Suplemento:Actualización y buenas prácticas en los usos de los medios de contraste
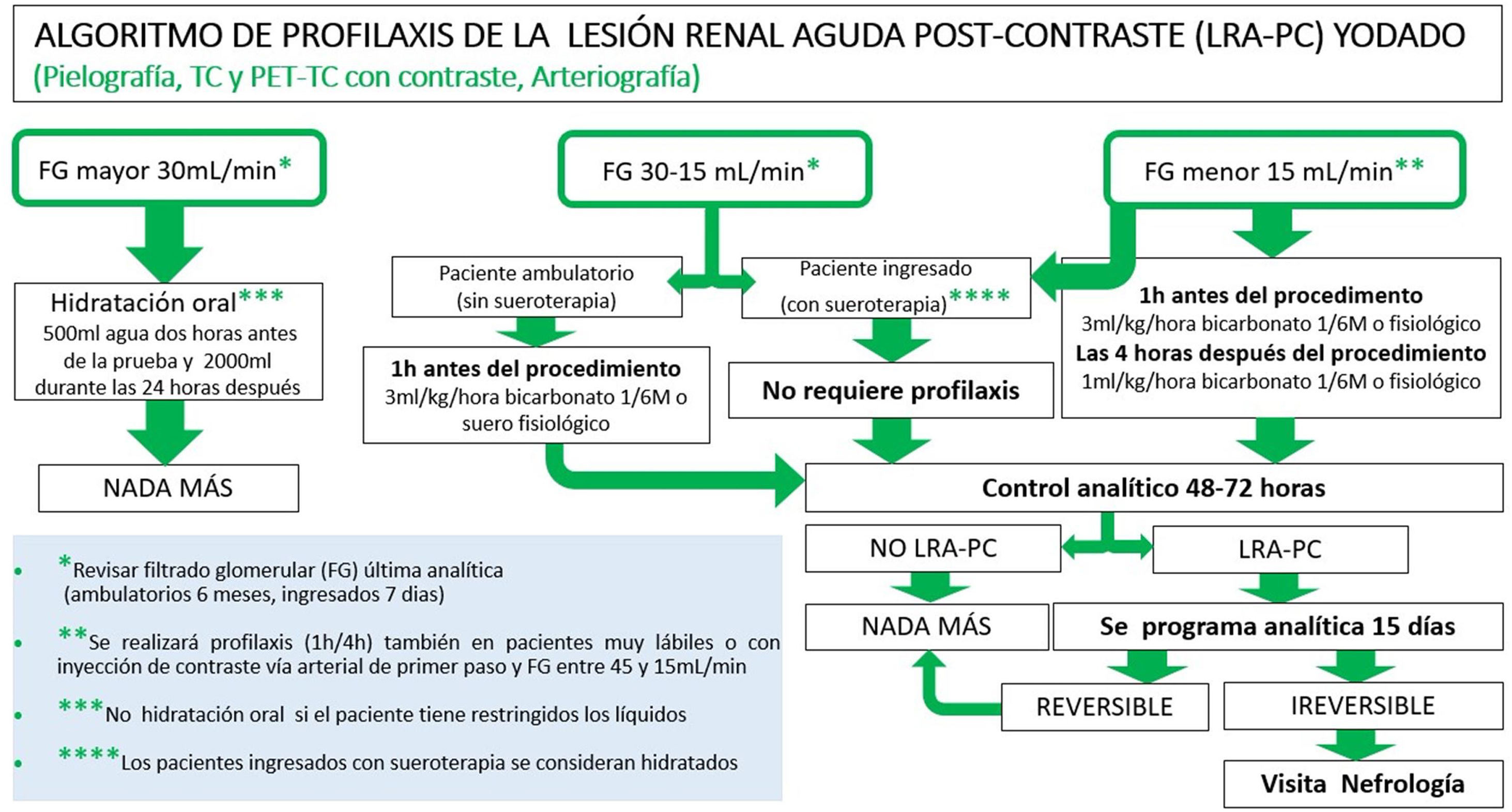
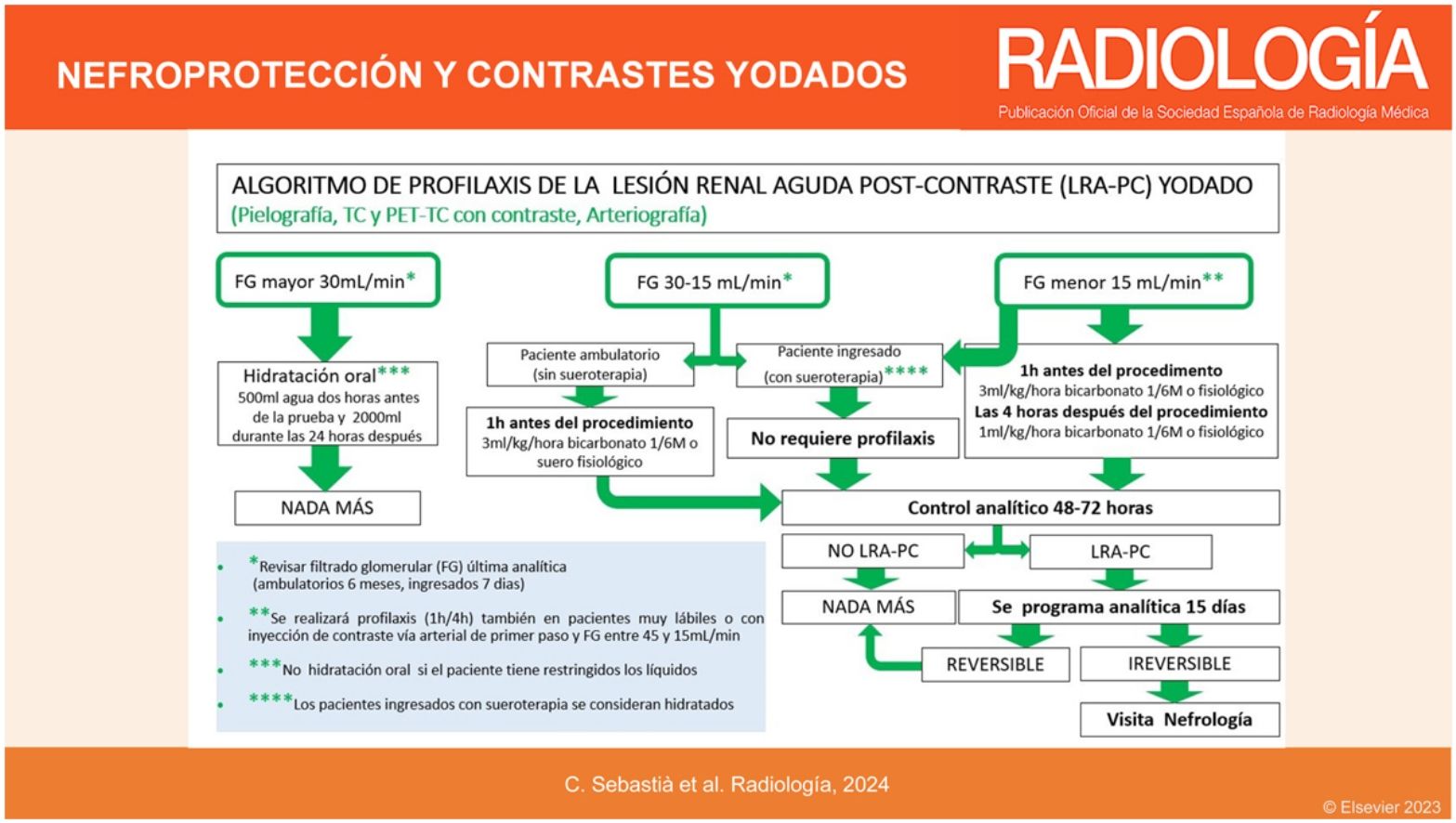
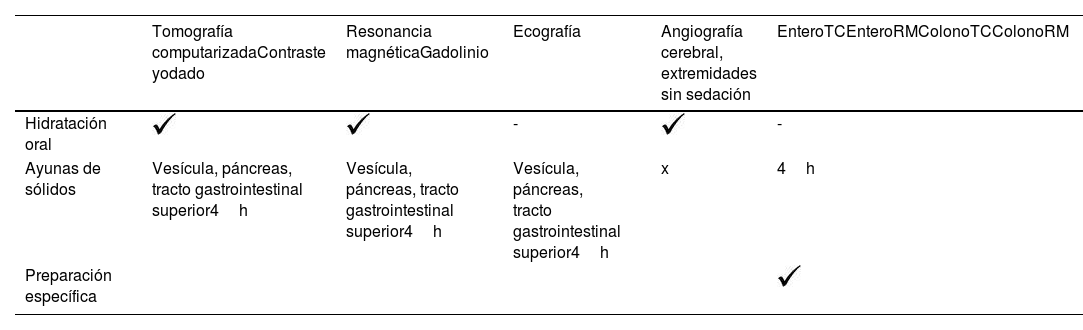
More infoLa incidencia de lesión renal aguda poscontraste (LRA-PC) es baja con los nuevos contrastes yodados no iónicos hipo- o isoosmolares. La única forma de profilaxis probada de LRA-PC es la hidratación, preferentemente intravenosa, aunque la hidratación por vía oral es igualmente efectiva. En este artículo definimos la LRA-PC y sus factores de riesgo, proponemos un protocolo de profilaxis y respondemos a las dudas más frecuentes que aparecen cuando realizamos dicha profilaxis. También actualizamos las pautas de ayunas que deben realizarse antes de las pruebas con contraste. En general no son necesarias las ayunas de sólidos antes de inyectar contraste yodado o gadolinio salvo en pruebas en las que se requiera estudiar específicamente el tracto digestivo superior y la vía biliar. E incluso en estos casos no se requiere ayunas de líquidos claros, cosa que nos es de gran ayuda para universalizar la hidratación oral y disminuir la incidencia de LRA-PC.
The incidence of post-contrast acute kidney injury (PC-AKI) is low with the new low- or iso-osmolar non-ionic iodinated contrast agents. The only proven form of prophylaxis for PC-AKI is hydration, preferably intravenous, although oral hydration is equally effective. In this article we define PC-AKI and its risk factors, propose a prophylaxis protocol and respond to the most common doubts that arise around prophylaxis. We also update the fasting guidelines to be followed prior to contrast testing. In general, fasting of solids is not necessary before injecting iodinated contrast or gadolinium except in tests in which it is necessary to specifically study the upper digestive tract and bile duct. Even in these cases, fasting clear liquids is not required, which is of great help for oral hydration and for reducing the incidence of PC-AKI.