Valorar objetivamente la afectación hepática y pancreática en el síndrome metabólico mediante biomarcadores de resonancia magnética (RM).
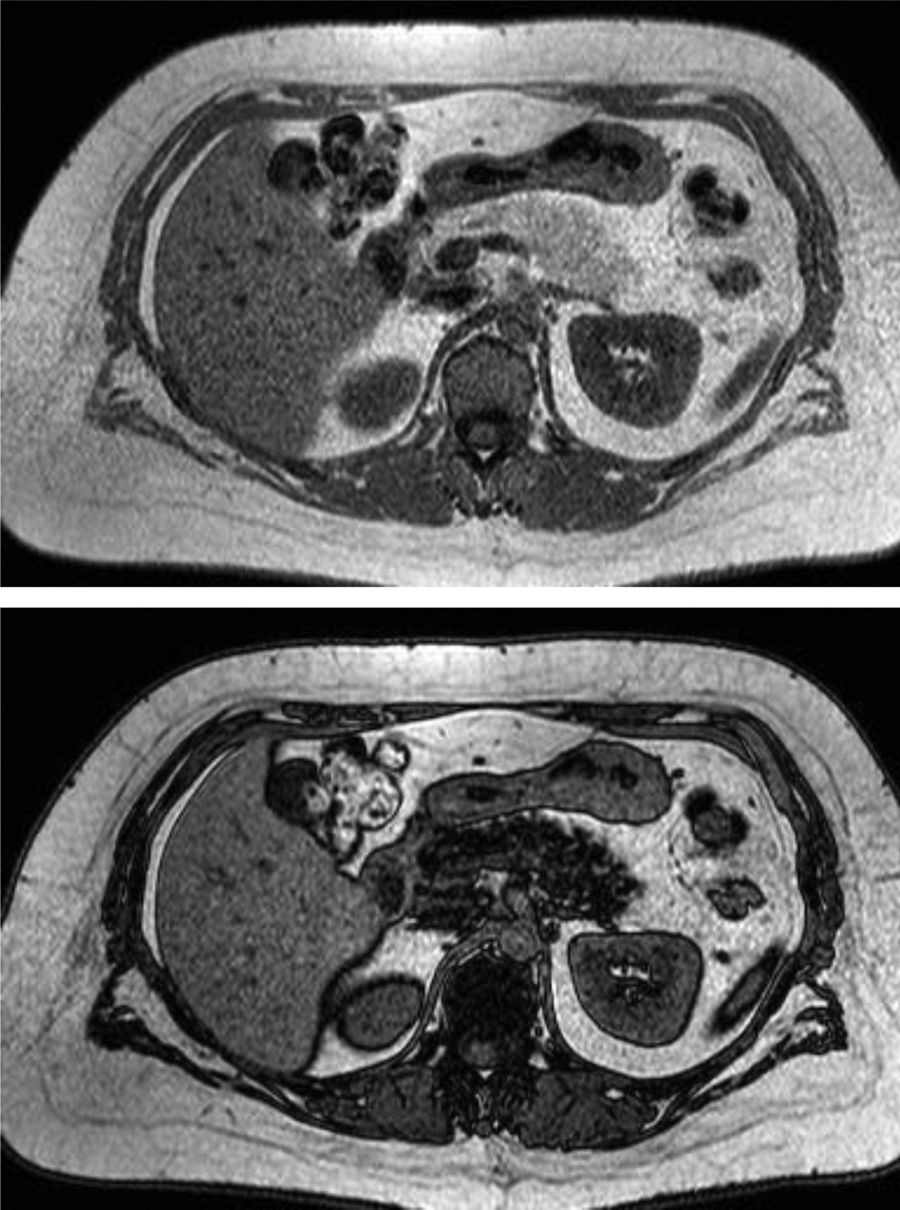
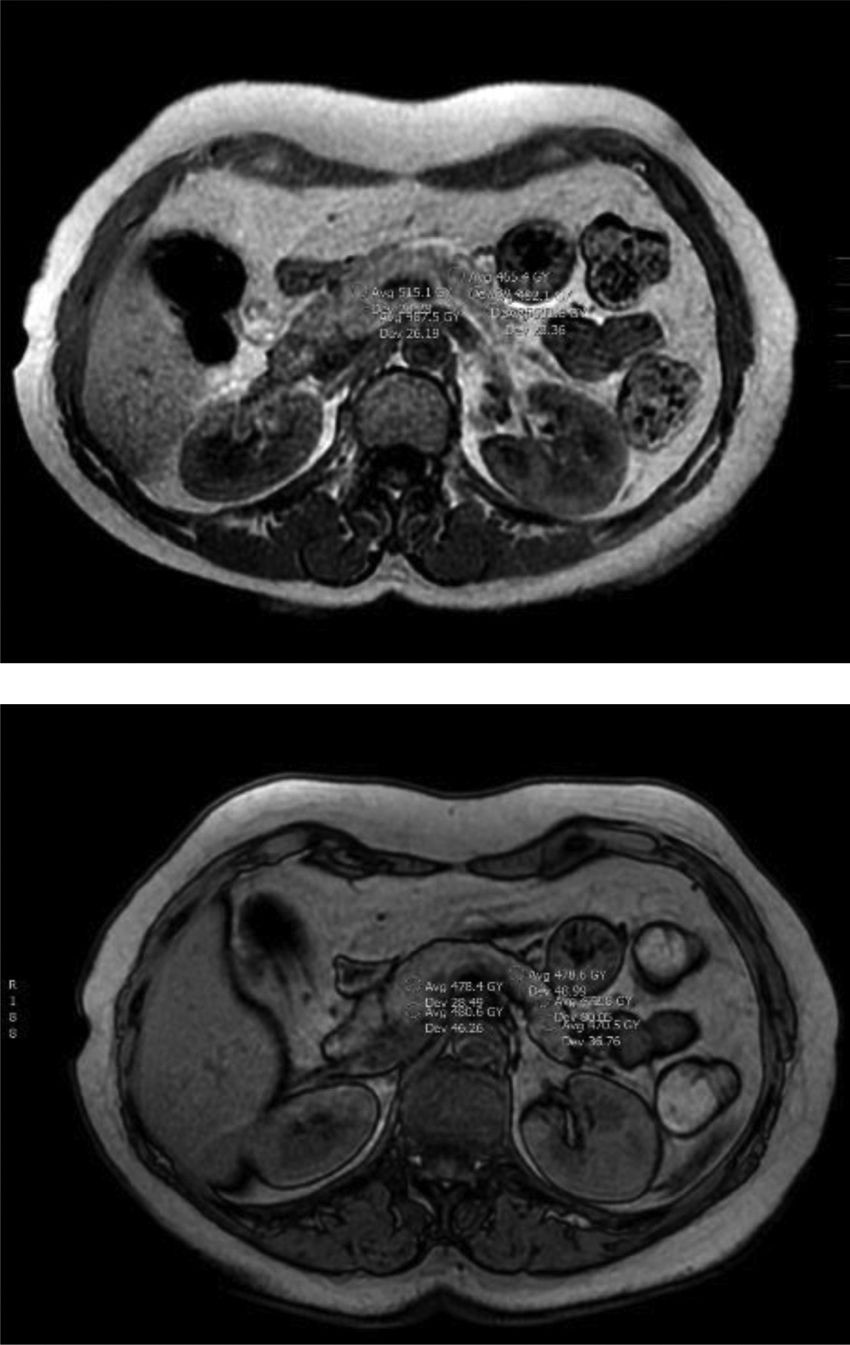
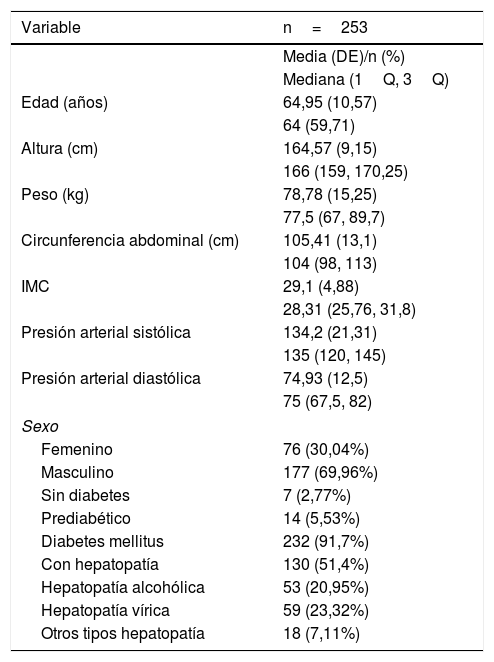
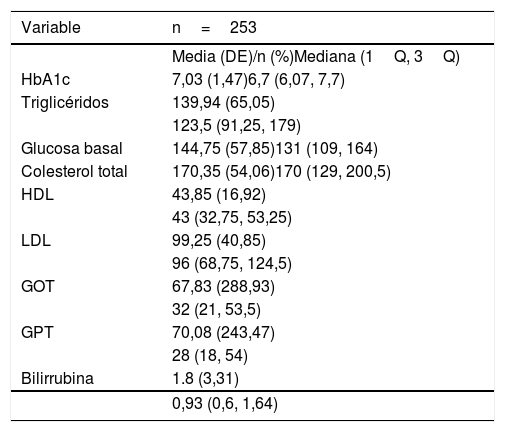
Material y métodosSerie retrospectiva inicial de 407 pacientes con diagnóstico de síndrome metabólico, estudiados con RM en un único centro durante 2 años. Se excluyeron 154 pacientes por falta de