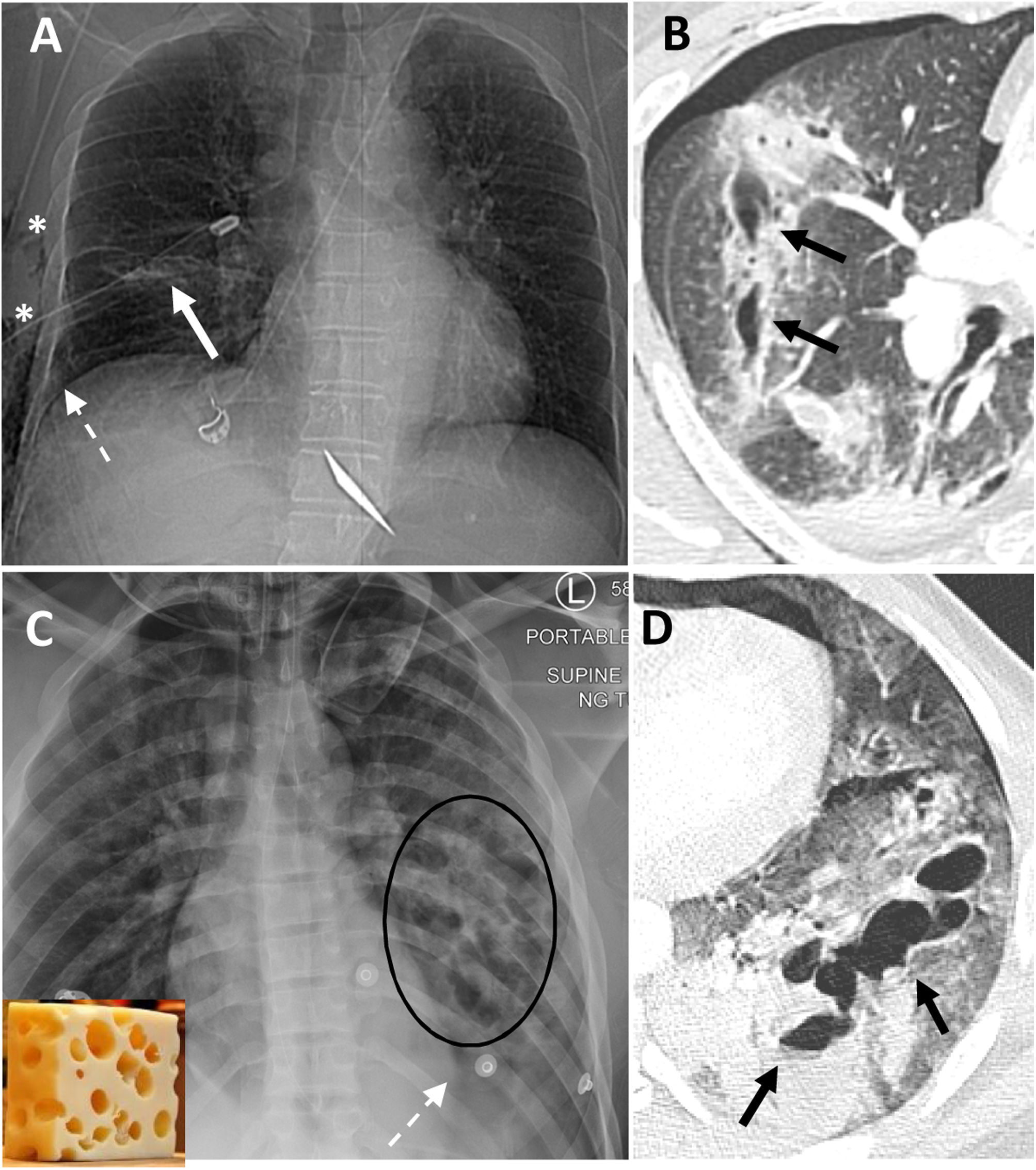
El traumatismo torácico ocurre en aproximadamente el 60% de los pacientes politraumatizados y es causa de muerte en un 10%. La tomografía computarizada (TC) es la prueba de imagen más sensible y específica en el diagnóstico de patología aguda y contribuye en el manejo y valoración del pronóstico en los pacientes con un traumatismo de alto impacto. El objetivo de este artículo es mostrar puntos clave y prácticos para el diagnóstico con TC de patología no cardiovascular en el traumatismo torácico grave.
ConclusiónEl conocimiento de los aspectos clave en la TC de patología aguda en el traumatismo torácico grave es crucial para evitar errores diagnósticos. El radiólogo tiene un papel fundamental en el diagnóstico correcto y precoz de dicha patología, ya que de ello dependerá en gran parte el manejo y evolución de los pacientes.
About 60% of polytrauma patients present thoracic traumatic injuries, accounting for approximately 10% of trauma-related deaths. Computed tomography (CT) is the most sensitive and specific imaging modality for the diagnosis of acute injuries, and it improves management and prognostic evaluation of patients with high-impact trauma. This paper aims to show practical clues that are key for diagnosing severe non-cardiovascular thoracic trauma by CT.
ConclusionKnowing the key features of severe acute thoracic trauma on CT is crucial to avoid diagnostic errors. Radiologists play a fundamental role in the accurate early diagnosis of severe non-cardiovascular thoracic trauma, because the patient's management and outcome will depend largely on the imaging findings.