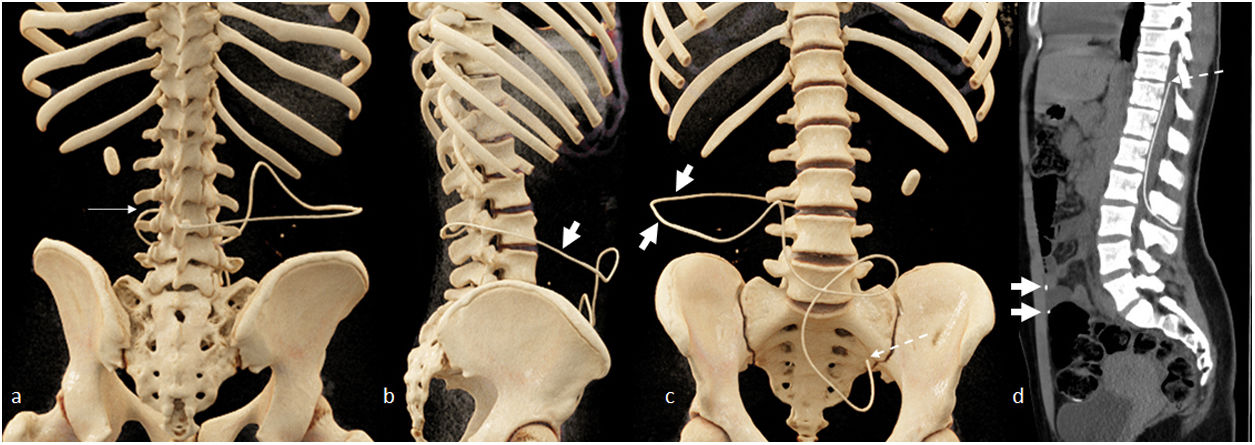
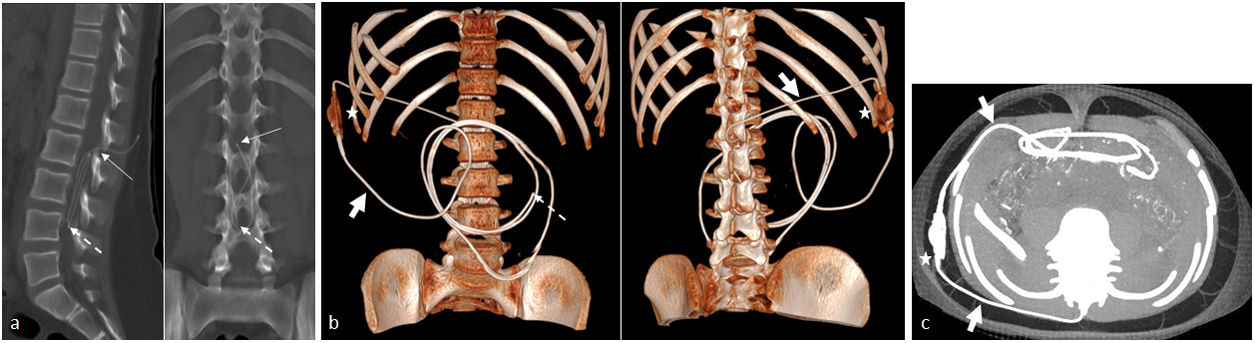
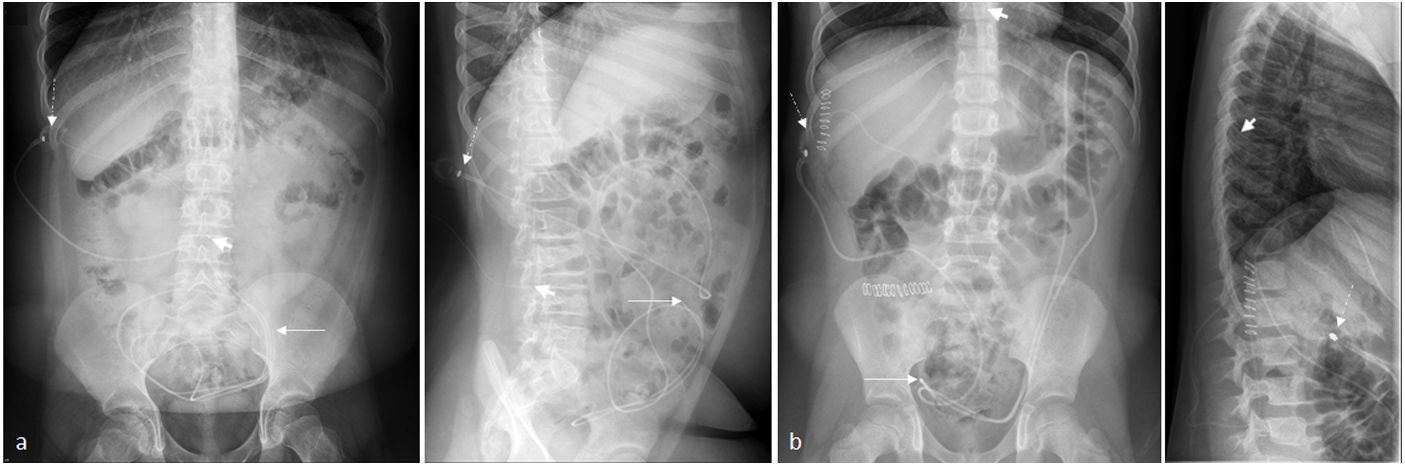
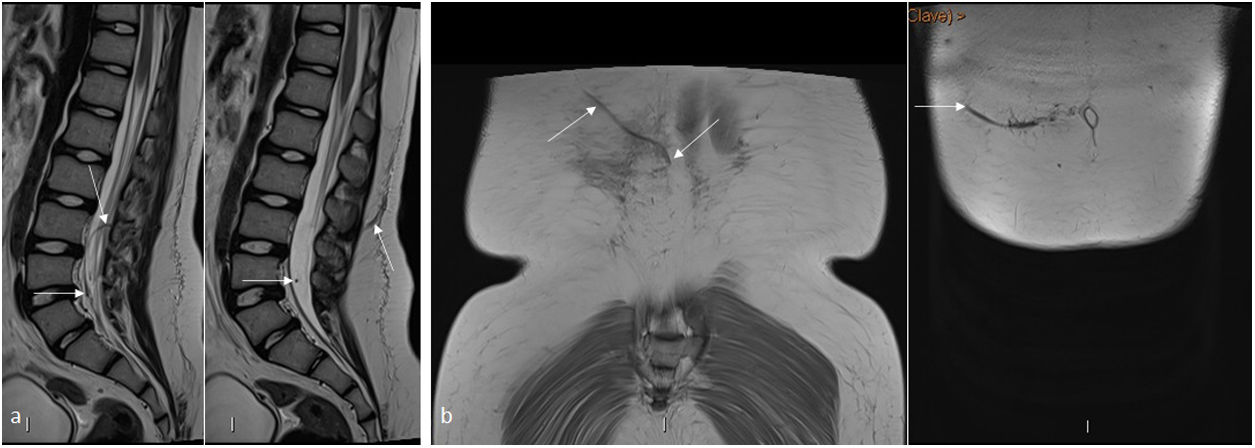
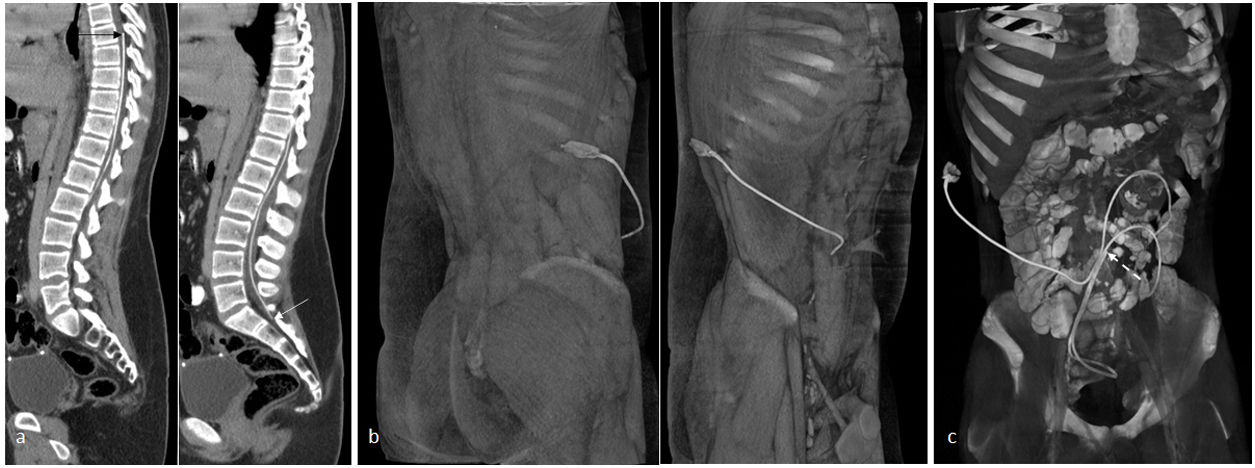
La derivación lumbo-peritoneal permite regular el flujo de líquido cefalorraquídeo estableciendo una conexión entre el saco tecal y la cavidad peritoneal. Entre las indicaciones en la población pediátrica se encuentra principalmente la hipertensión intracraneal idiopática, siendo también útil en el tratamiento de la hidrocefalia postinfecciosa, posthemorrágica y normotensiva, en el seudomeningocele posquirúrgico o ante una fuga de líquido cefalorraquídeo.