datos clínico-analíticos, alteraciones pancreáticas o inadecuada calidad de la RM. Para la medición de la grasa hepática y pancreática se utilizaron las imágenes con desplazamiento químico (en fase y fase opuesta), con medidas por regiones de interés de la fracción grasa (%) en el páncreas (FGP) e hígado (FGH). La asociación entre las variables clínico-analíticas seleccionadas y la fracción grasa se evaluó mediante modelos de regresión beta.
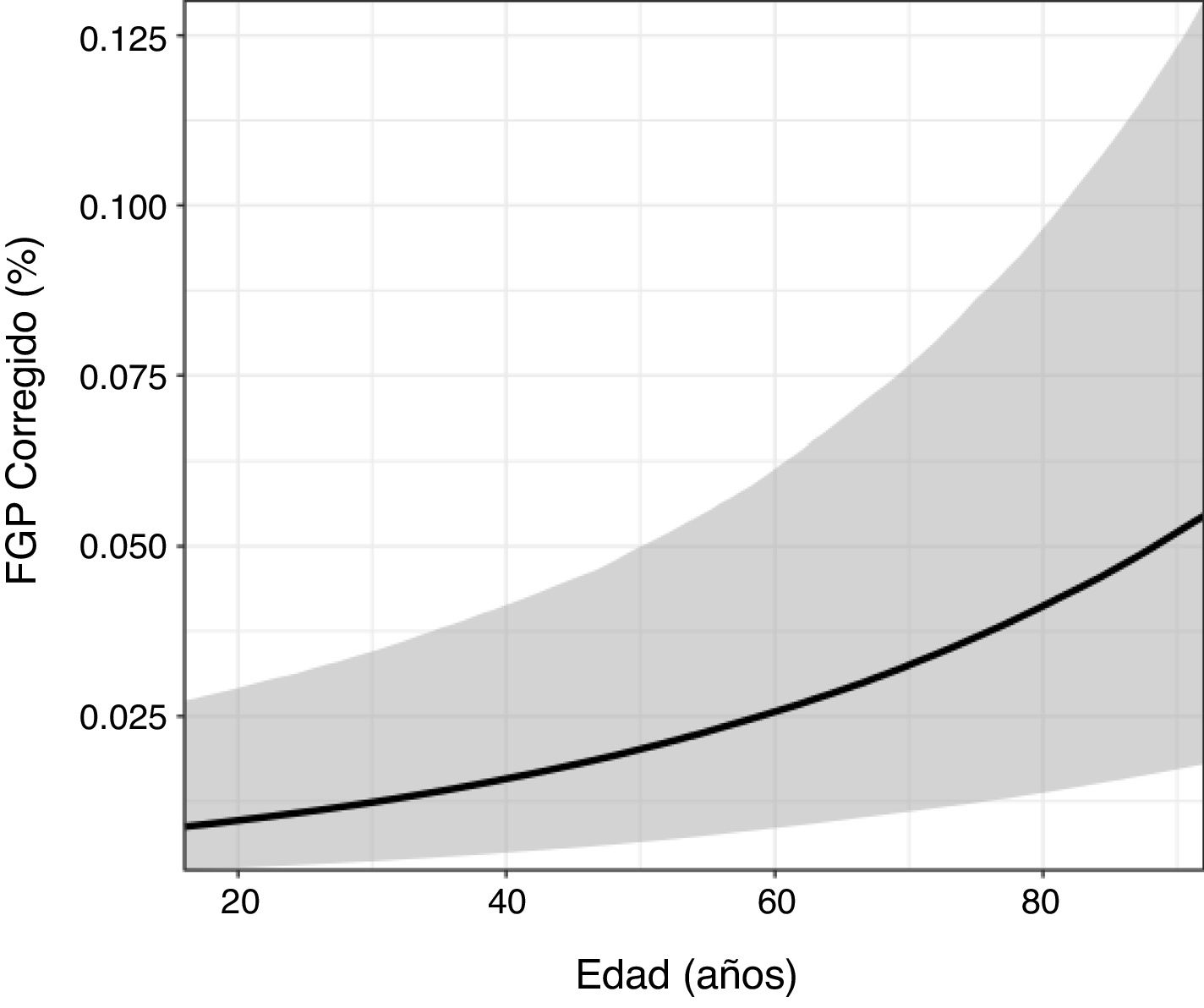
