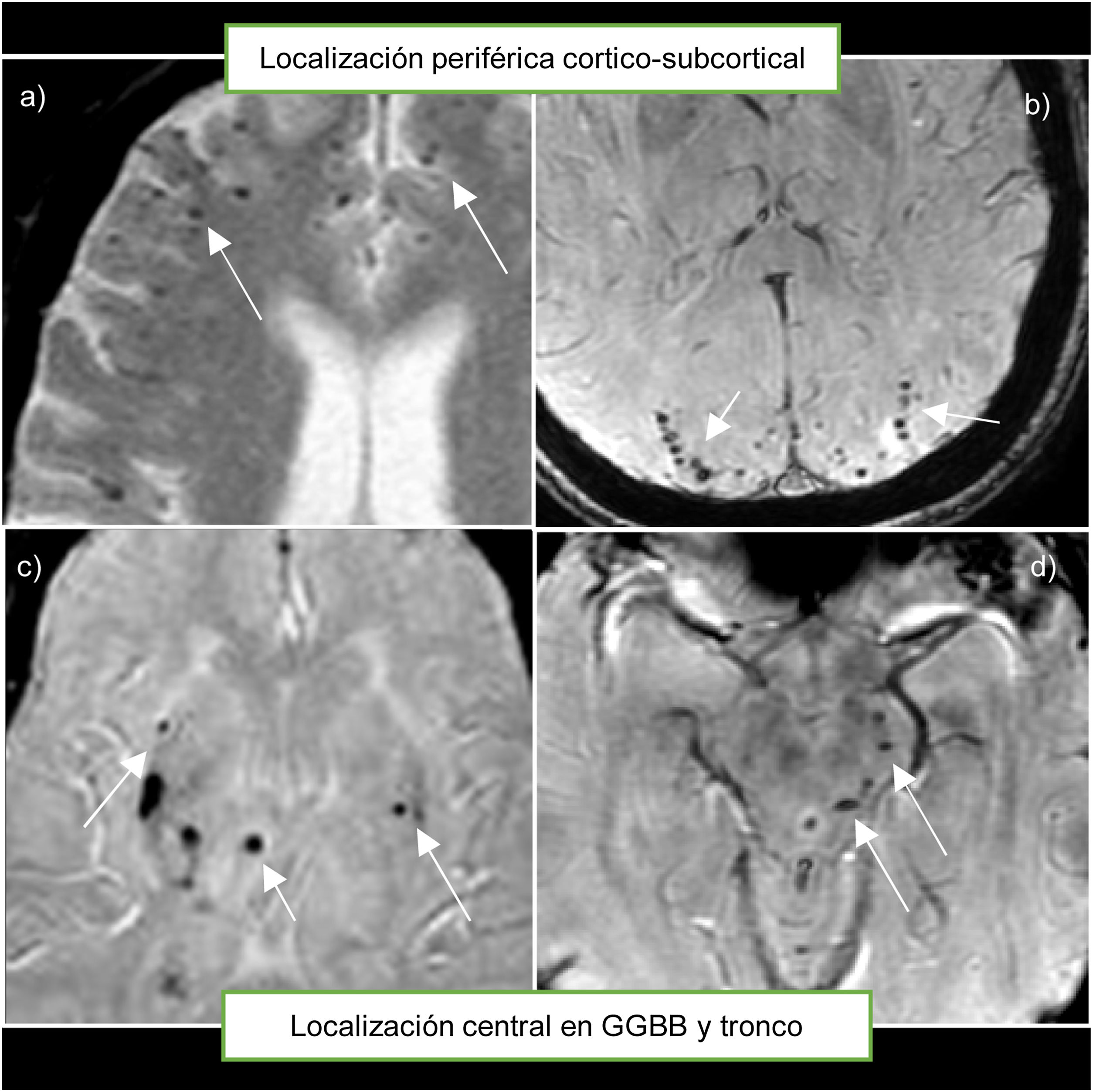
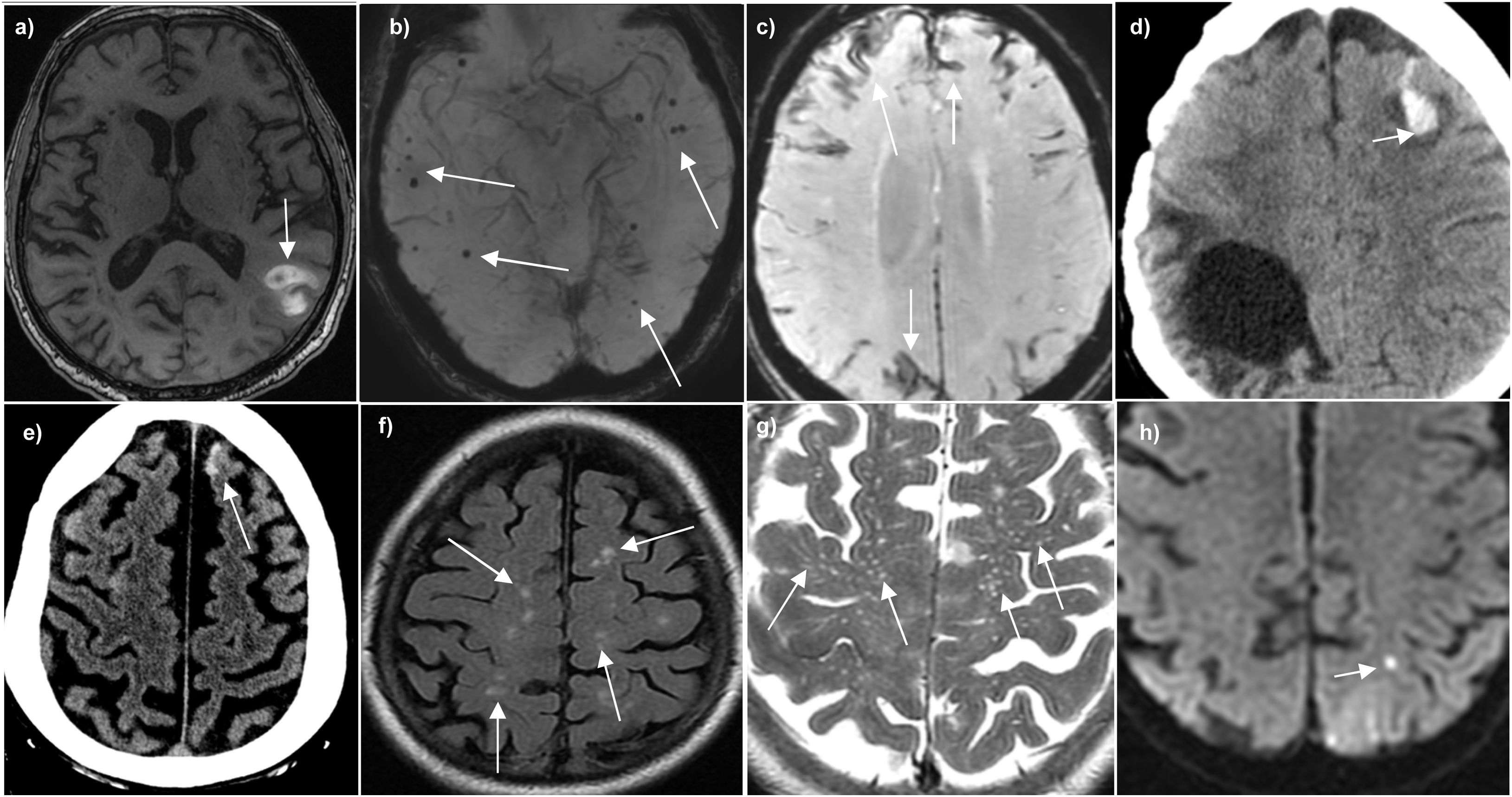
La hemorragia intracraneal (HIC) supone un 10-30% de los ictus, siendo la forma de peor pronóstico. Las causas de hemorragia cerebral pueden ser primarias, fundamentalmente la angiopatía hipertensiva y amiloide, o secundarias, como tumores o lesiones vasculares.
Identificar la etiología del sangrado es importante, ya que determina el tratamiento a realizar y el pronóstico del paciente. El objetivo principal de esta revisión es repasar los principales hallazgos por resonancia magnética (RM) de las causas de HIC primarias y secundarias, deteniéndonos en aquellos signos radiológicos que ayudan a orientar hacia un sangrado por una angiopatía primaria o bien secundario a una lesión subyacente. También se revisarán las indicaciones de RM ante una hemorragia intracraneal no traumática.
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) accounts for 10-30% of strokes, being the form with the worst prognosis. The causes of cerebral hemorrhage can be both primary, mainly hypertensive and amyloid angiopathy, and secondary, such as tumors or vascular lesions.
Identifying the etiology of bleeding is essential since it determines the treatment to be performed and the patient's prognosis. The main objective of this review is to review the main magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings of the primary and secondary causes of ICH, focusing on those radiological signs that help guide bleeding due to primary angiopathy or secondary to an underlying lesion. The indications for MRI in the event of non-traumatic intracranial hemorrhage will also be reviewed.