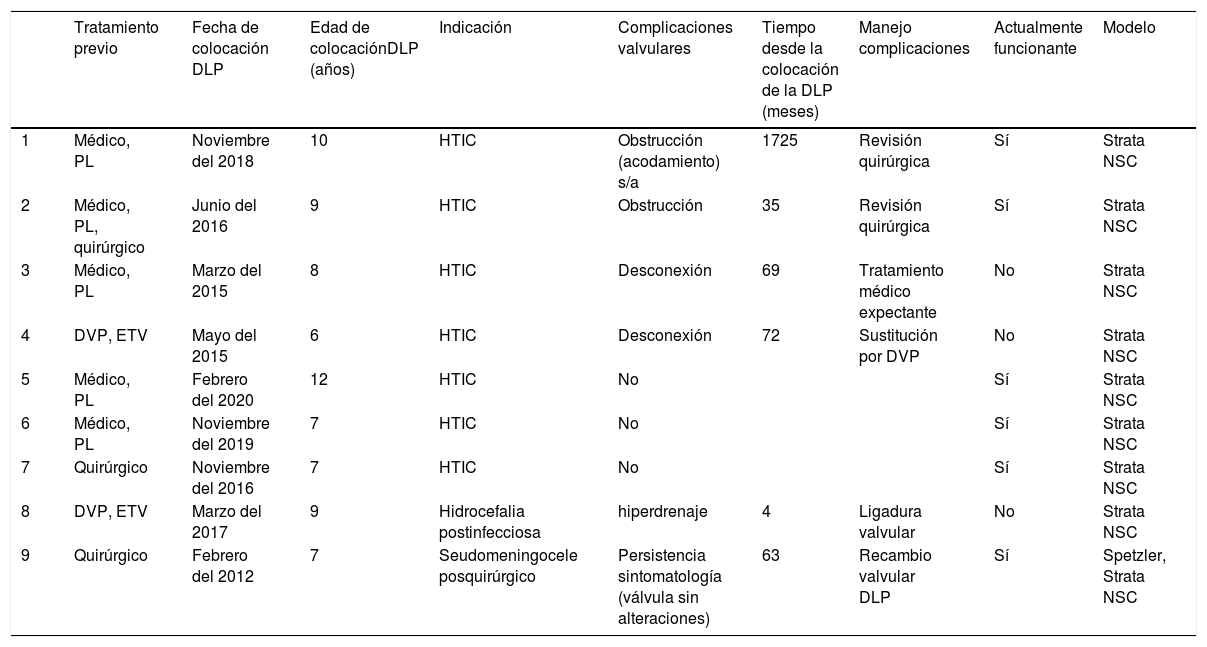
En este artículo, mediante la revisión de 9 casos de nuestro centro, se pretende mostrar la normalidad del dispositivo en las pruebas de imagen y realizar una breve revisión de las posibles complicaciones asociadas, neurológicas y abdominales.
Lumboperitoneal shunting makes it possible to regulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid by establishing a connection between the thecal sac and the peritoneal cavity. The main indication for lumboperitoneal shunting in children is idiopathic intracranial hypertension, but the technique is also useful in the treatment of postinfectious, posthemorrhagic, and normotensive hydrocephalus, as well as in the treatment of postsurgical pseudomeningocele or leakage of cerebrospinal fluid.
This article reviews nine cases treated at our center to show the normal imaging findings for lumboperitoneal shunts in children and to provide a succinct review of the possible neurological and abdominal complications associated with this treatment.