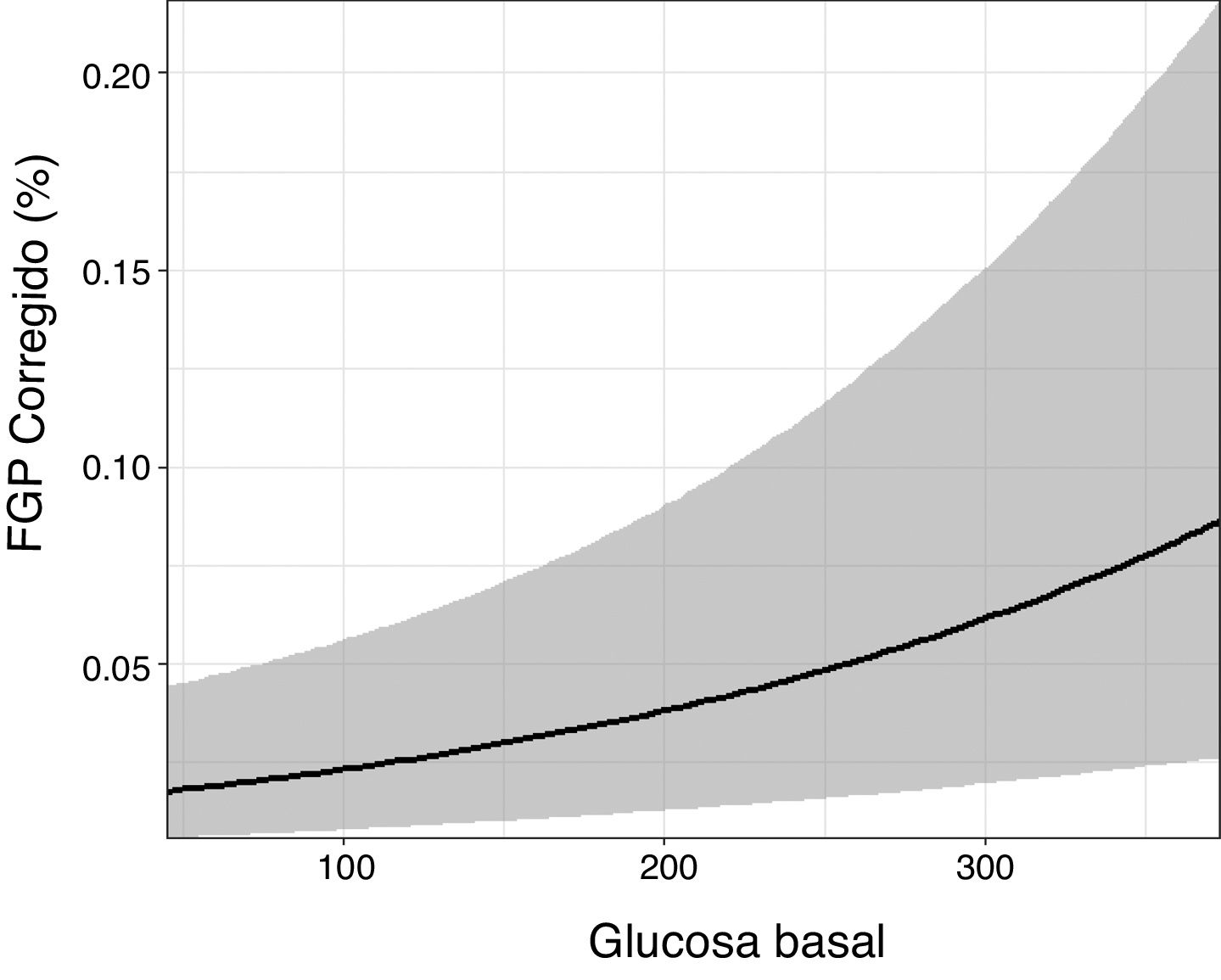
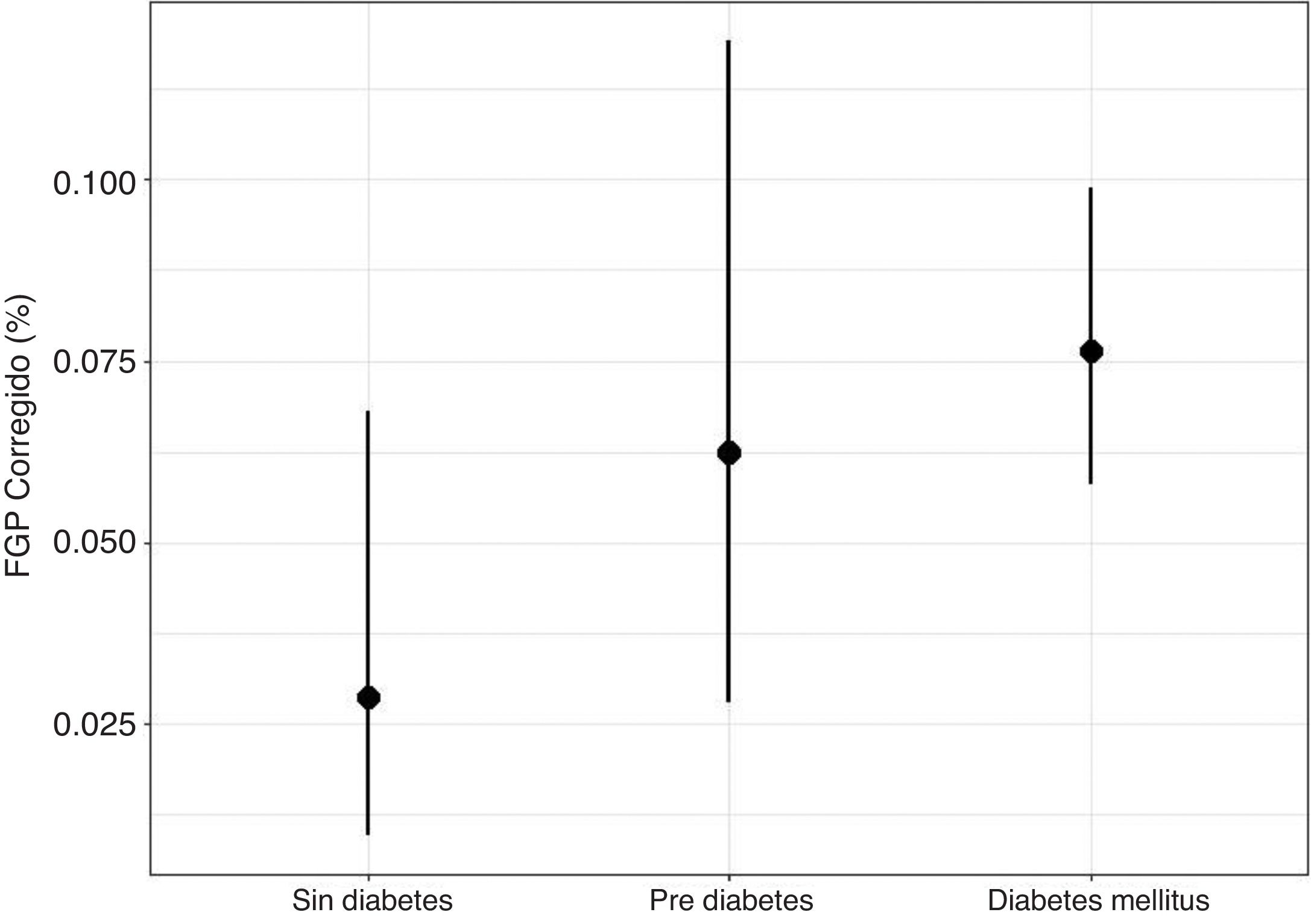
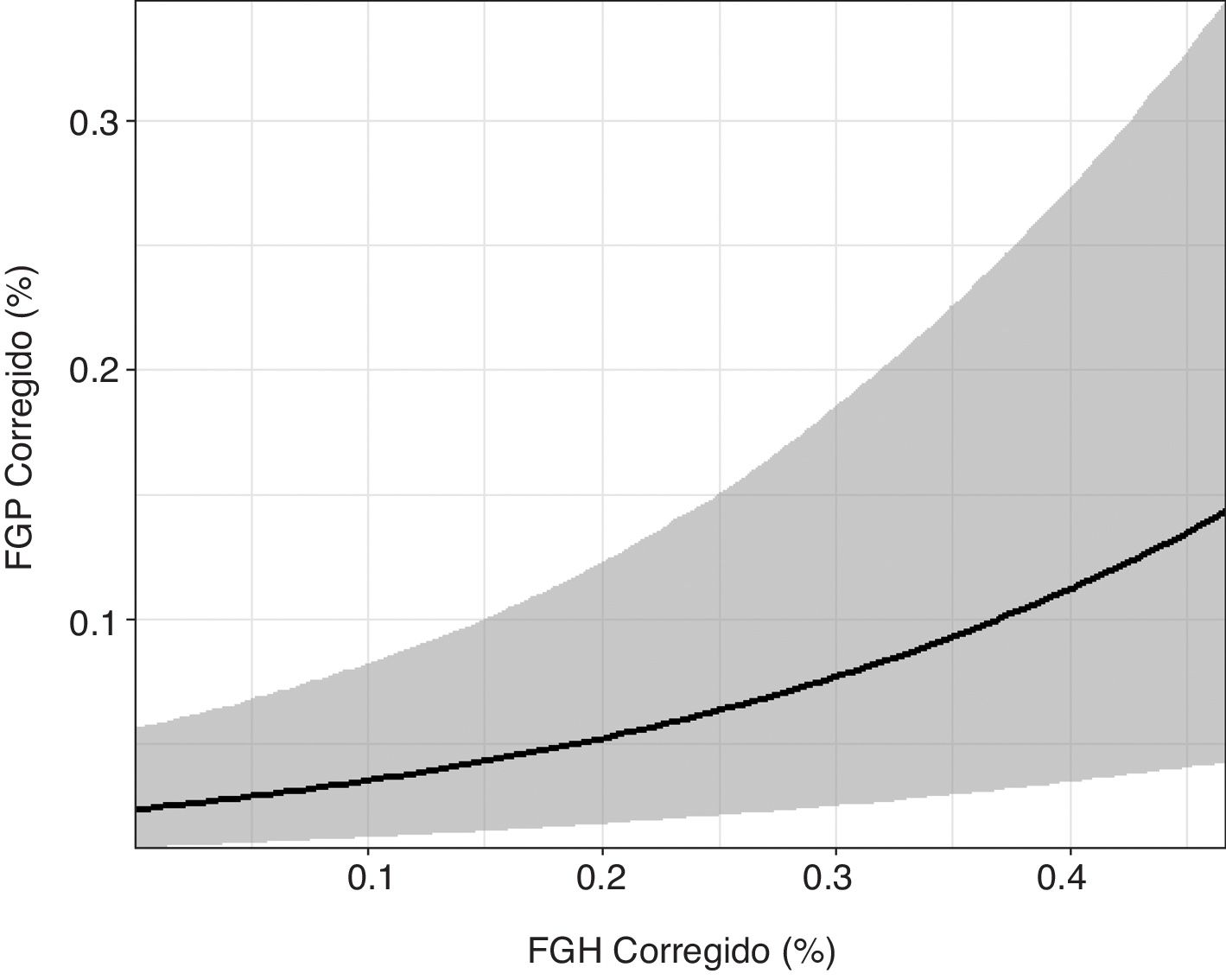
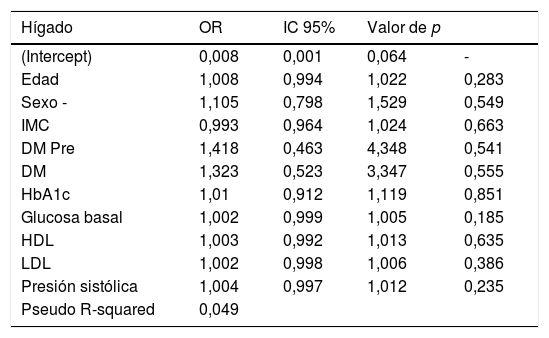
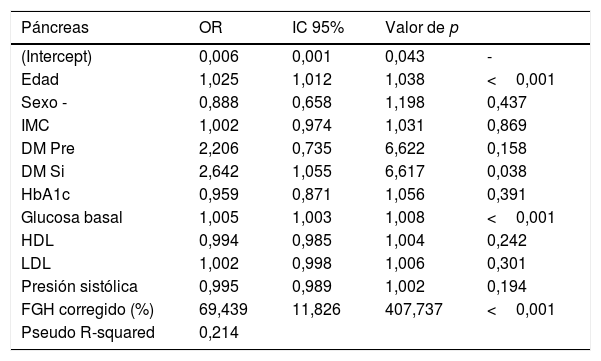
ResultadosSe incluyeron finalmente 253 pacientes. La FGH fue del 4,9% y la FGP del 7,9%. La FGH no presentó ninguna asociación estadística con las variables clínico-analíticas. Sin embargo, la FGP se asoció positivamente con la edad (odds ratio [OR]=1,025, p <0,001) y la glucosa basal (OR=1,005, p <0,001). Se observó que los pacientes con diabetes presentaban valores más altos de FGP (OR=2,64, p=0,038). La FGP y la FGH estaban relacionadas de manera estadísticamente positiva (OR=69,44, p <0,001).
ConclusionesLa esteatosis pancreática puede considerarse un marcador del síndrome metabólico y la diabetes. La RM cuantitativa permite el diagnóstico y la gradación de pacientes con páncreas graso mediante técnicas sencillas de desplazamiento químico.
To objectively evaluate hepatic and pancreatic involvement in metabolic syndrome through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) biomarkers.
Material and methodsFrom an initial retrospective sample of 407 patients diagnosed with metabolic syndrome studied by MRI in a single center during a 2-year period, 154 were excluded because of a lack of clinical and/or laboratory data, pancreatic abnormalities, or inadequate quality of MRI studies. To measure hepatic and pancreatic fat, we used chemical shift imaging (in-phase and out-of-phase), measuring the fat fraction (%) in regions of interest in the pancreas and liver. Associations between the fat fraction and selected clinical and laboratory variables were assessed with beta regression models.
ResultsIn the end, 253 patients were included. The hepatic fat fraction was 4.9% and the pancreatic fat fraction was 7.9%. We found no significant associations between the hepatic fat fraction and any of the clinical or laboratory variables. However, the pancreatic fat fraction was positively associated with age (OR=1.025, p<0.001) and baseline glucose (OR=1.005, p<0.001). Patients with diabetes had higher values of pancreatic fat fraction (OR=2.64, p=0.038). Pancreatic fat fraction and hepatic fat fraction were positively associated (OR=69.44, p<0.001).
ConclusionsPancreatic steatosis can be considered a marker of metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Quantitative MRI enables the diagnosis and grading of fatty pancreas through simple chemical shift techniques.